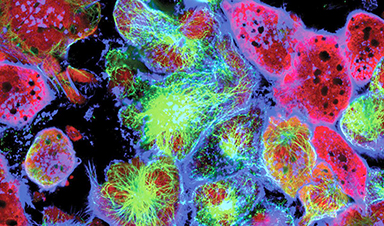
To grow and spread, cancer cells must evade the immune system. Investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital and MIT used the power of nanotechnology to discover a new way that cancer can disarm its would-be cellular attackers by extending out nanoscale tentacles that can reach into an immune cell and pull out its powerpack. Slurping out the immune cell’s mitochondria powers up the cancer cell and depletes the immune cell. The new findings, published in Nature Nanotechnology, could lead to new targets for developing the next generation of immunotherapy against cancer.
“Cancer kills when the immune system is suppressed and cancer cells are able to metastasize, and it appears that nanotubes can help them do both,” said corresponding author Shiladitya Sengupta, Ph.D., co-director of the Brigham’s Center for Engineered Therapeutics. “This is a completely new mechanism by which cancer cells evade the immune system and it gives us a new target to go after.”
To investigate how cancer cells and immune cells interact at the nanoscale level, Sengupta and colleagues set up experiments in which they co-cultured breast cancer cells and immune cells, such as T cells. Using field-emission scanning electron microscopy, they caught a glimpse of something unusual: Cancer cells and immune cells appeared to be physically connected by tiny tendrils, with widths mostly in the 100-1000 nanometer range. (For comparison, a human hair is approximately 80,000 to 100,000 nanometers). In some cases, the nanotubes came together to form thicker tubes. The team then stained mitochondria—which provide energy for cells—from the T cells with a fluorescent dye and watched as bright green mitochondria were pulled out of the immune cells, through the nanotubes, and into the cancer cells.
“By carefully preserving the cell culture condition and observing intracellular structures, we saw these delicate nanotubes and they were stealing the immune cells‘ energy source,” said co-corresponding author Hae Lin Jang, Ph.D., a principal investigator in the Center for Engineered Therapeutics. “It was very exciting because this kind of behavior had never been observed before in cancer cells. This was a tough project as the nanotubes are fragile and we had to handle the cells very gently to not break them.”
The researchers then looked to see what would happen if they prevented the cancer cells from hijacking mitochondria. When they injected an inhibitor of nanotube formation into mouse models used for studying lung cancer and breast cancer, they saw a significant reduction in tumor growth.
“One of the goals in cancer immunotherapy is to find combinations of therapies that can improve outcomes,” said lead author Tanmoy Saha, Ph.D., a postdoctoral researcher in the Center for Engineered Therapeutics. “Based on our observations, there is evidence that an inhibitor of nanotube formation could be combined with cancer immunotherapies and tested to see if it can improve outcomes for patients.”
News
Challenging Previous Beliefs: Japanese Scientists Discover Hidden Protector of Heart
A Japanese research team found that the oxidized form of glutathione (GSSG) may protect heart tissue by modifying a key protein, potentially offering a novel therapeutic approach for ischemic heart failure. A new study [...]
Millions May Have Long COVID – So Why Can’t They Get Diagnosed?
Millions of people in England may be living with Long Covid without even realizing it. A large-scale analysis found that nearly 10% suspect they might have the condition but remain uncertain, often due to [...]
Researchers Reveal What Happens to Your Brain When You Don’t Get Enough Sleep
What if poor sleep was doing more than just making you tired? Researchers have discovered that disrupted sleep in older adults interferes with the brain’s ability to clean out waste, leading to memory problems [...]
How to prevent chronic inflammation from zombie-like cells that accumulate with age
In humans and other multicellular organisms, cells multiply. This defining feature allows embryos to grow into adulthood, and enables the healing of the many bumps, bruises and scrapes along the way. Certain factors can [...]
Breakthrough for long Covid patients who lost sense of smell
A breakthrough nasal surgery has restored the sense of smell for a dozen long Covid patients. Experts at University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust successfully employed a technique typically used for correcting blocked nasal passages, [...]
Scientists Invent Plastic That Can Dissolve In Seawater In Just A Few Hours
Plastic waste and pollution in the sea have been among the most serious environmental problems for decades, causing immense damage to marine life and ecosystems. However, a breakthrough discovery may offer a game-changing solution. [...]
Muscles from the 3D printer
Swiss researchers have developed a method for printing artificial muscles out of silicone. In the future, these could be used on both humans and robots. Swiss researchers have succeeded in printing artificial muscles out [...]
Beneficial genetic changes observed in regular blood donors
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have identified genetic changes in blood stem cells from frequent blood donors that support the production of new, non-cancerous cells. Understanding the differences in the mutations that accumulate [...]
Shocking Amounts of Microplastics in the Brain – It Could Be Increasing Our Risk of Dementia
The brain has higher concentrations of plastic particles compared to other organs, with increased levels found in dementia patients. In a comprehensive commentary published in Brain Medicine, researchers highlight alarming new evidence of microplastic accumulation [...]
Baffling Scientists for Centuries: New Study Unravels Mystery of Static Electricity
ISTA physicists demonstrate that contact electrification depends on the contact history of materials. For centuries, static electricity has intrigued and perplexed scientists. Now, researchers from the Waitukaitis group at the Institute of Science and [...]
Tumor “Stickiness” – Scientists Develop Potential New Way To Predict Cancer’s Spread
UC San Diego researchers have developed a device that predicts breast cancer aggressiveness by measuring tumor cell adhesion. Weakly adherent cells indicate a higher risk of metastasis, especially in early-stage DCIS. This innovation could [...]
Scientists Just Watched Atoms Move for the First Time Using AI
Scientists have developed a groundbreaking AI-driven technique that reveals the hidden movements of nanoparticles, essential in materials science, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. By integrating artificial intelligence with electron microscopy, researchers can now visualize atomic-level changes that were [...]
Scientists Sound Alarm: “Safe” Antibiotic Has Led to an Almost Untreatable Superbug
A recent study reveals that an antibiotic used for liver disease patients may increase their risk of contracting a dangerous superbug. An international team of researchers has discovered that rifaximin, a commonly prescribed antibiotic [...]
Scientists Discover Natural Compound That Stops Cancer Progression
A discovery led by OHSU was made possible by years of study conducted by University of Portland undergraduates. Scientists have discovered a natural compound that can halt a key process involved in the progression [...]
Scientists Just Discovered an RNA That Repairs DNA Damage – And It’s a Game-Changer
Our DNA is constantly under threat — from cell division errors to external factors like sunlight and smoking. Fortunately, cells have intricate repair mechanisms to counteract this damage. Scientists have uncovered a surprising role played by [...]
What Scientists Just Discovered About COVID-19’s Hidden Death Toll
COVID-19 didn’t just claim lives directly—it reshaped mortality patterns worldwide. A major international study found that life expectancy plummeted across most of the 24 analyzed countries, with additional deaths from cardiovascular disease, substance abuse, and mental [...]