Parasites take an enormous toll on human and veterinary health. But researchers may have found a way for patients with brain disorders and a common brain parasite to become frenemies.
A new study published in Nature Microbiology has pioneered the use of a single-celled parasite, Toxoplasma gondii, to inject therapeutic proteins into brain cells. The brain is very picky about what it lets in, including many drugs, which limits treatment options for neurological conditions.
As a professor of microbiology, I’ve dedicated my career to finding ways to kill dangerous parasites such as Toxoplasma. I’m fascinated by the prospect that we may be able to use their weaponry to instead treat other maladies.
Microbes as medicine
Ever since scientists realized that microscopic organisms can cause illness—what’s called the 19th-century germ theory of disease—humanity has been on a quest to keep infectious agents out of our bodies. Many people’s understandable aversion to germs may make the idea of adapting these microbial adversaries for therapeutic purposes seem counterintuitive.
But preventing and treating disease by co-opting the very microbes that threaten us has a history that long predates germ theory. As early as the 1500s, people in the Middle East and Asia noted that those lucky enough to survive smallpox never got infected again. These observations led to the practice of purposefully exposing an uninfected person to the material from an infected person’s pus-filled sores—which unbeknownst to them contained weakened smallpox virus—to protect them from severe disease.
This concept of inoculation has yielded a plethora of vaccines that have saved countless lives.
Viruses, bacteria and parasites have also evolved many tricks to penetrate organs such as the brain and could be retooled to deliver drugs into the body. Such uses could include viruses for gene therapy and intestinal bacteria to treat a gut infection known as C. diff.
Why can’t we just take a pill for brain diseases?
Pills offer a convenient and effective way to get medicine into the body. Chemical drugs such as aspirin or penicillin are small and easily absorbed from the gut into the bloodstream.
Biologic drugs such as insulin or semaglutide, on the other hand, are large and complex molecules that are vulnerable to breaking down in the stomach before they can be absorbed. They are also too big to pass through the intestinal wall into the bloodstream.
All drugs, especially biologics, have great difficulty penetrating the brain due to the blood-brain barrier. The blood-brain barrier is a layer of cells lining the brain’s blood vessels that acts like a gatekeeper to block germs and other unwanted substances from gaining access to neurons.
Toxoplasma offers delivery service to brain cells
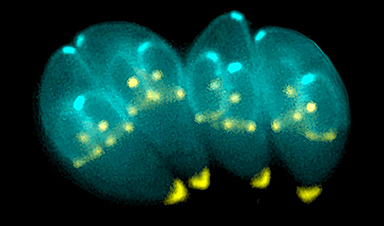
Toxoplasma parasites infect all animals, including humans. Infection can occur in multiple ways, including ingesting spores released in the stool of infected cats or consuming contaminated meat or water. Toxoplasmosis in otherwise healthy people produces only mild symptoms but can be serious in immunocompromised people and to gestating fetusus.
Unlike most pathogens, Toxoplasma can cross the blood-brain barrier and invade brain cells. Once inside neurons, the parasite releases a suite of proteins that alter gene expression in its host, which may be a factor in the behavioral changes it causes in infected animals and people.
In a new study, a global team of researchers hijacked the system Toxoplasma uses to secrete proteins into its host cell. The team genetically engineered Toxoplasma to make a hybrid protein, fusing one of its secreted proteins to a protein called MeCP2, which regulates gene activity in the brain—in effect, giving the MeCP2 a piggyback ride into neurons. Researchers found that the parasites secreted the MeCP2 protein hybrid into neurons grown in a petri dish as well as in the brains of infected mice.
A genetic deficiency in MECP2 causes a rare brain development disorder called Rett syndrome. Gene therapy trials using viruses to deliver the MeCP2 protein to treat Rett syndrome are underway. If Toxoplasma can deliver a form of MeCP2 protein into brain cells, it may provide another option to treat this currently incurable condition. It also may offer another treatment option for other neurological problems that arise from errant proteins, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
The long road ahead
The road from laboratory bench to bedside is long and filled with obstacles, so don’t expect to see engineered Toxoplasma in the clinic anytime soon.
The obvious complication in using Toxoplasma for medical purposes is that it can produce a serious, lifelong infection that is currently incurable. Infecting someone with Toxoplasma can damage critical organ systems, including the brain, eyes and heart.
However, up to one-third of people worldwide currently carry Toxoplasma in their brain, apparently without incident. Emerging studies have correlated infection with increased risk of schizophrenia, rage disorder and recklessness, hinting that this quiet infection may be predisposing some people to serious neurological problems.
The widespread prevalence of Toxoplasma infections may also be another complication, as it disqualifies many people from using it for treatment. Since the billions of people who already carry the parasite have developed immunity against future infection, therapeutic forms of Toxoplasma would be rapidly destroyed by their immune systems once injected.
In some cases, the benefits of using Toxoplasma as a drug delivery system may outweigh the risks. Engineering benign forms of this parasite could produce the proteins patients need without harming the organ—the brain—that defines who we are.
Journal information: Nature Microbiology
News
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]