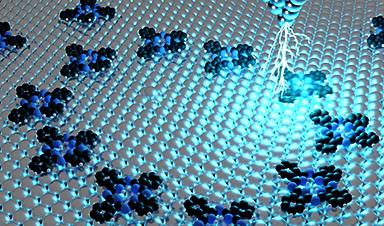
At TU Graz, a pioneering research group is leveraging artificial intelligence to drastically enhance the way nanostructures are constructed.
They aim to develop a self-learning AI system that can autonomously position molecules with unprecedented precision, potentially revolutionizing the creation of complex molecular structures and quantum corrals for advanced electronics.
Revolutionizing Nanostructure Construction with AI
The properties of a material are often shaped less by its chemical composition and more by how its molecules are arranged within the atomic lattice or on its surface. Materials scientists harness this principle by positioning individual atoms and molecules on surfaces using high-performance microscopes. However, this process is highly time-consuming, and the resulting nanostructures remain relatively simple.
A research group at TU Graz aims to revolutionize this approach with artificial intelligence. "We want to develop a self-learning AI system that positions individual molecules quickly, specifically and in the right orientation, and all this completely autonomously," says Oliver Hofmann from the Institute of Solid State Physics, who heads the research group. This advancement could enable the construction of highly complex molecular structures, including nanoscale logic circuits.
The research group, called "Molecule Arrangement through Artificial Intelligence," has secured €1.19 million ($1.23 million) in funding from the Austrian Science Fund to turn this vision into reality
Advanced Techniques in Molecular Positioning
The positioning of individual molecules on a material's surface is carried out using a scanning tunneling microscope. The tip of the probe emits an electrical impulse to deposit a molecule it is carrying. "A person needs a few minutes to complete this step for a simple molecule," says Oliver Hofmann. "But in order to build complicated structures with potentially exciting effects, many thousands of complex molecules have to be positioned individually and the result then tested. This of course takes a relatively long time."
AI Integration for Enhanced Precision
However, a scanning tunneling microscope can also be controlled by a computer. Oliver Hofmann's team now wants to use various machine learning methods to get such a computer system to place the molecules in the correct position independently. First, AI methods are used to calculate an optimal plan that describes the most efficient and reliable approach to building the structure. Self-learning AI algorithms then control the probe tip to place the molecules precisely according to the plan.
"Positioning complex molecules at the highest precision is a difficult process, as their alignment is always subject to a certain degree of chance despite the best possible control," explains Hofmann. The researchers will integrate this conditional probability factor into the AI system so that it still acts reliably.
The Future of Quantum Corrals
Using an AI-controlled scanning tunneling microscope that can work around the clock, the researchers ultimately want to build so-called quantum corrals. These are nanostructures in the shape of a gate, which can be used to trap electrons from the material on which they are deposited. The wave-like properties of the electrons then lead to quantum-mechanical interferences that can be utilized for practical applications. Until now, quantum corrals have mainly been built from single atoms.
Oliver Hofmann's team now wants to produce them from complex-shaped molecules: "Our hypothesis is that this will allow us to build much more diverse quantum corrals and thus specifically expand their effects." The researchers want to use these more complex quantum corrals to build logic circuits in order to fundamentally study how they work at the molecular level. Theoretically, such quantum corrals could one day be used to build computer chips.
Collaborative Research and Expertise Synergy
For its five-year program, the research group is pooling expertise from the fields of artificial intelligence, mathematics, physics, and chemistry. Bettina Könighofer from the Institute of Information Security is responsible for the development of the machine learning model. Her team must ensure that the self-learning system does not inadvertently destroy the nanostructures it constructs.
Jussi Behrndt from the Institute of Applied Mathematics will determine the fundamental properties of the structures to be developed on a theoretical basis, while Markus Aichhorn from the Institute of Theoretical Physics will translate these predictions into practical applications. Leonhard Grill from the Institute of Chemistry at the University of Graz is primarily responsible for the real experiments on the scanning tunneling microscope.
Reference: "MAM-STM: A software for autonomous control of single moieties towards specific surface positions" by Bernhard Ramsauer, Johannes J. Cartus and Oliver T. Hofmann, 6 June 2024, Computer Physics Communications.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cpc.2024.109264
News
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]
Analyzing Darwin’s specimens without opening 200-year-old jars
Scientists have successfully analyzed Charles Darwin's original specimens from his HMS Beagle voyage (1831 to 1836) to the Galapagos Islands. Remarkably, the specimens have been analyzed without opening their 200-year-old preservation jars. Examining 46 [...]
Scientists discover natural ‘brake’ that could stop harmful inflammation
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have uncovered a key mechanism that helps the body switch off inflammation—a breakthrough that could lead to new treatments for chronic diseases affecting millions worldwide. Inflammation is the [...]
A Forgotten Molecule Could Revive Failing Antifungal Drugs and Save Millions of Lives
Scientists have uncovered a way to make existing antifungal drugs work again against deadly, drug-resistant fungi. Fungal infections claim millions of lives worldwide each year, and current medical treatments are failing to keep pace. [...]
Scientists Trap Thyme’s Healing Power in Tiny Capsules
A new micro-encapsulation breakthrough could turn thyme’s powerful health benefits into safer, smarter nanodoses. Thyme extract is often praised for its wide range of health benefits, giving it a reputation as a natural medicinal [...]
Scientists Develop Spray-On Powder That Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds
KAIST scientists have created a fast-acting, stable powder hemostat that stops bleeding in one second and could significantly improve survival in combat and emergency medicine. Severe blood loss remains the primary cause of death from [...]
Oceans Are Struggling To Absorb Carbon As Microplastics Flood Their Waters
New research points to an unexpected way plastic pollution may be influencing Earth’s climate system. A recent study suggests that microscopic plastic pollution is reducing the ocean’s capacity to take in carbon dioxide, a [...]
Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine – New book from Frank Boehm
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
New Book! NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Global Health Care Equivalency in the Age of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine and Artificial Intelligence
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
Miller School Researchers Pioneer Nanovanilloid-Based Brain Cooling for Traumatic Injury
A multidisciplinary team at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine has developed a breakthrough nanodrug platform that may prove beneficial for rapid, targeted therapeutic hypothermia after traumatic brain injury (TBI). Their work, published in ACS [...]
COVID-19 still claims more than 100,000 US lives each year
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention researchers report national estimates of 43.6 million COVID-19-associated illnesses and 101,300 deaths in the US during October 2022 to September 2023, plus 33.0 million illnesses and 100,800 deaths [...]
Nanomedicine in 2026: Experts Predict the Year Ahead
Progress in nanomedicine is almost as fast as the science is small. Over the last year, we've seen an abundance of headlines covering medical R&D at the nanoscale: polymer-coated nanoparticles targeting ovarian cancer, Albumin recruiting nanoparticles for [...]
Lipid nanoparticles could unlock access for millions of autoimmune patients
Capstan Therapeutics scientists demonstrate that lipid nanoparticles can engineer CAR T cells within the body without laboratory cell manufacturing and ex vivo expansion. The method using targeted lipid nanoparticles (tLNPs) is designed to deliver [...]