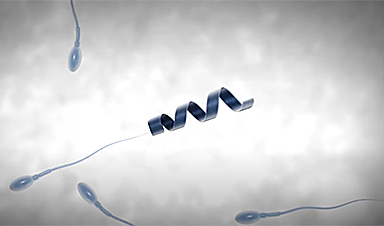
A black-and-white video shared on social media showed a microscopic corkscrew-shaped helix as it appeared to consume a sperm, transport it, and ultimately lead the little swimmer into the wall of an immature egg, or oocyte.
The video was released widely after being shared with Twitter by the Weird Science account on September 21, 2021, in which the video claimed that the video showed a nanobot as it “takes a lazy sperm by the tail and inseminates an egg with it.” The video was also posted on Reddit shortly thereafter, where it garnered 125,000 upvotes.
A glance at the scientific literature revealed that yes, the video in question is real. But there are a few caveats to note, namely that this is the second round of attention it is garnering on social media.
The assisted swimmer video first made headlines when it was first publication in a 2016 issue of the peer-reviewed journal Nano letters, a publication of the American Chemical Society. The so-called “spermbot” was developed by researchers at the German Institute for Integrative Nanosciences with the aim of finding new approaches to combat infertility.
Let’s be clear: the technology is a prototype that has been recorded propelling immobile sperm into an oocyte in a petri dish, or in vitro, and not into a living organism. From Latin for “in the glass”, in vitro studies are carried out using cells and biological molecules outside a living organism. (In vivo, on the other hand, translates to “in the living” and refers to work within an organism.)
The main cause of infertility is poor sperm motility or sperm that are otherwise healthy but cannot swim. Cue the spermbot, designed as an alternative to other infertility treatments such as artificial insemination and in vitro fertilization. The nanobot consists of a metal helix large enough to wrap around the sperm and uses a rotating magnetic field to hook onto the tail of the sperm to “push” it into an egg for potential fertilization.
Micromotors like the spermbot take inspiration from their natural counterparts and mimic natural processes with the help of human assistance, such as magnetic fields. But despite their promise, the accuracy of administration and biocompatibility, the compatibility of non-organic materials with living tissue, remain challenges in the human body.
The hybrid micromotor uses a sperm as the “on-board power supply” and coupled to the microtube which was remotely controlled by an external magnetic field, the sperm tail still provides the propulsion for “cellular cargo delivery”. In short, these “personalized micro helices” serve as motors that can transport sperm with movement impairments.
“Our results indicate that metal-coated polymer microhelices are suitable for this task due to powerful, controllable, and non-harmful 3D motion behavior,” the study authors wrote. “We are able to capture, transport and release live, immobile sperm into fluid channels that mimic physiological conditions.”
The successful capture, as seen in the video, shows that the tail is confined inside the inner part of the micro-helix, the head protrudes at the front end and is loosely tied with a ring that “acts like a noose to prevent the head of the sperm from sliding back. through the propeller.
Limitations of the technology arose when comparing different sperm and ova, each of which had to be transferred from the culture dishes to another platform for testing, resulting in delays and temperature fluctuations, both of which could influence success rates. Still, the authors say their work serves to demonstrate a new approach to artificial reproduction in the future.
“Unfortunately, like many promising applications in biomedical engineering, it appears that there is still a long road between artificially motorized sperm delivery and actual fertilization of oocytes,” the researchers wrote, adding that success of this new approach lies in its potential.
Petri dish testing was a “promising start” that could one day lead to treatment for male infertility, but needed more research before it could be applied to humans, the researchers concluded.
“Despite the fact that there are still challenges for successful fertilization with artificially motorized sperm, we believe that the potential of this new approach to assisted reproduction can already be put into perspective with the present work,” wrote the authors of the study. .
Snopes reached out to researchers to find out more about the current state of the technology and whether it could be suitable for human testing, but did not have a response in time for the publication. We will update the article accordingly.
News
Plastic Without End: Are We Polluting the Planet for Eternity?
The Kunming Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework calls for the elimination of plastic pollution by 2030. If that goal has been clearly set, why have meaningful measures that create real change still not been implemented? [...]
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]