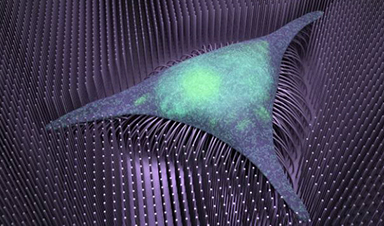
Nanotechnology that accelerates the transition of stem cells into bone could advance regenerative medicine.
A nanotechnology platform developed by KAUST scientists could lead to new treatments for degenerative bone diseases.
The system takes advantage of tiny iron wires that bend in response to magnetic fields. Bone-forming stem cells grown on a mesh of these nanowires get a kind of physical workout on the moving substrate. They then transform into mature bone much faster than is typical of other culturing conditions, with a differentiation protocol that lasts just a few days instead of a few weeks.
“This is a remarkable finding,” says bioscientist Jasmeen Merzaban. “We can achieve efficient bone cell formation in a shorter amount of time,” potentially paving the way for more efficient regeneration of bone. Merzaban co-led the study together with sensor scientist Jürgen Kosel and colleagues from their labs.
The researchers evaluated the bone-producing potential of their nanowire scaffold, both with and without magnetic signals. They patterned the tiny wires — each about the size of the tail-like appendage found on some bacteria — in an evenly spaced grid and then layered bone marrow–derived human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) on top.
Adding a low-frequency magnetic field, the researchers found, dramatically accelerated the process of bone development. Genetic markers of bone development could be detected within two days of incubation under mechanical stimulation, while genes linked to stemness and self-renewal quickly became inactive. Under a microscope, the researchers could also see the cells remodeling themselves to become more bone-like at an accelerated pace.
The KAUST team next plans to test its system in mouse models of degenerative bone disease, with the expectation that stem cell–seeded nanowire scaffolds can be safely implanted at sites of injury and promote tissue repair. An externally applied magnetic field would be used to speed the healing process.
Study author Jose Efrain Perez, a former Ph.D. student in Kosel’s lab, also sees potential applications in other disease settings. As he points out: “Varying the matrix stiffness by increasing or decreasing nanowire length and diameter could promote differential responses with MSCs.” Or they could use other types of stem cells to, for example, promote neuronal growth and brain repair after a stroke.
What’s more, Perez adds, “We could further customize the nanowire scaffold itself or the base material — for instance, by using different metals to exploit their magnetic responses or coating the nanowires with biomolecules for potential delivery upon cellular contact.”
For such a small technology, the possibilities are huge.
News
Scientists Invent Plastic That Can Dissolve In Seawater In Just A Few Hours
Plastic waste and pollution in the sea have been among the most serious environmental problems for decades, causing immense damage to marine life and ecosystems. However, a breakthrough discovery may offer a game-changing solution. [...]
Muscles from the 3D printer
Swiss researchers have developed a method for printing artificial muscles out of silicone. In the future, these could be used on both humans and robots. Swiss researchers have succeeded in printing artificial muscles out [...]
Beneficial genetic changes observed in regular blood donors
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have identified genetic changes in blood stem cells from frequent blood donors that support the production of new, non-cancerous cells. Understanding the differences in the mutations that accumulate [...]
Shocking Amounts of Microplastics in the Brain – It Could Be Increasing Our Risk of Dementia
The brain has higher concentrations of plastic particles compared to other organs, with increased levels found in dementia patients. In a comprehensive commentary published in Brain Medicine, researchers highlight alarming new evidence of microplastic accumulation [...]
Baffling Scientists for Centuries: New Study Unravels Mystery of Static Electricity
ISTA physicists demonstrate that contact electrification depends on the contact history of materials. For centuries, static electricity has intrigued and perplexed scientists. Now, researchers from the Waitukaitis group at the Institute of Science and [...]
Tumor “Stickiness” – Scientists Develop Potential New Way To Predict Cancer’s Spread
UC San Diego researchers have developed a device that predicts breast cancer aggressiveness by measuring tumor cell adhesion. Weakly adherent cells indicate a higher risk of metastasis, especially in early-stage DCIS. This innovation could [...]
Scientists Just Watched Atoms Move for the First Time Using AI
Scientists have developed a groundbreaking AI-driven technique that reveals the hidden movements of nanoparticles, essential in materials science, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. By integrating artificial intelligence with electron microscopy, researchers can now visualize atomic-level changes that were [...]
Scientists Sound Alarm: “Safe” Antibiotic Has Led to an Almost Untreatable Superbug
A recent study reveals that an antibiotic used for liver disease patients may increase their risk of contracting a dangerous superbug. An international team of researchers has discovered that rifaximin, a commonly prescribed antibiotic [...]
Scientists Discover Natural Compound That Stops Cancer Progression
A discovery led by OHSU was made possible by years of study conducted by University of Portland undergraduates. Scientists have discovered a natural compound that can halt a key process involved in the progression [...]
Scientists Just Discovered an RNA That Repairs DNA Damage – And It’s a Game-Changer
Our DNA is constantly under threat — from cell division errors to external factors like sunlight and smoking. Fortunately, cells have intricate repair mechanisms to counteract this damage. Scientists have uncovered a surprising role played by [...]
What Scientists Just Discovered About COVID-19’s Hidden Death Toll
COVID-19 didn’t just claim lives directly—it reshaped mortality patterns worldwide. A major international study found that life expectancy plummeted across most of the 24 analyzed countries, with additional deaths from cardiovascular disease, substance abuse, and mental [...]
Self-Propelled Nanoparticles Improve Immunotherapy for Non-Invasive Bladder Cancer
A study led by Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) and the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) in South Korea details the creation of urea-powered nanomotors that enhance immunotherapy for bladder cancer. The nanomotors [...]
Scientists Develop New System That Produces Drinking Water From Thin Air
UT Austin researchers have developed a biodegradable, biomass-based hydrogel that efficiently extracts drinkable water from the air, offering a scalable, sustainable solution for water access in off-grid communities, emergency relief, and agriculture. Discarded food [...]
AI Unveils Hidden Nanoparticles – A Breakthrough in Early Disease Detection
Deep Nanometry (DNM) is an innovative technique combining high-speed optical detection with AI-driven noise reduction, allowing researchers to find rare nanoparticles like extracellular vesicles (EVs). Since EVs play a role in disease detection, DNM [...]
Inhalable nanoparticles could help treat chronic lung disease
Nanoparticles designed to release antibiotics deep inside the lungs reduced inflammation and improved lung function in mice with symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By Grace Wade Delivering medication to the lungs with inhalable nanoparticles [...]
New MRI Study Uncovers Hidden Lung Abnormalities in Children With Long COVID
Long COVID is more than just lingering symptoms—it may have a hidden biological basis that standard medical tests fail to detect. A groundbreaking study using advanced MRI technology has uncovered significant lung abnormalities in [...]