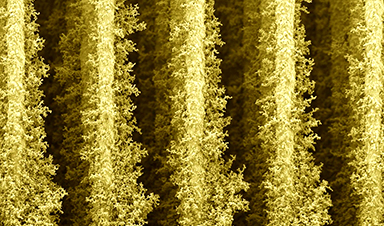
Researchers have made tiny ‘skyscrapers’ for communities of bacteria, helping them to generate electricity from just sunlight and water.
The researchers, from the University of Cambridge, used 3D printing to create grids of high-rise ‘nano-housing’ where sun-loving bacteria can grow quickly. The researchers were then able to extract the bacteria’s waste electrons, left over from photosynthesis, which could be used to power small electronics.
Other research teams have extracted energy from photosynthetic bacteria, but the Cambridge researchers have found that providing them with the right kind of home increases the amount of energy they can extract by over an order of magnitude. The approach is competitive against traditional methods of renewable bioenergy generation and has already reached solar conversion efficiencies that can outcompete many current methods of biofuel generation.
Their results, reported in the journal Nature Materials, open new avenues in bioenergy generation and suggest that ‘biohybrid’ sources of solar energy could be an important component in the zero-carbon energy mix.
Current renewable technologies, such as silicon-based solar cells and biofuels, are far superior to fossil fuels in terms of carbon emissions, but they also have limitations, such as a reliance on mining, challenges in recycling, and a reliance on farming and land use, which results in biodiversity loss.
“Our approach is a step towards making even more sustainable renewable energy devices for the future,” said Dr. Jenny Zhang from the Yusuf Hamied Department of Chemistry, who led the research.
Zhang and her colleagues from the Department of Biochemistry and the Department of Materials Science and Metallurgy are working to rethink bioenergy into something that is sustainable and scalable.
Photosynthetic bacteria, or cyanobacteria, are the most abundant life form on Earth. For several years, researchers have been attempting to ‘re-wire’ the photosynthesis mechanisms of cyanobacteria in order to extract energy from them.
“There’s been a bottleneck in terms of how much energy you can actually extract from photosynthetic systems, but no one understood where the bottleneck was,” said Zhang. “Most scientists assumed that the bottleneck was on the biological side, in the bacteria, but we’ve found that a substantial bottleneck is actually on the material side.”
In order to grow, cyanobacteria need lots of sunlight – like the surface of a lake in the summertime. And in order to extract the energy they produce through photosynthesis, the bacteria need to be attached to electrodes.
The Cambridge team 3D-printed custom electrodes out of metal oxide nanoparticles that are tailored to work with the cyanobacteria as they perform photosynthesis. The electrodes were printed as highly branched, densely packed pillar structures, like a tiny city.
Zhang’s team developed a printing technique that allows control over multiple length scales, making the structures highly customizable, which could benefit a wide range of fields.
“The electrodes have excellent light-handling properties, like a high-rise apartment with lots of windows,” said Zhang. “Cyanobacteria need something they can attach to and form a community with their neighbors. Our electrodes allow for a balance between lots of surface area and lots of light – like a glass skyscraper.”
Once the self-assembling cyanobacteria were in their new ‘wired’ home, the researchers found that they were more efficient than other current bioenergy technologies, such as biofuels. The technique increased the amount of energy extracted by over an order of magnitude over other methods for producing bioenergy from photosynthesis.
“I was surprised we were able to achieve the numbers we did – similar numbers have been predicted for many years, but this is the first time that these numbers have been shown experimentally,” said Zhang. “Cyanobacteria are versatile chemical factories. Our approach allows us to tap into their energy conversion pathway at an early point, which helps us understand how they carry out energy conversion so we can use their natural pathways for renewable fuel or chemical generation.”
News
Millions May Have Long COVID – So Why Can’t They Get Diagnosed?
Millions of people in England may be living with Long Covid without even realizing it. A large-scale analysis found that nearly 10% suspect they might have the condition but remain uncertain, often due to [...]
Researchers Reveal What Happens to Your Brain When You Don’t Get Enough Sleep
What if poor sleep was doing more than just making you tired? Researchers have discovered that disrupted sleep in older adults interferes with the brain’s ability to clean out waste, leading to memory problems [...]
How to prevent chronic inflammation from zombie-like cells that accumulate with age
In humans and other multicellular organisms, cells multiply. This defining feature allows embryos to grow into adulthood, and enables the healing of the many bumps, bruises and scrapes along the way. Certain factors can [...]
Breakthrough for long Covid patients who lost sense of smell
A breakthrough nasal surgery has restored the sense of smell for a dozen long Covid patients. Experts at University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust successfully employed a technique typically used for correcting blocked nasal passages, [...]
Scientists Invent Plastic That Can Dissolve In Seawater In Just A Few Hours
Plastic waste and pollution in the sea have been among the most serious environmental problems for decades, causing immense damage to marine life and ecosystems. However, a breakthrough discovery may offer a game-changing solution. [...]
Muscles from the 3D printer
Swiss researchers have developed a method for printing artificial muscles out of silicone. In the future, these could be used on both humans and robots. Swiss researchers have succeeded in printing artificial muscles out [...]
Beneficial genetic changes observed in regular blood donors
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have identified genetic changes in blood stem cells from frequent blood donors that support the production of new, non-cancerous cells. Understanding the differences in the mutations that accumulate [...]
Shocking Amounts of Microplastics in the Brain – It Could Be Increasing Our Risk of Dementia
The brain has higher concentrations of plastic particles compared to other organs, with increased levels found in dementia patients. In a comprehensive commentary published in Brain Medicine, researchers highlight alarming new evidence of microplastic accumulation [...]
Baffling Scientists for Centuries: New Study Unravels Mystery of Static Electricity
ISTA physicists demonstrate that contact electrification depends on the contact history of materials. For centuries, static electricity has intrigued and perplexed scientists. Now, researchers from the Waitukaitis group at the Institute of Science and [...]
Tumor “Stickiness” – Scientists Develop Potential New Way To Predict Cancer’s Spread
UC San Diego researchers have developed a device that predicts breast cancer aggressiveness by measuring tumor cell adhesion. Weakly adherent cells indicate a higher risk of metastasis, especially in early-stage DCIS. This innovation could [...]
Scientists Just Watched Atoms Move for the First Time Using AI
Scientists have developed a groundbreaking AI-driven technique that reveals the hidden movements of nanoparticles, essential in materials science, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. By integrating artificial intelligence with electron microscopy, researchers can now visualize atomic-level changes that were [...]
Scientists Sound Alarm: “Safe” Antibiotic Has Led to an Almost Untreatable Superbug
A recent study reveals that an antibiotic used for liver disease patients may increase their risk of contracting a dangerous superbug. An international team of researchers has discovered that rifaximin, a commonly prescribed antibiotic [...]
Scientists Discover Natural Compound That Stops Cancer Progression
A discovery led by OHSU was made possible by years of study conducted by University of Portland undergraduates. Scientists have discovered a natural compound that can halt a key process involved in the progression [...]
Scientists Just Discovered an RNA That Repairs DNA Damage – And It’s a Game-Changer
Our DNA is constantly under threat — from cell division errors to external factors like sunlight and smoking. Fortunately, cells have intricate repair mechanisms to counteract this damage. Scientists have uncovered a surprising role played by [...]
What Scientists Just Discovered About COVID-19’s Hidden Death Toll
COVID-19 didn’t just claim lives directly—it reshaped mortality patterns worldwide. A major international study found that life expectancy plummeted across most of the 24 analyzed countries, with additional deaths from cardiovascular disease, substance abuse, and mental [...]
Self-Propelled Nanoparticles Improve Immunotherapy for Non-Invasive Bladder Cancer
A study led by Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) and the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) in South Korea details the creation of urea-powered nanomotors that enhance immunotherapy for bladder cancer. The nanomotors [...]