AI is evolving at an incredible pace, but its growing energy demands pose a major challenge. Enter spintronic devices—new technology that mimics the brain’s efficiency by integrating memory and processing.
Scientists in Japan have now developed a groundbreaking spintronic device that allows for electrical control of magnetic states, drastically reducing power consumption. This breakthrough could revolutionize AI hardware by making chips far more energy-efficient, mirroring the way neural networks function.
Spintronic Devices: A Game-Changer for AI Hardware
AI is rapidly transforming industries, but as these technologies evolve, so does their demand for power. To sustain further advancements, AI chips must become more energy efficient.
This is where spintronic devices come in. By integrating memory and computing functions—similar to how the human brain operates—they offer a promising foundation for low-power AI chips.
Now, researchers from Tohoku University, the National Institute for Materials Science, and the Japan Atomic Energy Agency have developed a groundbreaking spintronic device. This new technology enables the electrical mutual control of non-collinear antiferromagnets and ferromagnets, allowing for efficient switching of magnetic states. In practical terms, it can store and process information using significantly less energy, much like a brain-inspired AI chip.
This breakthrough could pave the way for a new generation of AI hardware that is both highly efficient and energy-saving. The findings were published in Nature Communications on February 5, 2025.
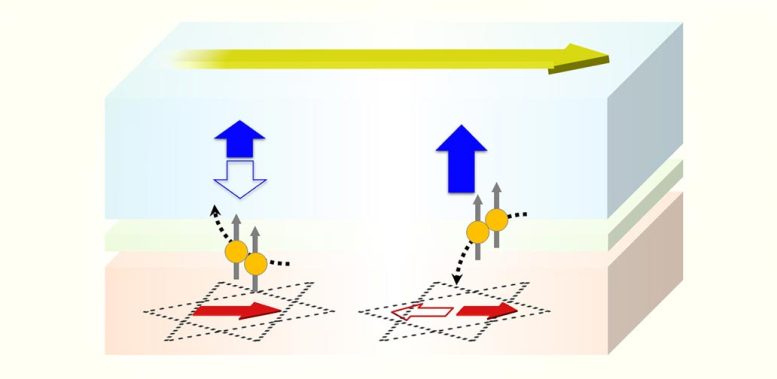
Revolutionizing AI with Multi-State Magnetic Control
“While spintronic research has made significant strides in controlling magnetic order electrically, most existing spintronic devices separate the role of the magnetic material to be controlled and the material providing the driving force,” says Tohoku University’s Shunsuke Fukami, who supervised the research.
These devices have a fixed operation scheme once fabricated, typically switching information from “0” to “1” in a binary fashion. However, the new research team’s breakthrough offers a major innovation in electrically programmable switching of multiple magnetic states.
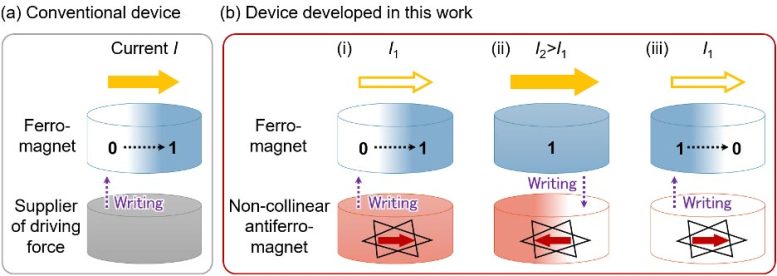
Harnessing the Power of the Magnetic Spin Hall Effect
Fukami and his colleagues employed the non-collinear antiferromagnet Mn3Sn as the core magnetic material. By applying an electrical current, Mn3Sn generates a spin current that drives the switching of a neighboring ferromagnet, CoFeB, through a process known as the magnetic spin Hall effect. Not only does the ferromagnet respond to the spin-polarized current, but it also influences the magnetic state of Mn3Sn, enabling the electrical mutual switching between the two materials.
In their proof-of-concept experiment, the team demonstrated that information written to the ferromagnet can be electrically controlled via the magnetic state of Mn3Sn. By adjusting the set current, they were able to switch the magnetization of CoFeB in different traces representing multiple states. This analog switching mechanism, where the polarity of the current can change the sign of the information written, is a key operation in neural networks, mimicking the way synaptic weights (analog values) function in AI processing.
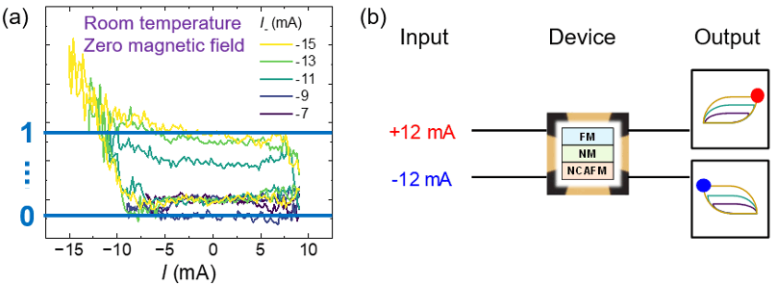
Paving the Way for Energy-Efficient AI Chips
“This discovery represents an important step toward the development of more energy-efficient AI chips. By realizing the electrical mutual switching between a non-collinear antiferromagnet and a ferromagnet, we have opened new possibilities for current-programmable neural networks,” said Fukami. “We are now focusing on further reducing operating currents and increasing readout signals, which will be crucial for practical applications in AI chips.”
The team’s research opens new pathways for improving the energy efficiency of AI chips and minimizing their environmental impacts.
Reference: “Electrical mutual switching in a noncollinear-antiferromagnetic–ferromagnetic heterostructure” by Ju-Young Yoon, Yutaro Takeuchi, Ryota Takechi, Jiahao Han, Tomohiro Uchimura, Yuta Yamane, Shun Kanai, Jun’ichi Ieda, Hideo Ohno and Shunsuke Fukami, 5 February 2025, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-56157-6
News
A Grain of Brain, 523 Million Synapses, Most Complicated Neuroscience Experiment Ever Attempted
A team of over 150 scientists has achieved what once seemed impossible: a complete wiring and activity map of a tiny section of a mammalian brain. This feat, part of the MICrONS Project, rivals [...]
The Secret “Radar” Bacteria Use To Outsmart Their Enemies
A chemical radar allows bacteria to sense and eliminate predators. Investigating how microorganisms communicate deepens our understanding of the complex ecological interactions that shape our environment is an area of key focus for the [...]
Psychologists explore ethical issues associated with human-AI relationships
It's becoming increasingly commonplace for people to develop intimate, long-term relationships with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. At their extreme, people have "married" their AI companions in non-legally binding ceremonies, and at least two people [...]
When You Lose Weight, Where Does It Actually Go?
Most health professionals lack a clear understanding of how body fat is lost, often subscribing to misconceptions like fat converting to energy or muscle. The truth is, fat is actually broken down into carbon [...]
How Everyday Plastics Quietly Turn Into DNA-Damaging Nanoparticles
The same unique structure that makes plastic so versatile also makes it susceptible to breaking down into harmful micro- and nanoscale particles. The world is saturated with trillions of microscopic and nanoscopic plastic particles, some smaller [...]
AI Outperforms Physicians in Real-World Urgent Care Decisions, Study Finds
The study, conducted at the virtual urgent care clinic Cedars-Sinai Connect in LA, compared recommendations given in about 500 visits of adult patients with relatively common symptoms – respiratory, urinary, eye, vaginal and dental. [...]
Challenging the Big Bang: A Multi-Singularity Origin for the Universe
In a study published in the journal Classical and Quantum Gravity, Dr. Richard Lieu, a physics professor at The University of Alabama in Huntsville (UAH), which is a part of The University of Alabama System, suggests that [...]
New drug restores vision by regenerating retinal nerves
Vision is one of the most crucial human senses, yet over 300 million people worldwide are at risk of vision loss due to various retinal diseases. While recent advancements in retinal disease treatments have [...]
Shingles vaccine cuts dementia risk by 20%, new study shows
A shingles shot may do more than prevent rash — it could help shield the aging brain from dementia, according to a landmark study using real-world data from the UK. A routine vaccine could [...]
AI Predicts Sudden Cardiac Arrest Days Before It Strikes
AI can now predict deadly heart arrhythmias up to two weeks in advance, potentially transforming cardiac care. Artificial intelligence could play a key role in preventing many cases of sudden cardiac death, according to [...]
NanoApps Medical is a Top 20 Feedspot Nanotech Blog
There is an ocean of Nanotechnology news published every day. Feedspot saves us a lot of time and we recommend it. We have been using it since 2018. Feedspot is a freemium online RSS [...]
This Startup Says It Can Clean Your Blood of Microplastics
This is a non-exhaustive list of places microplastics have been found: Mount Everest, the Mariana Trench, Antarctic snow, clouds, plankton, turtles, whales, cattle, birds, tap water, beer, salt, human placentas, semen, breast milk, feces, testicles, [...]
New Blood Test Detects Alzheimer’s and Tracks Its Progression With 92% Accuracy
The new test could help identify which patients are most likely to benefit from new Alzheimer’s drugs. A newly developed blood test for Alzheimer’s disease not only helps confirm the presence of the condition but also [...]
The CDC buried a measles forecast that stressed the need for vaccinations
This story was originally published on ProPublica, a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive our biggest stories as soon as they’re published. ProPublica — Leaders at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [...]
Light-Driven Plasmonic Microrobots for Nanoparticle Manipulation
A recent study published in Nature Communications presents a new microrobotic platform designed to improve the precision and versatility of nanoparticle manipulation using light. Led by Jin Qin and colleagues, the research addresses limitations in traditional [...]
Cancer’s “Master Switch” Blocked for Good in Landmark Study
Researchers discovered peptides that permanently block a key cancer protein once thought untreatable, using a new screening method to test their effectiveness inside cells. For the first time, scientists have identified promising drug candidates [...]