“Listen, if there’s one thing the history of evolution has taught us is that life will not be contained. Life breaks free. It expands to new territories, and it crashes through barriers painfully, maybe even dangerously, but . . . life finds a way,” said Ian Malcolm, Jeff Goldblum’s character in Jurassic Park, the 1993 science fiction film about a park with living dinosaurs.
“Listen, if there’s one thing the history of evolution has taught us is that life will not be contained. Life breaks free. It expands to new territories, and it crashes through barriers painfully, maybe even dangerously, but . . . life finds a way,” said Ian Malcolm, Jeff Goldblum’s character in Jurassic Park, the 1993 science fiction film about a park with living dinosaurs.
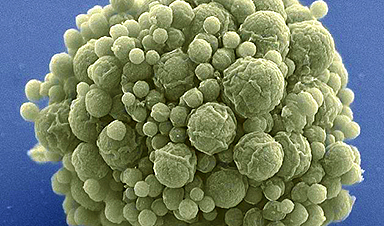
You won’t find any Velociraptors lurking around evolutionary biologist Jay T. Lennon’s lab; however, Lennon, a professor in the College of Arts and Sciences Department of Biology at Indiana University Bloomington, and his colleagues have found that life does indeed find a way. Lennon’s research team has been studying a synthetically constructed minimal cell that has been stripped of all but its essential genes. The team found that the streamlined cell can evolve just as fast as a normal cell—demonstrating the capacity for organisms to adapt, even with an unnatural genome that would seemingly provide little flexibility.
“It appears there’s something about life that’s really robust,” says Lennon. “We can simplify it down to just the bare essentials, but that doesn’t stop evolution from going to work.”
For their study, Lennon’s team used the synthetic organism, Mycoplasma mycoides JCVI-syn3B—a minimized version of the bacterium M. mycoides commonly found in the guts of goats and similar animals. Over millennia, the parasitic bacterium has naturally lost many of its genes as it evolved to depend on its host for nutrition. Researchers at the J. Craig Venter Institute in California took this one step further. In 2016, they eliminated 45 percent of the 901 genes from the natural M. mycoides genome—reducing it to the smallest set of genes required for autonomous cellular life. At 493 genes, the minimal genome of M. mycoides JCVI-syn3B is the smallest of any known free-living organism. In comparison, many animal and plant genomes contain more than 20,000 genes.
In principle, the simplest organism would have no functional redundancies and possess only the minimum number of genes essential for life. Any mutation in such an organism could lethally disrupt one or more cellular functions, placing constraints on evolution. Organisms with streamlined genomes have fewer targets upon which positive selection can act, thus limiting opportunities for adaptation.
Although M. mycoides JCVI-syn3B could grow and divide in laboratory conditions, Lennon and colleagues wanted to know how a minimal cell would respond to the forces of evolution over time, particularly given the limited raw materials upon which natural selection could operate as well as the uncharacterized input of new mutations.
“Every single gene in its genome is essential,” says Lennon in reference to M. mycoides JCVI-syn3B. “One could hypothesize that there is no wiggle room for mutations, which could constrain its potential to evolve.”
The researchers established that M. mycoides JCVI-syn3B, in fact, has an exceptionally high mutation rate. They then grew it in the lab where it was allowed to evolve freely for 300 days, equivalent to 2000 bacterial generations or about 40,000 years of human evolution.
The next step was to set up experiments to determine how the minimal cells that had evolved for 300 days performed in comparison to the original, non-minimal M. mycoides as well as to a strain of minimal cells that hadn’t evolved for 300 days. In the comparison tests, the researchers put equal amounts of the strains being assessed together in a test tube. The strain better suited to its environment became the more common strain.
They found that the non-minimal version of the bacterium easily outcompeted the unevolved minimal version. The minimal bacterium that had evolved for 300 days, however, did much better, effectively recovering all of the fitness that it had lost due to genome streamlining. The researchers identified the genes that changed the most during evolution. Some of these genes were involved in constructing the surface of the cell, while the functions of several others remain unknown.
Details about the study can be found in a paper recently featured in Nature. Roy Z. Moger-Reischer, a Ph.D. student in the Lennon lab at the time of the study, is first author on the paper.
Understanding how organisms with simplified genomes overcome evolutionary challenges has important implications for long-standing problems in biology—including the treatment of clinical pathogens, the persistence of host-associated endosymbionts, the refinement of engineered microorganisms, and the origin of life itself. The research done by Lennon and his team demonstrates the power of natural selection to rapidly optimize fitness in the simplest autonomous organism, with implications for the evolution of cellular complexity.
In other words, it shows that life finds a way.
News
Studies detail high rates of long COVID among healthcare, dental workers
Researchers have estimated approximately 8% of Americas have ever experienced long COVID, or lasting symptoms, following an acute COVID-19 infection. Now two recent international studies suggest that the percentage is much higher among healthcare workers [...]
Melting Arctic Ice May Unleash Ancient Deadly Diseases, Scientists Warn
Melting Arctic ice increases human and animal interactions, raising the risk of infectious disease spread. Researchers urge early intervention and surveillance. Climate change is opening new pathways for the spread of infectious diseases such [...]
Scientists May Have Found a Secret Weapon To Stop Pancreatic Cancer Before It Starts
Researchers at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory have found that blocking the FGFR2 and EGFR genes can stop early-stage pancreatic cancer from progressing, offering a promising path toward prevention. Pancreatic cancer is expected to become [...]
Breakthrough Drug Restores Vision: Researchers Successfully Reverse Retinal Damage
Blocking the PROX1 protein allowed KAIST researchers to regenerate damaged retinas and restore vision in mice. Vision is one of the most important human senses, yet more than 300 million people around the world are at [...]
Differentiating cancerous and healthy cells through motion analysis
Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have found that the motion of unlabeled cells can be used to tell whether they are cancerous or healthy. They observed malignant fibrosarcoma cells and [...]
This Tiny Cellular Gate Could Be the Key to Curing Cancer – And Regrowing Hair
After more than five decades of mystery, scientists have finally unveiled the detailed structure and function of a long-theorized molecular machine in our mitochondria — the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier. This microscopic gatekeeper controls how [...]
Unlocking Vision’s Secrets: Researchers Reveal 3D Structure of Key Eye Protein
Researchers have uncovered the 3D structure of RBP3, a key protein in vision, revealing how it transports retinoids and fatty acids and how its dysfunction may lead to retinal diseases. Proteins play a critical [...]
5 Key Facts About Nanoplastics and How They Affect the Human Body
Nanoplastics are typically defined as plastic particles smaller than 1000 nanometers. These particles are increasingly being detected in human tissues: they can bypass biological barriers, accumulate in organs, and may influence health in ways [...]
Measles Is Back: Doctors Warn of Dangerous Surge Across the U.S.
Parents are encouraged to contact their pediatrician if their child has been exposed to measles or is showing symptoms. Pediatric infectious disease experts are emphasizing the critical importance of measles vaccination, as the highly [...]
AI at the Speed of Light: How Silicon Photonics Are Reinventing Hardware
A cutting-edge AI acceleration platform powered by light rather than electricity could revolutionize how AI is trained and deployed. Using photonic integrated circuits made from advanced III-V semiconductors, researchers have developed a system that vastly [...]
A Grain of Brain, 523 Million Synapses, Most Complicated Neuroscience Experiment Ever Attempted
A team of over 150 scientists has achieved what once seemed impossible: a complete wiring and activity map of a tiny section of a mammalian brain. This feat, part of the MICrONS Project, rivals [...]
The Secret “Radar” Bacteria Use To Outsmart Their Enemies
A chemical radar allows bacteria to sense and eliminate predators. Investigating how microorganisms communicate deepens our understanding of the complex ecological interactions that shape our environment is an area of key focus for the [...]
Psychologists explore ethical issues associated with human-AI relationships
It's becoming increasingly commonplace for people to develop intimate, long-term relationships with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. At their extreme, people have "married" their AI companions in non-legally binding ceremonies, and at least two people [...]
When You Lose Weight, Where Does It Actually Go?
Most health professionals lack a clear understanding of how body fat is lost, often subscribing to misconceptions like fat converting to energy or muscle. The truth is, fat is actually broken down into carbon [...]
How Everyday Plastics Quietly Turn Into DNA-Damaging Nanoparticles
The same unique structure that makes plastic so versatile also makes it susceptible to breaking down into harmful micro- and nanoscale particles. The world is saturated with trillions of microscopic and nanoscopic plastic particles, some smaller [...]
AI Outperforms Physicians in Real-World Urgent Care Decisions, Study Finds
The study, conducted at the virtual urgent care clinic Cedars-Sinai Connect in LA, compared recommendations given in about 500 visits of adult patients with relatively common symptoms – respiratory, urinary, eye, vaginal and dental. [...]