Researchers have developed an artificial intelligence which can differentiate cancer cells from normal cells, as well as detect the very early stages of viral infection inside cells. The findings, published today in a study in the journal Nature Machine Intelligence, pave the way for improved diagnostic techniques and new monitoring strategies for disease. The researchers are from the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG), the University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU), Donostia International Physics Center (DIPC) and the Fundación Biofisica Bizkaia (FBB, located in Biofisika Institute).
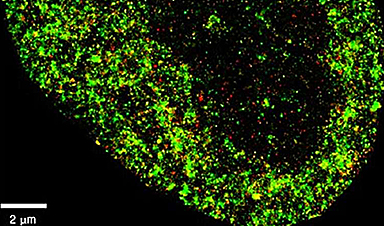
The tool, AINU (AI of the NUcleus), scans high-resolution images of cells. The images are obtained with a special microscopy technique called STORM, which creates a picture that captures many finer details than what regular microscopes can see. The high-definition snapshots reveal structures at nanoscale resolution.
A nanometer (nm) is one-billionth of a meter, and a strand of human hair is about 100,000nm wide. The AI can detect rearrangements inside cells as small as 20nm, or 5,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair. These alterations are too small and subtle for human observers to find with traditional methods alone.
“The resolution of these images is powerful enough for our AI to recognize specific patterns and differences with remarkable accuracy, including changes in how DNA is arranged inside cells, helping spot alterations very soon after they occur. We think that, one day, this type of information can buy doctors valuable time to monitor disease, personalize treatments and improve patient outcomes,” says ICREA Research Professor Pia Cosma, co-corresponding author of the study and researcher at the Centre for Genomic Regulation in Barcelona.
‘Facial recognition’ at the molecular level
AINU is a convolutional neural network, a type of AI specifically designed to analyze visual data like images. Examples of convolutional neural networks include AI tools which enable users to unlock smartphones with their face, or others used by self-driving cars to understand and navigate environments by recognizing objects on the road.
In medicine, convolutional neural networks are used to analyze medical images like mammograms or CT scans and identify signs of cancer that might be missed by the human eye. They can also help doctors detect abnormalities in MRI scans or X-ray images, helping make a faster and more accurate diagnosis.
AINU detects and analyzes tiny structures inside cells at the molecular level. The researchers trained the model by feeding it with nanoscale-resolution images of the nucleus of many different types of cells in different states. The model learned to recognize specific patterns in cells by analyzing how nuclear components are distributed and arranged in three-dimensional space.
For example, cancer cells have distinct changes in their nuclear structure compared to normal cells, such as alterations to how their DNA is organized or the distribution of enzymes within the nucleus. After training, AINU could analyze new images of cell nuclei and classify them as cancerous or normal based on these features alone.
The nanoscale resolution of the images enabled the AI to detect changes in a cell’s nucleus as soon as one hour after it was infected by the herpes simplex virus type-1. The model could detect the presence of the virus by finding slight differences in how tightly DNA is packed, which happens when a virus starts to alter the structure of the cell’s nucleus.
“Our method can detect cells that have been infected by a virus very soon after the infection starts. Normally, it takes time for doctors to spot an infection because they rely on visible symptoms or larger changes in the body. But with AINU, we can see tiny changes in the cell’s nucleus right away,” says Ignacio Arganda-Carreras, co-corresponding author of the study and Ikerbasque Research Associate at UPV/EHU and affiliated with the FBB-Biofisika Institute and the DIPC in San Sebastián/Donostia.
“Researchers can use this technology to see how viruses affect cells almost immediately after they enter the body, which could help in developing better treatments and vaccines. In hospitals and clinics, AINU could be used to quickly diagnose infections from a simple blood or tissue sample, making the process faster and more accurate,” adds Limei Zhong, co-first author of the study and researcher at the Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital (GDPH) in Guangzhou, China.
Laying the groundwork for clinical readiness
The researchers have to overcome important limitations before the technology is ready to be tested or deployed in a clinical setting. For example, STORM images can only be taken with specialized equipment normally only found in biomedical research labs. Setting up and maintaining the imaging systems required by the AI is a significant investment in both equipment and technical expertise.
Another constraint is that STORM imaging typically analyzes only a few cells at a time. For diagnostic purposes, especially in clinical settings where speed and efficiency are crucial, doctors would need to capture many more numbers of cells in a single image to be able to detect or monitor a disease.
“There are many rapid advances in the field of STORM imaging which mean that microscopes may soon be available in smaller or less specialized labs, and eventually, even in the clinic. The limitations of accessibility and throughput are more tractable problems than we previously thought and we hope to carry out preclinical experiments soon,” says Dr. Cosma.
Though clinical benefits might be years away, AINU is expected to accelerate scientific research in the short term. The researchers found the technology could identify stem cells with very high precision. Stem cells can develop into any type of cell in the body, an ability known as pluripotency. Pluripotent cells are studied for their potential in helping repair or replace damaged tissues.
AINU can make the process of detecting pluripotent cells quicker and more accurate, helping make stem cell therapies safer and more effective.
“Current methods to detect high-quality stem cells rely on animal testing. However, all our AI model needs to work is a sample that is stained with specific markers that highlight key nuclear features. As well as being easier and faster, it can accelerate stem cell research while contributing to the shift in reducing animal use in science,” says Davide Carnevali, first author of the research and researcher at the CRG.
More information: A deep learning method that identifies cellular heterogeneity using nanoscale nuclear features, Nature Machine Intelligence (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s42256-024-00883-x
News
Breakthrough Drug Restores Vision: Researchers Successfully Reverse Retinal Damage
Blocking the PROX1 protein allowed KAIST researchers to regenerate damaged retinas and restore vision in mice. Vision is one of the most important human senses, yet more than 300 million people around the world are at [...]
Differentiating cancerous and healthy cells through motion analysis
Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have found that the motion of unlabeled cells can be used to tell whether they are cancerous or healthy. They observed malignant fibrosarcoma cells and [...]
This Tiny Cellular Gate Could Be the Key to Curing Cancer – And Regrowing Hair
After more than five decades of mystery, scientists have finally unveiled the detailed structure and function of a long-theorized molecular machine in our mitochondria — the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier. This microscopic gatekeeper controls how [...]
Unlocking Vision’s Secrets: Researchers Reveal 3D Structure of Key Eye Protein
Researchers have uncovered the 3D structure of RBP3, a key protein in vision, revealing how it transports retinoids and fatty acids and how its dysfunction may lead to retinal diseases. Proteins play a critical [...]
5 Key Facts About Nanoplastics and How They Affect the Human Body
Nanoplastics are typically defined as plastic particles smaller than 1000 nanometers. These particles are increasingly being detected in human tissues: they can bypass biological barriers, accumulate in organs, and may influence health in ways [...]
Measles Is Back: Doctors Warn of Dangerous Surge Across the U.S.
Parents are encouraged to contact their pediatrician if their child has been exposed to measles or is showing symptoms. Pediatric infectious disease experts are emphasizing the critical importance of measles vaccination, as the highly [...]
AI at the Speed of Light: How Silicon Photonics Are Reinventing Hardware
A cutting-edge AI acceleration platform powered by light rather than electricity could revolutionize how AI is trained and deployed. Using photonic integrated circuits made from advanced III-V semiconductors, researchers have developed a system that vastly [...]
A Grain of Brain, 523 Million Synapses, Most Complicated Neuroscience Experiment Ever Attempted
A team of over 150 scientists has achieved what once seemed impossible: a complete wiring and activity map of a tiny section of a mammalian brain. This feat, part of the MICrONS Project, rivals [...]
The Secret “Radar” Bacteria Use To Outsmart Their Enemies
A chemical radar allows bacteria to sense and eliminate predators. Investigating how microorganisms communicate deepens our understanding of the complex ecological interactions that shape our environment is an area of key focus for the [...]
Psychologists explore ethical issues associated with human-AI relationships
It's becoming increasingly commonplace for people to develop intimate, long-term relationships with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. At their extreme, people have "married" their AI companions in non-legally binding ceremonies, and at least two people [...]
When You Lose Weight, Where Does It Actually Go?
Most health professionals lack a clear understanding of how body fat is lost, often subscribing to misconceptions like fat converting to energy or muscle. The truth is, fat is actually broken down into carbon [...]
How Everyday Plastics Quietly Turn Into DNA-Damaging Nanoparticles
The same unique structure that makes plastic so versatile also makes it susceptible to breaking down into harmful micro- and nanoscale particles. The world is saturated with trillions of microscopic and nanoscopic plastic particles, some smaller [...]
AI Outperforms Physicians in Real-World Urgent Care Decisions, Study Finds
The study, conducted at the virtual urgent care clinic Cedars-Sinai Connect in LA, compared recommendations given in about 500 visits of adult patients with relatively common symptoms – respiratory, urinary, eye, vaginal and dental. [...]
Challenging the Big Bang: A Multi-Singularity Origin for the Universe
In a study published in the journal Classical and Quantum Gravity, Dr. Richard Lieu, a physics professor at The University of Alabama in Huntsville (UAH), which is a part of The University of Alabama System, suggests that [...]
New drug restores vision by regenerating retinal nerves
Vision is one of the most crucial human senses, yet over 300 million people worldwide are at risk of vision loss due to various retinal diseases. While recent advancements in retinal disease treatments have [...]
Shingles vaccine cuts dementia risk by 20%, new study shows
A shingles shot may do more than prevent rash — it could help shield the aging brain from dementia, according to a landmark study using real-world data from the UK. A routine vaccine could [...]