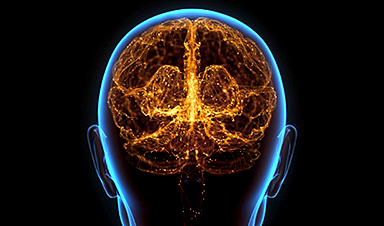
Cambridge researchers found that sex differences in brain structure exist from birth, with males having more white matter and females more grey matter, highlighting early neurodiversity.
Research from the Autism Research Centre at the University of Cambridge has found that sex differences in brain structure are present from birth.
On average, male infants have larger overall brain volumes than female infants. However, when accounting for total brain size, female infants tend to have significantly more grey matter, while male infants have significantly more white matter.
Grey matter consists of neuron cell bodies and dendrites, playing a key role in processing and interpreting information related to sensation, perception, learning, speech, and cognition. In contrast, white matter is composed of axons—long nerve fibers that connect neurons across different brain regions, enabling communication throughout the brain.
Yumnah Khan, a PhD student at the Autism Research Centre, who led the study, said: “Our study settles an age-old question of whether male and female brains differ at birth. We know there are differences in the brains of older children and adults, but our findings show that they are already present in the earliest days of life.
“Because these sex differences are evident so soon after birth, they might in part reflect biological sex differences during prenatal brain development, which then interact with environmental experiences over time to shape further sex differences in the brain.”
Overcoming Past Research Limitations
One problem that has plagued past research in this area is sample size. The Cambridge team tackled this by analyzing data from the Developing Human Connectome Project, where infants receive an MRI brain scan soon after birth. Having over 500 newborn babies in the study means that, statistically, the sample is ideal for detecting sex differences if they are present.
A second problem is whether any observed sex differences could be due to other factors, such as differences in body size. The Cambridge team found that, on average, male infants had significantly larger brain volumes than did females, and this was true even after sex differences in birth weight were taken into account.
After taking this difference in total brain volume into account, at a regional level, females on average showed larger volumes in grey matter areas related to memory and emotional regulation, while males on average had larger volumes in grey matter areas involved in sensory processing and motor control.
The findings of the study, the largest to date to investigate this question, are published in the journal Biology of Sex Differences.
Investigating Underlying Biological Factors
Dr Alex Tsompanidis who supervised the study, said: “This is the largest such study to date, and we took additional factors into account, such as birth weight, to ensure that these differences are specific to the brain and not due to general size differences between the sexes.
“To understand why males and females show differences in their relative grey and white matter volume, we are now studying the conditions of the prenatal environment, using population birth records, as well as in vitro cellular models of the developing brain. This will help us compare the progression of male and female pregnancies and determine if specific biological factors, such as hormones or the placenta, contribute to the differences we see in the brain.”
The researchers stress that the differences between males and females are average differences.
Dr Carrie Allison, Deputy Director of the Autism Research Centre, said: “The differences we see do not apply to all males or all females, but are only seen when you compare groups of males and females together. There is a lot a variation within, and a lot of overlap between, each group.”
Professor Simon Baron-Cohen, Director of the Autism Research Centre, added: “These differences do not imply the brains of males and females are better or worse. It’s just one example of neurodiversity. This research may be helpful in understanding other kinds of neurodiversity, such as the brain in children who are later diagnosed as autistic, since this is diagnosed more often in males.”
Reference: “Sex Differences in Human Brain Structure at Birth” by Yumnah T. Khan, Alex Tsompanidis, Marcin A. Radecki, Lena Dorfschmidt, APEX Consortium, Topun Austin, John Suckling, Carrie Allison, Meng-Chuan Lai, Richard A. I. Bethlehem and Simon Baron-Cohen, 17 October 2024, Biology of Sex Differences.
DOI: 10.1186/s13293-024-00657-5
The research was funded by Cambridge University Development and Research, Trinity College, Cambridge, the Cambridge Trust, and the Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative.
These results were obtained using data made available from the Developing Human Connectome Project funded by the European Research Council under the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP/2007-2013) / ERC Grant Agreement no. [319456].
News
Measles Is Back: Doctors Warn of Dangerous Surge Across the U.S.
Parents are encouraged to contact their pediatrician if their child has been exposed to measles or is showing symptoms. Pediatric infectious disease experts are emphasizing the critical importance of measles vaccination, as the highly [...]
AI at the Speed of Light: How Silicon Photonics Are Reinventing Hardware
A cutting-edge AI acceleration platform powered by light rather than electricity could revolutionize how AI is trained and deployed. Using photonic integrated circuits made from advanced III-V semiconductors, researchers have developed a system that vastly [...]
A Grain of Brain, 523 Million Synapses, Most Complicated Neuroscience Experiment Ever Attempted
A team of over 150 scientists has achieved what once seemed impossible: a complete wiring and activity map of a tiny section of a mammalian brain. This feat, part of the MICrONS Project, rivals [...]
The Secret “Radar” Bacteria Use To Outsmart Their Enemies
A chemical radar allows bacteria to sense and eliminate predators. Investigating how microorganisms communicate deepens our understanding of the complex ecological interactions that shape our environment is an area of key focus for the [...]
Psychologists explore ethical issues associated with human-AI relationships
It's becoming increasingly commonplace for people to develop intimate, long-term relationships with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. At their extreme, people have "married" their AI companions in non-legally binding ceremonies, and at least two people [...]
When You Lose Weight, Where Does It Actually Go?
Most health professionals lack a clear understanding of how body fat is lost, often subscribing to misconceptions like fat converting to energy or muscle. The truth is, fat is actually broken down into carbon [...]
How Everyday Plastics Quietly Turn Into DNA-Damaging Nanoparticles
The same unique structure that makes plastic so versatile also makes it susceptible to breaking down into harmful micro- and nanoscale particles. The world is saturated with trillions of microscopic and nanoscopic plastic particles, some smaller [...]
AI Outperforms Physicians in Real-World Urgent Care Decisions, Study Finds
The study, conducted at the virtual urgent care clinic Cedars-Sinai Connect in LA, compared recommendations given in about 500 visits of adult patients with relatively common symptoms – respiratory, urinary, eye, vaginal and dental. [...]
Challenging the Big Bang: A Multi-Singularity Origin for the Universe
In a study published in the journal Classical and Quantum Gravity, Dr. Richard Lieu, a physics professor at The University of Alabama in Huntsville (UAH), which is a part of The University of Alabama System, suggests that [...]
New drug restores vision by regenerating retinal nerves
Vision is one of the most crucial human senses, yet over 300 million people worldwide are at risk of vision loss due to various retinal diseases. While recent advancements in retinal disease treatments have [...]
Shingles vaccine cuts dementia risk by 20%, new study shows
A shingles shot may do more than prevent rash — it could help shield the aging brain from dementia, according to a landmark study using real-world data from the UK. A routine vaccine could [...]
AI Predicts Sudden Cardiac Arrest Days Before It Strikes
AI can now predict deadly heart arrhythmias up to two weeks in advance, potentially transforming cardiac care. Artificial intelligence could play a key role in preventing many cases of sudden cardiac death, according to [...]
NanoApps Medical is a Top 20 Feedspot Nanotech Blog
There is an ocean of Nanotechnology news published every day. Feedspot saves us a lot of time and we recommend it. We have been using it since 2018. Feedspot is a freemium online RSS [...]
This Startup Says It Can Clean Your Blood of Microplastics
This is a non-exhaustive list of places microplastics have been found: Mount Everest, the Mariana Trench, Antarctic snow, clouds, plankton, turtles, whales, cattle, birds, tap water, beer, salt, human placentas, semen, breast milk, feces, testicles, [...]
New Blood Test Detects Alzheimer’s and Tracks Its Progression With 92% Accuracy
The new test could help identify which patients are most likely to benefit from new Alzheimer’s drugs. A newly developed blood test for Alzheimer’s disease not only helps confirm the presence of the condition but also [...]
The CDC buried a measles forecast that stressed the need for vaccinations
This story was originally published on ProPublica, a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive our biggest stories as soon as they’re published. ProPublica — Leaders at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [...]