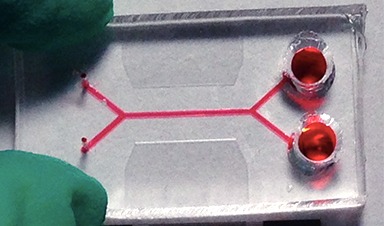
Circulating tumour cells (CTCs) are cancer cells that escape from primary tumour sites and enter the bloodstream. This metastasis is responsible for the majority of deaths from cancer. Monitoring the level of CTC levels in blood is thus important but has proved difficult to do. A team of researchers in China and the US has now developed a new way to isolate these cells using a technique called size-amplified acoustofluidics in which the CTCs selectively bind to microbeads.
The bound cancer cells are significantly different in terms of size and physical properties (they are stiffer, for example) compared to normal cells, explain the researchers led by Feng Guo of Indiana University in Bloomington in the US. This means that their acoustic radiation force is a 100-fold higher than that of bare CTCs or normal blood cells. They can thus be efficiently sorted from blood using microbeads (the “size-amplifiers”) in a travelling acoustic wave microfluidic device, and then released from the amplifiers by being degraded with enzymes.
The technique is 77% efficient and produces CTCs with a 96% yield.
Image Credit: Huiqin Liu
News This Week
Scientists Unlock a New Way to Hear the Brain’s Hidden Language
Scientists can finally hear the brain’s quietest messages—unlocking the hidden code behind how neurons think, decide, and remember. Scientists have created a new protein that can capture the incoming chemical signals received by brain [...]
Does being infected or vaccinated first influence COVID-19 immunity?
A new study analyzing the immune response to COVID-19 in a Catalan cohort of health workers sheds light on an important question: does it matter whether a person was first infected or first vaccinated? [...]
We May Never Know if AI Is Conscious, Says Cambridge Philosopher
As claims about conscious AI grow louder, a Cambridge philosopher argues that we lack the evidence to know whether machines can truly be conscious, let alone morally significant. A philosopher at the University of [...]
AI Helped Scientists Stop a Virus With One Tiny Change
Using AI, researchers identified one tiny molecular interaction that viruses need to infect cells. Disrupting it stopped the virus before infection could begin. Washington State University scientists have uncovered a method to interfere with a key [...]
Deadly Hospital Fungus May Finally Have a Weakness
A deadly, drug-resistant hospital fungus may finally have a weakness—and scientists think they’ve found it. Researchers have identified a genetic process that could open the door to new treatments for a dangerous fungal infection [...]
Fever-Proof Bird Flu Variant Could Fuel the Next Pandemic
Bird flu viruses present a significant risk to humans because they can continue replicating at temperatures higher than a typical fever. Fever is one of the body’s main tools for slowing or stopping viral [...]
What could the future of nanoscience look like?
Society has a lot to thank for nanoscience. From improved health monitoring to reducing the size of electronics, scientists’ ability to delve deeper and better understand chemistry at the nanoscale has opened up numerous [...]
Scientists Melt Cancer’s Hidden “Power Hubs” and Stop Tumor Growth
Researchers discovered that in a rare kidney cancer, RNA builds droplet-like hubs that act as growth control centers inside tumor cells. By engineering a molecular switch to dissolve these hubs, they were able to halt cancer [...]













Leave A Comment