A group of scientists collaborated to release comprehensive structures of the entire human opioid receptor family, with the aim of facilitating the development of more precise pain medications.
In an ongoing endeavor to enhance opioid pain medications, scientists from the United States and China utilized cryoEM technology to determine the comprehensive structures of the entire family of opioid receptors when bound to their natural peptides. Further structure-informed biochemical studies were conducted to gain a deeper comprehension of the peptide-receptor selectivity and drug signaling mechanisms.
The findings, published in the journal Cell, offer a comprehensive structural framework that should assist drug developers in creating safer drugs for the alleviation of severe pain.
Opioid drugs relieve pain by mimicking a naturally occurring pain-relief function within our nervous symptoms. They are the best, strongest pain relievers we have. Unfortunately, they come with side effects, some severe such as numbness, addiction, and respiratory depression, leading to overdose deaths.
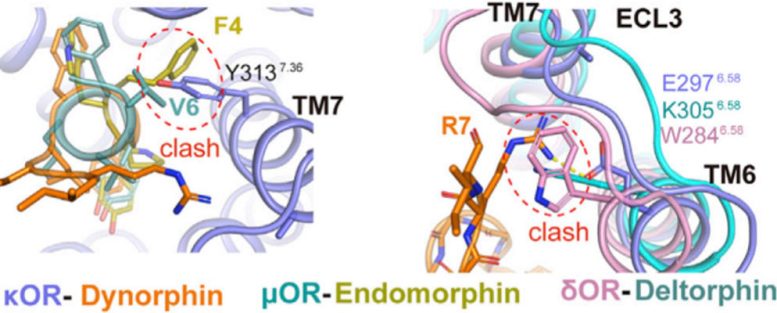
Alignment of peptide-bound opioid receptors reveals structural features, such as steric effects, that contribute to the subtype-selective binding and functional outcomes observed in biochemical assays. Credit: Roth Lab, UNC School of Medicine
Scientists have been trying for many years to overcome the side-effect problem in various ways, all involving one or more of four opioid receptors to no avail. One way scientists continue to explore is the creation of peptide or peptide-inspired small molecule drugs.
Peptides are short chains of amino acids; think of them as short proteins. Certain naturally occurring, or endogenous, peptides bind to opioid receptors on the surface of cells to create an analgesic effect, also known as pain relief. Think of an analgesic like an anesthetic, except that analgesics do not “turn off” the nerves to numb the body or alter consciousness. So, the idea is to create a peptide drug that has a strong analgesic effect, without numbing nerves or altering consciousness, or causing digestive, respiratory, or addiction issues.
“The problem in the field is we’ve lacked the molecular understanding of the interplay between opioid peptides and their receptors,” said Roth, co-senior author and the Michael Hooker Distinguished Professor of Pharmacology. “We’ve needed this understanding in order to try to rationally design potent and safe peptide or peptide-inspired drugs.”
Using cryogenic electron microscopy, or cryoEM, and a battery of biomechanistic experiments in cells, the Xu and Roth labs systematically solved the detailed structures of endogenous peptides bound to all four opioid receptors. These structures revealed details and insights into how specific naturally occurring opioid peptides selectively recognize and activate opioid receptors. The researchers also used exogenous peptides, or drug-like compounds, in some of their experiments to learn how they activate the receptors.
The cryoEM structures of agonist-bound receptors in complex with their G protein effectors (called their “active state”) represent what these receptors look like when they are signaling in cells, giving a detailed view of peptide-receptor interactions. The Roth lab used the structures solved by the Xu lab to guide the design of mutant receptors and then tested these receptors in biochemical assays in cells to determine how they alter receptor signaling. Understanding these interactions can then be used to design drugs that are selective for opioid receptor subtypes, as well as to produce certain signaling outcomes that may be more beneficial than those of conventional opioids.
“This collaboration revealed conserved, or shared, mechanisms of activation and recognition of all four opioid receptors, as well as differences in peptide recognition that can be exploited for creating subtype-selective drugs,” said DiBerto, first author and Ph.D. candidate in the Roth lab. “We provide more needed information to keep pushing the field forward, to answer basic science questions we hadn’t been able to answer before now.”
Previous research showed the structure of opioid receptors in their inactive or active-like states, with active state structures only existing for the mu-opioid receptor subtype, the primary target of drugs like fentanyl and morphine. In the Cell paper, the authors show agonist-bound receptors in complex with their G protein effectors, made possible through cryoEM technology that did not exist when currently used medications were being developed.
Drugs such as oxycontin, oxycodone, and morphine cause various effects inside cells and throughout the nervous symptom, including pain relief. But they have effects in the digestive and respiratory systems, too, and interact with cells to lead to addiction. Fentanyl, meanwhile, is another powerful pain reliever, but it binds to opioid receptors in such a way as to cause severe side effects, including the shutdown of the respiratory system.
The thrust behind such research led by Xu and Roth is to home in on the mechanistic reasons for pain relief potency without triggering the cellular mechanisms that lead to severe side effects and overdosing.
“We are attempting to build a better kind of opioid,” Roth says, “We’re never going to get there without these kind of basic molecular insights, wherein we can see why pain is relieved and why side effects occur.”
News
Baffling Scientists for Centuries: New Study Unravels Mystery of Static Electricity
ISTA physicists demonstrate that contact electrification depends on the contact history of materials. For centuries, static electricity has intrigued and perplexed scientists. Now, researchers from the Waitukaitis group at the Institute of Science and [...]
Tumor “Stickiness” – Scientists Develop Potential New Way To Predict Cancer’s Spread
UC San Diego researchers have developed a device that predicts breast cancer aggressiveness by measuring tumor cell adhesion. Weakly adherent cells indicate a higher risk of metastasis, especially in early-stage DCIS. This innovation could [...]
Scientists Just Watched Atoms Move for the First Time Using AI
Scientists have developed a groundbreaking AI-driven technique that reveals the hidden movements of nanoparticles, essential in materials science, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. By integrating artificial intelligence with electron microscopy, researchers can now visualize atomic-level changes that were [...]
Scientists Sound Alarm: “Safe” Antibiotic Has Led to an Almost Untreatable Superbug
A recent study reveals that an antibiotic used for liver disease patients may increase their risk of contracting a dangerous superbug. An international team of researchers has discovered that rifaximin, a commonly prescribed antibiotic [...]
Scientists Discover Natural Compound That Stops Cancer Progression
A discovery led by OHSU was made possible by years of study conducted by University of Portland undergraduates. Scientists have discovered a natural compound that can halt a key process involved in the progression [...]
Scientists Just Discovered an RNA That Repairs DNA Damage – And It’s a Game-Changer
Our DNA is constantly under threat — from cell division errors to external factors like sunlight and smoking. Fortunately, cells have intricate repair mechanisms to counteract this damage. Scientists have uncovered a surprising role played by [...]
What Scientists Just Discovered About COVID-19’s Hidden Death Toll
COVID-19 didn’t just claim lives directly—it reshaped mortality patterns worldwide. A major international study found that life expectancy plummeted across most of the 24 analyzed countries, with additional deaths from cardiovascular disease, substance abuse, and mental [...]
Self-Propelled Nanoparticles Improve Immunotherapy for Non-Invasive Bladder Cancer
A study led by Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) and the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) in South Korea details the creation of urea-powered nanomotors that enhance immunotherapy for bladder cancer. The nanomotors [...]
Scientists Develop New System That Produces Drinking Water From Thin Air
UT Austin researchers have developed a biodegradable, biomass-based hydrogel that efficiently extracts drinkable water from the air, offering a scalable, sustainable solution for water access in off-grid communities, emergency relief, and agriculture. Discarded food [...]
AI Unveils Hidden Nanoparticles – A Breakthrough in Early Disease Detection
Deep Nanometry (DNM) is an innovative technique combining high-speed optical detection with AI-driven noise reduction, allowing researchers to find rare nanoparticles like extracellular vesicles (EVs). Since EVs play a role in disease detection, DNM [...]
Inhalable nanoparticles could help treat chronic lung disease
Nanoparticles designed to release antibiotics deep inside the lungs reduced inflammation and improved lung function in mice with symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By Grace Wade Delivering medication to the lungs with inhalable nanoparticles [...]
New MRI Study Uncovers Hidden Lung Abnormalities in Children With Long COVID
Long COVID is more than just lingering symptoms—it may have a hidden biological basis that standard medical tests fail to detect. A groundbreaking study using advanced MRI technology has uncovered significant lung abnormalities in [...]
AI Struggles with Abstract Thought: Study Reveals GPT-4’s Limits
While GPT-4 performs well in structured reasoning tasks, a new study shows that its ability to adapt to variations is weak—suggesting AI still lacks true abstract understanding and flexibility in decision-making. Artificial Intelligence (AI), [...]
Turning Off Nerve Signals: Scientists Develop Promising New Pancreatic Cancer Treatment
Pancreatic cancer reprograms nerve cells to fuel its growth, but blocking these connections can shrink tumors and boost treatment effectiveness. Pancreatic cancer is closely linked to the nervous system, according to researchers from the [...]
New human antibody shows promise for Ebola virus treatment
New research led by scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) reveals the workings of a human antibody called mAb 3A6, which may prove to be an important component for Ebola virus therapeutics. [...]
Early Alzheimer’s Detection Test – Years Before Symptoms Appear
A new biomarker test can detect early-stage tau protein clumping up to a decade before it appears on brain scans, improving early Alzheimer’s diagnosis. Unlike amyloid-beta, tau neurofibrillary tangles are directly linked to cognitive decline. Years [...]