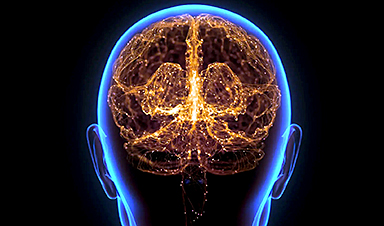
Brain waves act as carriers of information. A recently proposed "Cytoelectric Coupling" hypothesis suggests that these wavering electric fields contribute to the optimization of the brain network's efficiency and robustness. They do this by influencing the physical configuration of the brain's molecular framework.
In order to carry out its multifaceted functions, which include thought, the brain operates on various levels. Information like objectives or visuals is depicted through synchronized electrical activity among neuronal networks. Simultaneously, a combination of proteins and other biochemicals within and surrounding each neuron physically execute the mechanics required for participation in these networks.
A new paper by researchers at MIT, City University of London, and Johns Hopkins University posits that the electrical fields of the network influence the physical configuration of neurons' sub-cellular components to optimize network stability and efficiency, a hypothesis the authors call "Cytoelectric Coupling."

Earl K. Miller delivers a talk on his recent work at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory. Credit: MIT Picower Institute
"The information the brain is processing has a role in fine-tuning the network down to the molecular level," said Earl K. Miller, Picower Professor in The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT, who co-authored the paper in Progress in Neurobiology with Associate Professor Dimitris Pinotsis of MIT and City —University of London, and Professor Gene Fridman of Johns Hopkins.
"The brain adapts to a changing world," Pinotsis said. "Its proteins and molecules change too. They can have electric charges and need to catch up with neurons that process, store, and transmit information using electric signals. Interacting with the neurons' electric fields seems necessary."
Thinking in fields
A major focus of Miller's lab is studying how higher-level cognitive functions such as working memory can rapidly, flexibly, and yet reliably emerge from the activity of millions of individual neurons. Neurons are capable of dynamically forming circuits by creating and removing connections, called synapses, as well as strengthening or weakening those junctions. But, that merely forms a "roadmap" around which information could flow, Miller said.
The specific neural circuits that collectively represent one thought or another, Miller has found, are coordinated by rhythmic activity, more colloquially known as "brain waves" of different frequencies.
Fast "gamma" rhythms help transmit images from our vision (e.g. a muffin), while slower "beta" waves might carry our deeper thoughts about that image, (e.g. "too many calories"). Properly timed, bursts of these waves can carry predictions, enable writing in, holding onto, and reading out information in working memory, Miller's lab has shown.
They break down when working memory does, too. The lab has reported evidence that the brain might distinctly manipulate rhythms in specific physical locations to further organize neurons for flexible cognition, a concept called "Spatial Computing."
Other recent work from the lab has shown that while the participation of individual neurons within networks may be fickle and unreliable, the information carried by the networks they are part of is stably represented by the overall electric fields generated by their collective activity.
Cytoelectric coupling
In the new study, the authors combine this model of rhythmic electrical activity coordinating neural networks with other lines of evidence that electrical fields can influence neurons at the molecular level.
Researchers, for example, have studied ephaptic coupling, in which neurons influence each other's electrical properties via the proximity of their membranes, rather than solely relying on electrochemical exchanges across synapses. This electrical cross-talk can affect neural functions including when and whether they spike to relay electrical signals to other neurons in a circuit.
Miller, Pinotsis, and Fridman also cite research showing other electrical influences on cells and their components including how neural development is guided by fields and that microtubules can be aligned by them.
If the brain carries information in electric fields and those electric fields are capable of configuring neurons and other elements in the brain that form a network, then the brain is likely to use this capability. The brain can use fields to ensure the network does what it is supposed to do, the authors suggest.
To put it (loosely) in couch potato terms, the success of a television network isn't just its ability to transmit a clear signal to millions of homes. What's also important is the details as fine as the way each viewer household arranges its TV, sound system, and living room furniture to maximize the experience. Both in this metaphor and in the brain, Miller said, the presence of the network motivates the individual participants to configure their own infrastructure to participate optimally.
"Cytoelectric Coupling connects information at the meso‐ and macroscopic level down to the microscopic level of proteins that are the molecular basis of memory," the authors wrote in the paper.
The article lays out the logic inspiring Cytoelectic Coupling. "We're offering a hypothesis that anybody can test," Miller said.
Reference: "Cytoelectric coupling: Electric fields sculpt neural activity and "tune" the brain's infrastructure" by Dimitris A. Pinotsis, Gene Fridman and Earl K. Miller, 18 May 2023, Progress in Neurobiology.
News
A Forgotten Molecule Could Revive Failing Antifungal Drugs and Save Millions of Lives
Scientists have uncovered a way to make existing antifungal drugs work again against deadly, drug-resistant fungi. Fungal infections claim millions of lives worldwide each year, and current medical treatments are failing to keep pace. [...]
Scientists Trap Thyme’s Healing Power in Tiny Capsules
A new micro-encapsulation breakthrough could turn thyme’s powerful health benefits into safer, smarter nanodoses. Thyme extract is often praised for its wide range of health benefits, giving it a reputation as a natural medicinal [...]
Scientists Develop Spray-On Powder That Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds
KAIST scientists have created a fast-acting, stable powder hemostat that stops bleeding in one second and could significantly improve survival in combat and emergency medicine. Severe blood loss remains the primary cause of death from [...]
Oceans Are Struggling To Absorb Carbon As Microplastics Flood Their Waters
New research points to an unexpected way plastic pollution may be influencing Earth’s climate system. A recent study suggests that microscopic plastic pollution is reducing the ocean’s capacity to take in carbon dioxide, a [...]
Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine – New book from Frank Boehm
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
New Book! NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Global Health Care Equivalency in the Age of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine and Artificial Intelligence
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
Miller School Researchers Pioneer Nanovanilloid-Based Brain Cooling for Traumatic Injury
A multidisciplinary team at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine has developed a breakthrough nanodrug platform that may prove beneficial for rapid, targeted therapeutic hypothermia after traumatic brain injury (TBI). Their work, published in ACS [...]
COVID-19 still claims more than 100,000 US lives each year
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention researchers report national estimates of 43.6 million COVID-19-associated illnesses and 101,300 deaths in the US during October 2022 to September 2023, plus 33.0 million illnesses and 100,800 deaths [...]
Nanomedicine in 2026: Experts Predict the Year Ahead
Progress in nanomedicine is almost as fast as the science is small. Over the last year, we've seen an abundance of headlines covering medical R&D at the nanoscale: polymer-coated nanoparticles targeting ovarian cancer, Albumin recruiting nanoparticles for [...]
Lipid nanoparticles could unlock access for millions of autoimmune patients
Capstan Therapeutics scientists demonstrate that lipid nanoparticles can engineer CAR T cells within the body without laboratory cell manufacturing and ex vivo expansion. The method using targeted lipid nanoparticles (tLNPs) is designed to deliver [...]
The Brain’s Strange Way of Computing Could Explain Consciousness
Consciousness may emerge not from code, but from the way living brains physically compute. Discussions about consciousness often stall between two deeply rooted viewpoints. One is computational functionalism, which holds that cognition can be [...]
First breathing ‘lung-on-chip’ developed using genetically identical cells
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and AlveoliX have developed the first human lung-on-chip model using stem cells taken from only one person. These chips simulate breathing motions and lung disease in an individual, [...]
Cell Membranes May Act Like Tiny Power Generators
Living cells may generate electricity through the natural motion of their membranes. These fast electrical signals could play a role in how cells communicate and sense their surroundings. Scientists have proposed a new theoretical [...]
This Viral RNA Structure Could Lead to a Universal Antiviral Drug
Researchers identify a shared RNA-protein interaction that could lead to broad-spectrum antiviral treatments for enteroviruses. A new study from the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC), published in Nature Communications, explains how enteroviruses begin reproducing [...]
New study suggests a way to rejuvenate the immune system
Stimulating the liver to produce some of the signals of the thymus can reverse age-related declines in T-cell populations and enhance response to vaccination. As people age, their immune system function declines. T cell [...]