Scientists have recently applied cellulose nanofibers to mitigate the fire damage in historic papers. This study has been recently published in Nano-Micro Small.
Importance of Conserving Historical Papers
The Latin proverb “verba volant, scripta manent” has rightly indicated that spoken word flies away but written words stay.
A major part of our culture has been documented in the form of scripts, books, musical scores, drawings, and paintings, which need to be conserved.
The future generations must be given a chance to be inspired by past scripture and learn from the historic data. Hence, it is imperative to preserve historical documents properly.
Historical papers are often damaged by fire and these are far more complex to restore, compared to damages caused by aging or usual wear and tear.
In 2004, a catastrophic fire in the historic library of Duchess Anna Amalia in Weimar, Germany, destroyed a large invaluable collection of hand-written musical literature between the 17th and 19th centuries.
This incident emphasized the importance of developing scientific means to determine the extent of damage caused and preserving the documents as much as possible.
Additionally, the newly developed method must be suitable for high-throughput as thousands of sheets are required to be treated.
How to Conserve and Restore Damaged Papers?
Papers are not only damaged due to direct exposure to the flames but also damaged due to indirect heat effects and the impact of water and other extinguishing agents.
Therefore, papers that are not burnt but indirectly damaged, undergo drastic changes in appearance and physiochemical properties due to a series of chemical processes, such as dehydration, oxidation, hydrolysis, gasification, and cross-linking.
Although the legibility of the manuscripts is greatly deteriorated by charring, it could be partially improved by lamination, digitalization, and multispectral imaging.
The papers retrieved from the Anna Amalia library after the fire have been restored by two methods, namely, the leaf casting of the papers and lamination of the damaged and stabilized paper.
However, historians have pointed out that these methods have reduced the readability of the treated papers.
Papers are also restored using an adhesive mixture of different cellulose ethers, such as carboxymethyl, hydroxypropyl, methyl hydroxyethyl. This method has a lesser impact on optical properties.
New Stabilization Method for Severely Fire-Damaged Manuscripts
Scientists have performed an in-depth analysis of fire-damaged papers, bearing different degrees of fire damages, to understand their chemical and surface properties.
They categorized the chemical and structural changes into L-, M-, and H-heat damage.
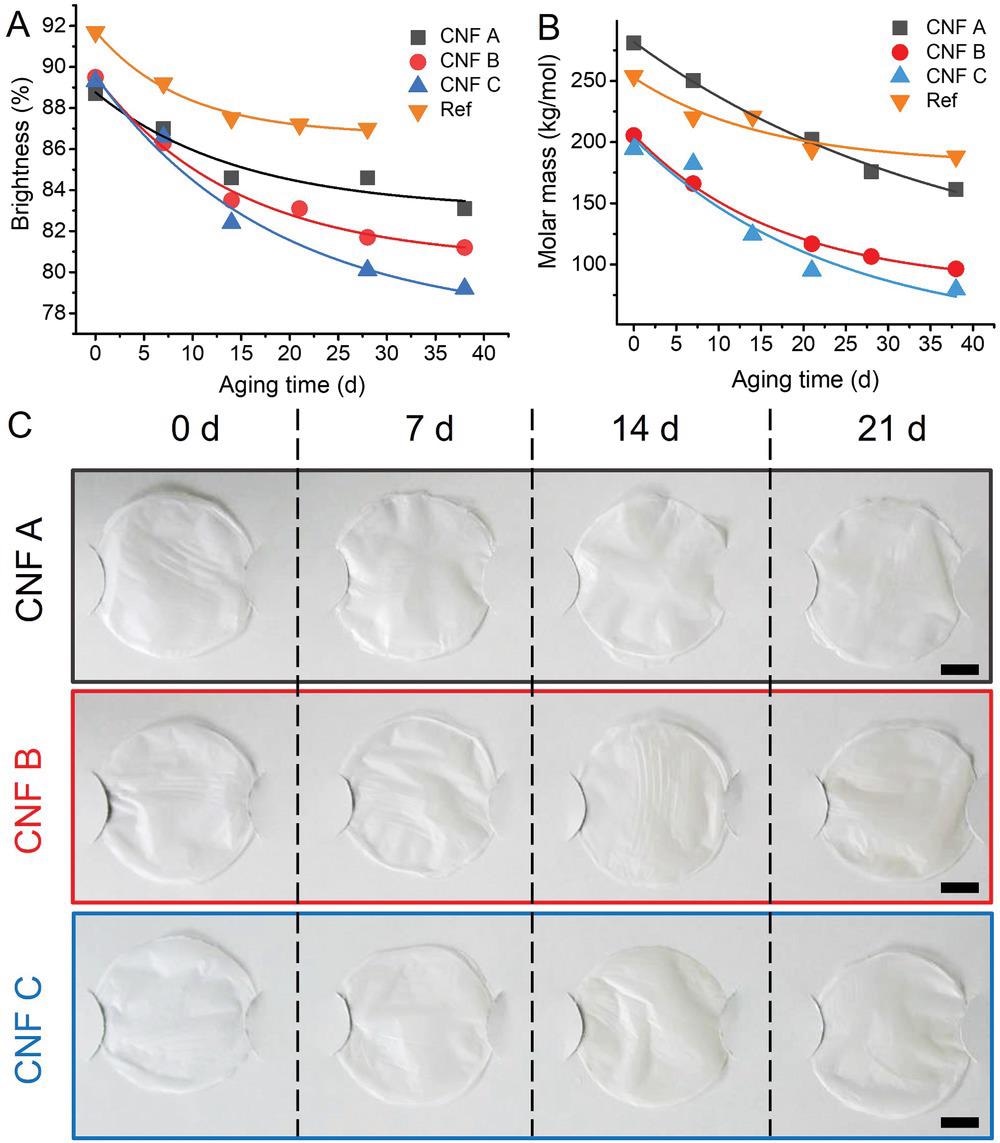
Research revealed a progressively increased carbon content in the papers by analyzing the presence of C-C bonds and decrease in C-O bonds. This finding implies the formation of hydrophobic carbon-rich layers on the fire-damaged papers.
The charred papers exhibit structural changes at nano-micro scale, with increased porosity and water sorption. In the less charred areas, the cellulose was found to be affected by both chain cleavage and cross-linking.
The authors used these data to develop a new stabilization method for severely fire-damaged manuscripts and prints. This method is based on the coating of suspensions of aqueous cellulose nanofibers (CNFs) on the damaged papers.
They predominantly selected CNFs owing to their chemical compatibility and low visual effect on surfaces. This stabilization method can restore historical manuscripts for a longer period.
In addition to the porosity, highly charred carbonaceous material contains sites of high-surface energy and polar groups. These enable good wetting, penetration, and adhesion of polar stabilizing agents.
In this study, CNF acts as a reinforcing agent and is applied as a 0.5–1 wt.% aqueous suspension.
Absorption and retention of CNFs occur due to the porosity and the remaining polar groups of the charred material, chemical and structural similarities between less damaged areas of the paper, and CNFs the extraordinary network and film-forming properties of CNFs.
The authors revealed that this method improved the mechanical stabilization of paper without affecting visibility and legibility.
At present, scientists are testing this method to rescue and preserve selected specimens from the ducal collection of musical literature from the remains of Anna Amalia Library.
Conclusion
The newly developed stabilization method involves the coating of the damaged papers with a thin layer of CNFs.
The main advantage of this method is that it enables the preservation of papers as well as retrieval of the contained historical information.
The latter function has been possible because CNF develops a flexible, transparent film on the surface and adheres strongly to the damaged matrix which significantly reduces the fragility of the paper.
Hence, this technique provides stability and facilitates digitization and further handling. In the future, the possibility of applying CNFs by spraying must be studied.
News
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]
Analyzing Darwin’s specimens without opening 200-year-old jars
Scientists have successfully analyzed Charles Darwin's original specimens from his HMS Beagle voyage (1831 to 1836) to the Galapagos Islands. Remarkably, the specimens have been analyzed without opening their 200-year-old preservation jars. Examining 46 [...]
Scientists discover natural ‘brake’ that could stop harmful inflammation
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have uncovered a key mechanism that helps the body switch off inflammation—a breakthrough that could lead to new treatments for chronic diseases affecting millions worldwide. Inflammation is the [...]
A Forgotten Molecule Could Revive Failing Antifungal Drugs and Save Millions of Lives
Scientists have uncovered a way to make existing antifungal drugs work again against deadly, drug-resistant fungi. Fungal infections claim millions of lives worldwide each year, and current medical treatments are failing to keep pace. [...]
Scientists Trap Thyme’s Healing Power in Tiny Capsules
A new micro-encapsulation breakthrough could turn thyme’s powerful health benefits into safer, smarter nanodoses. Thyme extract is often praised for its wide range of health benefits, giving it a reputation as a natural medicinal [...]
Scientists Develop Spray-On Powder That Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds
KAIST scientists have created a fast-acting, stable powder hemostat that stops bleeding in one second and could significantly improve survival in combat and emergency medicine. Severe blood loss remains the primary cause of death from [...]
Oceans Are Struggling To Absorb Carbon As Microplastics Flood Their Waters
New research points to an unexpected way plastic pollution may be influencing Earth’s climate system. A recent study suggests that microscopic plastic pollution is reducing the ocean’s capacity to take in carbon dioxide, a [...]
Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine – New book from Frank Boehm
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
New Book! NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Global Health Care Equivalency in the Age of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine and Artificial Intelligence
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
Miller School Researchers Pioneer Nanovanilloid-Based Brain Cooling for Traumatic Injury
A multidisciplinary team at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine has developed a breakthrough nanodrug platform that may prove beneficial for rapid, targeted therapeutic hypothermia after traumatic brain injury (TBI). Their work, published in ACS [...]