Several difficulties have been associated with developing robust nanoscale coating on the surface of electrospun nanofibers. In a recent study published in Nature Communications, scientists have successfully produced a facile, controllable, and versatile method to develop superlubricated nano-skin (SLNS) on the single electrospun nanofiber in situ.
Electrospun Nanofibers
Nanofibers synthesized through electrospinning are commonly applied in several areas, including biomedical engineering, energy, and the environment. This is because electrospinning is responsible for producing highly controllable structures with specific functions.
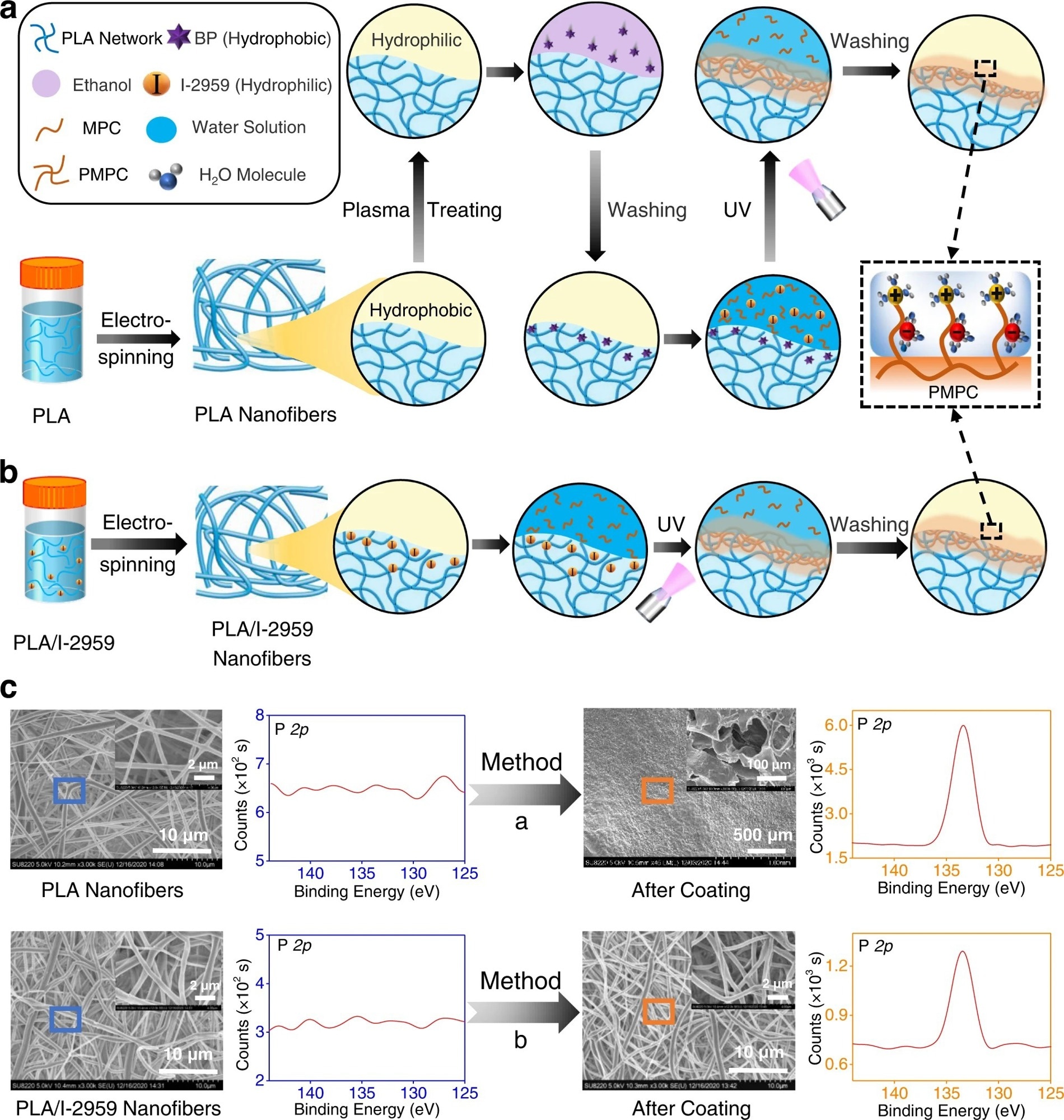
Figure 1. The comparison of our developed surface coating strategy to construct superlubricated nano-skin on electrospun nanofibers with previously reported method. a Schematic diagram of a slightly changed procedure from previous method17,18. PLA polylactic acid, BP benzophenone, MPC 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine, PMPC poly MPC, UV ultraviolet. b Schematic diagram of our optimized method of subsurface-initiated polymerization. c Representative SEM and XPS results of electrospun nanofibers for the comparison of surface morphology and elemental composition between the method in a and in b. The experiments are replicated three times independently with similar results. © Wang, Y., Xu, Y., Zhai, W. et al. (2022)
These nanofibrous membranes are also used for in vivo treatments that require direct human tissue contact. The effectiveness of the application of electrospun nanofibers depends on their surface performance. The electrospun nanofiber’s surface properties, such as patterned structure and fiber orientation, are effectively adjusted via various methods.
The incorporation of these properties improves the cell growth capacity on the fiber surface along with cellular adhesion, which plays an important role in the acceleration of the tissue regeneration process. Nevertheless, uncontrolled cell growth and adhesion to adjacent tissues lead to irretrievable consequences.
Non-Specific Cell Adhesion Property of Electrospun Membranes
Electrospun polylactic acid (PLA)-based membranes (e.g., DK-film) are clinically used for anti-adhesion purposes. This membrane forms a barrier between the injured tissues. However, one of the disadvantages of this membrane is that it adheres to the tissue surface. Therefore, it is extremely crucial to create an electrospun membrane with superior non-adhesive surface properties to prevent post-operative adhesion.
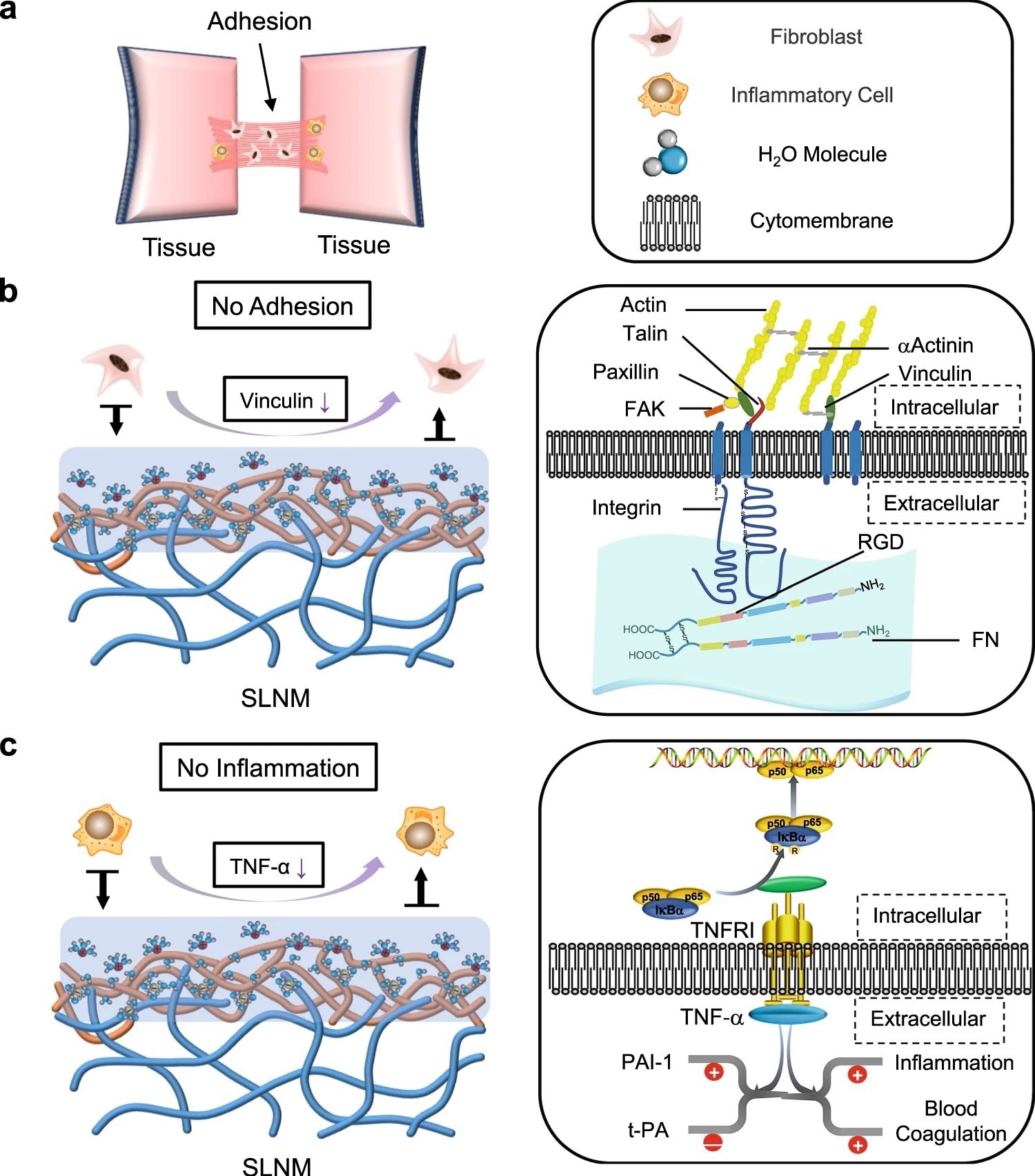
Hydration lubrication could be effectively used to develop nanofibrous membranes with non-adhesive surfaces. Mechanistically, polyelectrolyte polymers (e.g., poly (2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) (PMPC)) exhibit strong adsorption to the hydration layer due to the zwitterionic charges and, subsequently, promote an extremely low coefficient of friction (COF) between the sliding surfaces. This condition prevents non-specific cell adhesion.
Optimization of the interfacial bonding between the substrate polymer chains of nanofibers and the zwitterionic polymer chains in the coating is a challenging task. Although surface modification methods (e.g., grafting polymer chains) are used for this purpose, they cannot develop strong zwitterionic coatings. This is because PLA is sensitive to organic solvents and gets dissolved during surface modification.
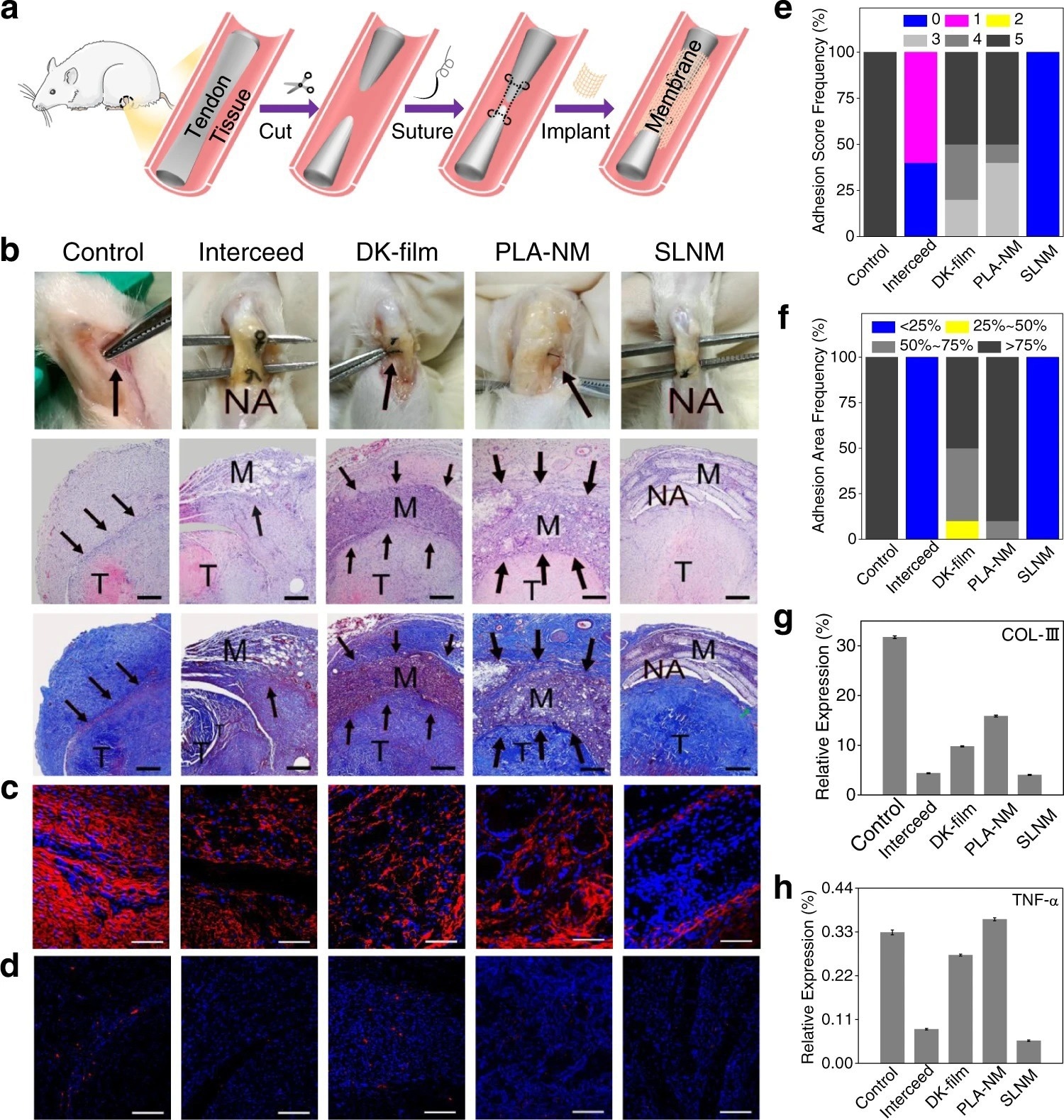
Figure 2. In vivo antitissue adhesion properties of the superlubricated electrospun nanofibrous membranes based on rat tendon adhesion model. a Schematic diagram showing the overall animal test process. b Photos of the harvested tendon on 14 d following implantation and H&E staining as well as Masson staining images. Scale bar: 500 µm. The black arrows point to adhesion site. M membrane. T tendon. NA no adhesion. Representative confocal laser scanning microscopic images for the immunofluorescent staining of c COL-III (scale bar: 100 µm) and d TNF-α (scale bar: 200 µm). Red color represents targeted protein and blue color represents cell nucleus. Comparison of e Adhesion score, f Adhesion area, and relative expression levels of g COL-III as well as h TNF-α for the control, Interceed, DK-film, PLA-NM, and SLNM groups, respectively. The experiments in b–d are replicated three times independently with similar results. © Wang, Y., Xu, Y., Zhai, W. et al. (2022)
Development of Superlubricated Nano-skin on Electrospun Nanofibers
In a previous method, after soaking in benzophenone, the electrospun nanofibrous membranes were immersed in an aqueous solution of methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine (MPC) monomer, which is a hydrophilic initiator 2-hydroxy-1-[4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)phenyl]-2-methyl-1-propanone (I-2959). The next step was to expose to ultraviolet light, for 30 minutes, on each side. The membrane was rinsed with enough deionized water to remove the weakly linked PMPC molecules. The newly synthesized surface-functionalized electrospun PLA nanofibers containing PMPC on the surface exhibited hydration lubrication performance.
Recently, in situ superlubricated nano-skin (SLNS) was grown (inside-out) on an electrospun nanofiber surface. During the electrospinning process, I-2959 (hydrophilic small molecules) self-arranged in the subsurface of the PLA nanofibers (hydrophobic polymer). The main advantage of this technique is that the second initiator outside the nanofibers is not required. As stated above, photopolymerization was performed by subjecting both sides of the electrospun PLA/I-2959 nanofibrous membranes to ultraviolet rays for 30 minutes, which was then immersed in an aqueous MPC monomer solution. The electrospun nanofiber membrane was rinsed with deionized water to remove unbound MPC and, thereby, superlubricated membranes were synthesized.
Both the techniques described were compared using various analytical tools, such as X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The surface elemental compositions of the newly synthesized superlubricated membranes were analyzed using XPS.
The electrospun nanofiber synthesized using the first method showed the presence of a phosphorous element, which originates from PMPC. Hence, XPS data indicated that PMPC coating was successfully prepared in the first method. However, a SEM analysis showed prominent damage to nanofibers, which strongly suggests that hydrogel-skin coating cannot be applied to nanofibers. Nevertheless, SEM and XPS data of the newly developed superlubricated nano-skin (SLNS) showed successful coating without destroying nanofiber structures.
Importantly, the in situ grown superlubricated coating formed on the electrospun nanofiber surface with a thickness of around 1 to 10 nm. Additionally, the COF was lower than 0.025. The newly developed nanofibrous membranes exhibited ideal tensile property and biocompatibility.
Figure 3. Potential antiadhesion mechanism of the superlubricated electrospun nanofibrous membranes. a Schematic diagram showing the occurrence of postoperative tissue adhesion. Interstitial fibrosis and inflammation are involved in this process. Schematic diagrams showing the mechanisms of b inhibiting fibrosis and c reducing inflammation based on the tenacious hydration layer formed surrounding the zwitterionic phosphorylcholine groups on the SLNM surface. © Wang, Y., Xu, Y., Zhai, W. et al. (2022)
Anti-adhesion Performance of Superlubricated Nano-Skin on Electrospun Nanofibers
The newly developed SLNM with the superlubricated nano-skin exhibited significant anti-adhesion performance. Importantly, compared to two commercially used anti-adhesion products, namely, DK-film and intercede, the newly synthesized material showed greater anti-adhesion performance with a lower production cost. This finding was validated using an in vitro anti-cell adhesion test and an in vivo study (anti-tissue adhesion test) was also performed using rat abdominal adhesion and tendon adhesion models. In the future, the application of the newly developed superlubricated biomaterial could prevent post-operative adhesion.
News
Long COVID Is Taking A Silent Toll On Mental Health, Here’s What Experts Say
Months after recovering from COVID-19, many people continue to feel unwell. They speak of exhaustion that doesn’t fade, difficulty breathing, or an unsettling mental haze. What’s becoming increasingly clear is that recovery from the [...]
Study Delivers Cancer Drugs Directly to the Tumor Nucleus
A new peptide-based nanotube treatment sneaks chemo into drug-resistant cancer cells, providing a unique workaround to one of oncology’s toughest hurdles. CiQUS researchers have developed a novel molecular strategy that allows a chemotherapy drug to [...]
Scientists Begin $14.2 Million Project To Decode the Body’s “Hidden Sixth Sense”
An NIH-supported initiative seeks to unravel how the nervous system tracks and regulates the body’s internal organs. How does your brain recognize when it’s time to take a breath, when your blood pressure has [...]
Scientists Discover a New Form of Ice That Shouldn’t Exist
Researchers at the European XFEL and DESY are investigating unusual forms of ice that can exist at room temperature when subjected to extreme pressure. Ice comes in many forms, even when made of nothing but water [...]
Nobel-winning, tiny ‘sponge crystals’ with an astonishing amount of inner space
The 2025 Nobel Prize in chemistry was awarded to Richard Robson, Susumu Kitagawa and Omar Yaghi on Oct. 8, 2025, for the development of metal-organic frameworks, or MOFs, which are tunable crystal structures with extremely [...]
Harnessing Green-Synthesized Nanoparticles for Water Purification
A new review reveals how plant- and microbe-derived nanoparticles can power next-gen water disinfection, delivering cleaner, safer water without the environmental cost of traditional treatments. A recent review published in Nanomaterials highlights the potential of green-synthesized nanomaterials (GSNMs) in [...]
Brainstem damage found to be behind long-lasting effects of severe Covid-19
Damage to the brainstem - the brain's 'control center' - is behind long-lasting physical and psychiatric effects of severe Covid-19 infection, a study suggests. Using ultra-high-resolution scanners that can see the living brain in [...]
CT scan changes over one year predict outcomes in fibrotic lung disease
Researchers at National Jewish Health have shown that subtle increases in lung scarring, detected by an artificial intelligence-based tool on CT scans taken one year apart, are associated with disease progression and survival in [...]
AI Spots Hidden Signs of Disease Before Symptoms Appear
Researchers suggest that examining the inner workings of cells more closely could help physicians detect diseases earlier and more accurately match patients with effective therapies. Researchers at McGill University have created an artificial intelligence tool capable of uncovering [...]
Breakthrough Blood Test Detects Head and Neck Cancer up to 10 Years Before Symptoms
Mass General Brigham’s HPV-DeepSeek test enables much earlier cancer detection through a blood sample, creating a new opportunity for screening HPV-related head and neck cancers. Human papillomavirus (HPV) is responsible for about 70% of [...]
Study of 86 chikungunya outbreaks reveals unpredictability in size and severity
The symptoms come on quickly—acute fever, followed by debilitating joint pain that can last for months. Though rarely fatal, the chikungunya virus, a mosquito-borne illness, can be particularly severe for high-risk individuals, including newborns and older [...]
Tiny Fat Messengers May Link Obesity to Alzheimer’s Plaque Buildup
Summary: A groundbreaking study reveals how obesity may drive Alzheimer’s disease through tiny messengers called extracellular vesicles released from fat tissue. These vesicles carry lipids that alter how quickly amyloid-β plaques form, a hallmark of [...]
Ozone exposure weakens lung function and reshapes the oral microbiome
Scientists reveal that short-term ozone inhalation doesn’t just harm the lungs; it reshapes the microbes in your mouth, with men facing the greatest risks. Ozone is a toxic environmental pollutant with wide-ranging effects on [...]
New study reveals molecular basis of Long COVID brain fog
Even though many years have passed since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, the effects of infection with SARS-CoV-2 are not completely understood. This is especially true for Long COVID, a chronic condition that [...]
Scientists make huge Parkinson’s breakthrough as they discover ‘protein trigger’
Scientists have, for the first time, directly visualised the protein clusters in the brain believed to trigger Parkinson's disease, bringing them one step closer to potential treatments. Parkinson's is a progressive incurable neurological disorder [...]
Alpha amino acids’ stability may explain their role as early life’s protein building blocks
A new study from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences sheds light on one of life's greatest mysteries: why biology is based on a very specific set [...]