A team of international researchers led by Prof Martin Hegner, Investigator in CRANN and Trinity’s School of Physics developed an automated diagnostic platform that indicates bleeding – and thrombotic risks in one drop of blood within seconds (Nanoscale, “Towards personalised rapid label free miRNA detection for cancer and liver injury diagnostics in cell lysates and blood based samples”).
They exploit micro-resonators for real-time measurements of the evolving blood plasma clot strength. Along with the clinically measured clotting time, other parameters, from specific factor deficiency to global coagulation parameters to assess fibrinolysis, can be extracted.
These technical developments now open up the possibility to introduce a miniaturized global haemostasis assay with capability to fine-tune anti-coagulation therapies.
In collaboration with the multinational Hoffman-la-Roche they report a novel strategy for quick, reliable and quantitative diagnostics of expression patterns of non-coding short RNA in blood plasma or cell cultures. They directly detect label-free specific miRNA biomarkers relevant to cancer and adverse drug effects in blood-based samples (right image).
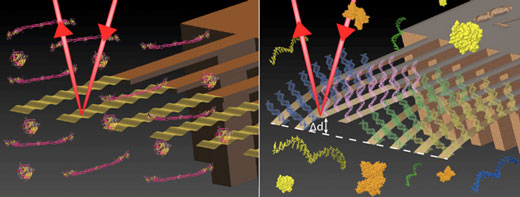
Image Credit: CRANN
News This Week
5 Key Facts About Nanoplastics and How They Affect the Human Body
Nanoplastics are typically defined as plastic particles smaller than 1000 nanometers. These particles are increasingly being detected in human tissues: they can bypass biological barriers, accumulate in organs, and may influence health in ways [...]
Measles Is Back: Doctors Warn of Dangerous Surge Across the U.S.
Parents are encouraged to contact their pediatrician if their child has been exposed to measles or is showing symptoms. Pediatric infectious disease experts are emphasizing the critical importance of measles vaccination, as the highly [...]
AI at the Speed of Light: How Silicon Photonics Are Reinventing Hardware
A cutting-edge AI acceleration platform powered by light rather than electricity could revolutionize how AI is trained and deployed. Using photonic integrated circuits made from advanced III-V semiconductors, researchers have developed a system that vastly [...]
A Grain of Brain, 523 Million Synapses, Most Complicated Neuroscience Experiment Ever Attempted
A team of over 150 scientists has achieved what once seemed impossible: a complete wiring and activity map of a tiny section of a mammalian brain. This feat, part of the MICrONS Project, rivals [...]
The Secret “Radar” Bacteria Use To Outsmart Their Enemies
A chemical radar allows bacteria to sense and eliminate predators. Investigating how microorganisms communicate deepens our understanding of the complex ecological interactions that shape our environment is an area of key focus for the [...]
Psychologists explore ethical issues associated with human-AI relationships
It's becoming increasingly commonplace for people to develop intimate, long-term relationships with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. At their extreme, people have "married" their AI companions in non-legally binding ceremonies, and at least two people [...]
When You Lose Weight, Where Does It Actually Go?
Most health professionals lack a clear understanding of how body fat is lost, often subscribing to misconceptions like fat converting to energy or muscle. The truth is, fat is actually broken down into carbon [...]
How Everyday Plastics Quietly Turn Into DNA-Damaging Nanoparticles
The same unique structure that makes plastic so versatile also makes it susceptible to breaking down into harmful micro- and nanoscale particles. The world is saturated with trillions of microscopic and nanoscopic plastic particles, some smaller [...]












Leave A Comment