A new drug, donanemab, is being hailed as a turning point in the fight against Alzheimer’s, after a global trial confirms it slows cognitive decline.
The antibody medicine helps in the early stages of the disease by clearing a protein that builds up in the brains of people with this type of dementia.
Although not a cure, charities say the results in the journal JAMA mark a new era where Alzheimer’s can be treated.
The UK’s drugs watchdog has started assessing it for possible NHS use.
The drug works in Alzheimer’s disease, not in other types of dementia, such as vascular dementia.
In the trials, it appears to have slowed the pace of the disease by about a third, allowing people to retain more of their day-to-day lives and tasks, such as making meals and enjoying a hobby.
Mike gets an infusion each month at a clinic in London and says he is “one of the luckiest people you’ll ever meet”.
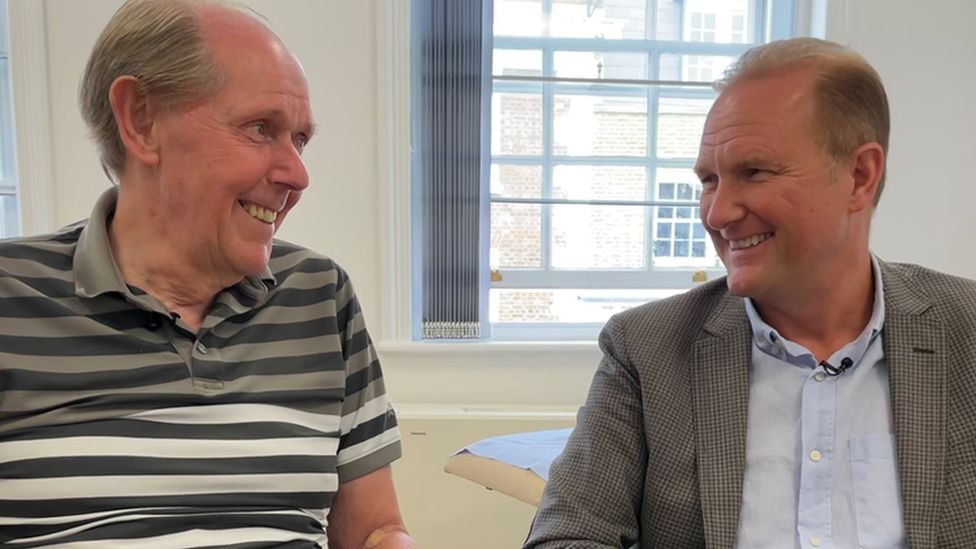

Mike and his family noticed he was having problems with memory and decision-making, not long before he started on the trial.
His son, Mark, said it was very hard to watch at the beginning: “Seeing him struggle with processing information and solving problems was very hard. But I think the decline is reaching a plateau now.”
Mike, who is from Kent, said: “I feel more confident every day.”
Donanemab, made by Eli Lilly, works in the same way as lecanemab – developed by companies Eisai and Biogen – which created headlines around the world when it was proven to slow the disease.
Brain swelling was a common side-effect in up to a third of patients in the donanemab trial. For most, this resolved without causing symptoms. However, two volunteers, and possibly a third, died as a result of dangerous swelling in the brain.
Another antibody Alzheimer’s drug, called aducanumab, was recently rejected by European regulators over safety concerns and a lack of evidence that it was effective enough for patients.
What is dementia and what can be done about it?
In the donanemab trial, researchers examined 1,736 people aged 60 to 85 with early-stage Alzheimer’s.
Half of them received a monthly infusion of the treatment and the other half were given a dummy drug, also known as a placebo, over 18 months.
The findings show:
- The drug seems to have a meaningful benefit, at least for some patients
- Those who had earlier disease and less brain amyloid at baseline derived greater benefit, in terms of clearance seen on brain scans
- Those given the drug also retained more of their day-to-day lives such as being able to discuss current events, answer the phone or pursue hobbies
- The pace of the disease, judged by what people could still do day-to-day, was slowed by about 20-30% overall – and by 30-40% in a set of patients who researchers thought more likely to respond
- There were significant side-effects and patients will need to be aware of risks of treatment
- Half of patients on donanemab were able to stop the treatment after a year, because it had cleared sufficient brain deposits
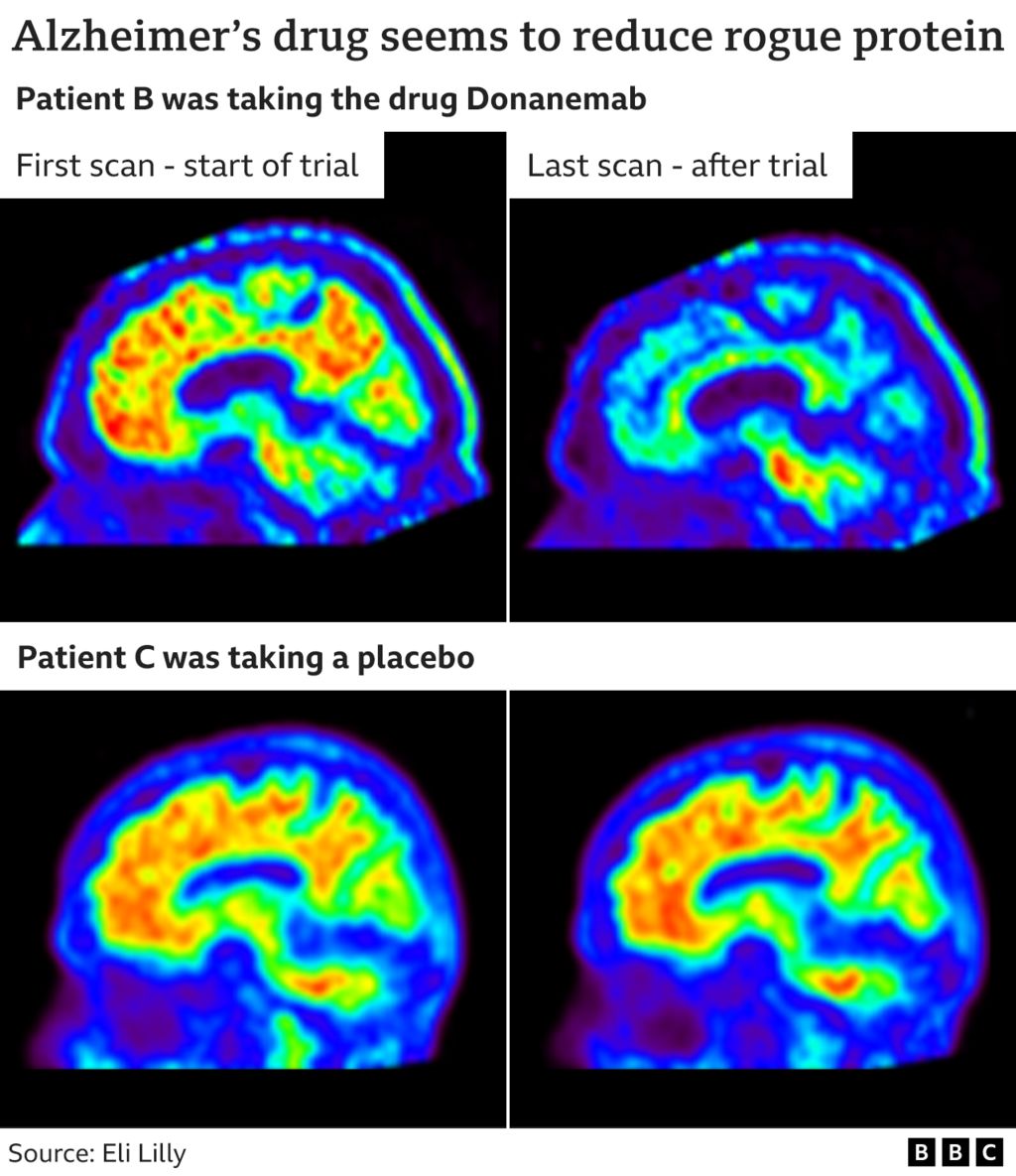
The drug’s effects may be modest, but the results provide further confirmation that removing amyloid from the brain may change the course of Alzheimer’s, and help people affected by this devastating disease if they’re treated at the right time, they say.
Prof Giles Hardingham from the UK Dementia Research Institute said: “It is terrific to see these results published in full today.
“We have waited a long time for Alzheimer’s treatments, so it’s really encouraging to see tangible progress continuing to gather pace in the field.”
Dr Susan Kohlhaas, from Alzheimer’s Research UK, said: “Today’s announcement marks another milestone.
“Thanks to decades of research, the outlook for dementia and its impact on people and society is finally changing, and we’re entering a new era where Alzheimer’s disease could become treatable.”
Speaking to BBC Radio 4’s PM programme, former Prime Minister David Cameron said resources should be put towards further research into what he called a “statin for the brain”.
“We want a pill that people who have the build-up of these proteins in the brain can take every day or every week in order to clear those proteins out of the brain and therefore reduce your chances of getting a disease that causes dementia,” he said.
Asked if the government were prepared to invest where needed to roll out new treatments, Mr Cameron said there was a real incentive to do so: “We’re a country of sixty million people, with a million people with dementia, many of them in very expensive residential care settings and so there is a lot of savings to be had from effectively treating people….I’m hopeful that our system can deliver.”
Lecanemab costs around $27,500 (£21,000) in the US, where it is licensed.
It is not clear how much donanemab may cost and how long it might take to get approval in the UK, but Alzheimer’s experts said having two drugs would help promote competition on price.
The UK’s drug’s watchdog NICE says it has already started work on its appraisal of donanemab for treating mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia caused by Alzheimer’s disease.
“Our aim is to produce recommendations on its use in the NHS as close as possible to it receiving its UK licence,” said a spokesperson.
Mike Colley turned 80 in April. At his birthday party, he surprised his family by singing My Way in front of 40 guests.
He told BBC News: “That’s the confidence I have now. I’d never have done that even 12 months ago.”
His son Mark added: “I never thought I would see my dad so full of life again. It was an incredible moment.”
Dr Emer MacSweeney, consultant neuroradiologist and medical director at Re:Cognition Health, led the trials of donanemab in the UK.
She said: “This is really significant and one of the biggest breakthroughs.”
The Alzheimer’s Society said: “This is truly a turning point in the fight against Alzheimer’s and science is proving that it is possible to slow down the disease.”
Around 720,000 people in the UK might potentially benefit from these emerging new Alzheimer’s disease treatments if they’re approved for use, but the Alzheimer’s Society said the NHS is “simply not ready to deliver them”.
Kate Lee, CEO for the charity, said: “Timely, accurate diagnosis is key, and currently only 2% of people in England and Wales receive their diagnosis through the specialist investigations needed to be eligible for these treatments.
“Alongside this, these emerging Alzheimer’s disease drugs require regular infusions and monitoring, and the NHS is not yet equipped to do this at scale.”
News
New study suggests a way to rejuvenate the immune system
Stimulating the liver to produce some of the signals of the thymus can reverse age-related declines in T-cell populations and enhance response to vaccination. As people age, their immune system function declines. T cell [...]
Nerve Damage Can Disrupt Immunity Across the Entire Body
A single nerve injury can quietly reshape the immune system across the entire body. Preclinical research from McGill University suggests that nerve injuries may lead to long-lasting changes in the immune system, and these [...]
Fake Science Is Growing Faster Than Legitimate Research, New Study Warns
New research reveals organized networks linking paper mills, intermediaries, and compromised academic journals Organized scientific fraud is becoming increasingly common, ranging from fabricated research to the buying and selling of authorship and citations, according [...]
Scientists Unlock a New Way to Hear the Brain’s Hidden Language
Scientists can finally hear the brain’s quietest messages—unlocking the hidden code behind how neurons think, decide, and remember. Scientists have created a new protein that can capture the incoming chemical signals received by brain [...]
Does being infected or vaccinated first influence COVID-19 immunity?
A new study analyzing the immune response to COVID-19 in a Catalan cohort of health workers sheds light on an important question: does it matter whether a person was first infected or first vaccinated? [...]
We May Never Know if AI Is Conscious, Says Cambridge Philosopher
As claims about conscious AI grow louder, a Cambridge philosopher argues that we lack the evidence to know whether machines can truly be conscious, let alone morally significant. A philosopher at the University of [...]
AI Helped Scientists Stop a Virus With One Tiny Change
Using AI, researchers identified one tiny molecular interaction that viruses need to infect cells. Disrupting it stopped the virus before infection could begin. Washington State University scientists have uncovered a method to interfere with a key [...]
Deadly Hospital Fungus May Finally Have a Weakness
A deadly, drug-resistant hospital fungus may finally have a weakness—and scientists think they’ve found it. Researchers have identified a genetic process that could open the door to new treatments for a dangerous fungal infection [...]
Fever-Proof Bird Flu Variant Could Fuel the Next Pandemic
Bird flu viruses present a significant risk to humans because they can continue replicating at temperatures higher than a typical fever. Fever is one of the body’s main tools for slowing or stopping viral [...]
What could the future of nanoscience look like?
Society has a lot to thank for nanoscience. From improved health monitoring to reducing the size of electronics, scientists’ ability to delve deeper and better understand chemistry at the nanoscale has opened up numerous [...]
Scientists Melt Cancer’s Hidden “Power Hubs” and Stop Tumor Growth
Researchers discovered that in a rare kidney cancer, RNA builds droplet-like hubs that act as growth control centers inside tumor cells. By engineering a molecular switch to dissolve these hubs, they were able to halt cancer [...]
Platelet-inspired nanoparticles could improve treatment of inflammatory diseases
Scientists have developed platelet-inspired nanoparticles that deliver anti-inflammatory drugs directly to brain-computer interface implants, doubling their effectiveness. Scientists have found a way to improve the performance of brain-computer interface (BCI) electrodes by delivering anti-inflammatory drugs directly [...]
After 150 years, a new chapter in cancer therapy is finally beginning
For decades, researchers have been looking for ways to destroy cancer cells in a targeted manner without further weakening the body. But for many patients whose immune system is severely impaired by chemotherapy or radiation, [...]
Older chemical libraries show promise for fighting resistant strains of COVID-19 virus
SARS‑CoV‑2, the virus that causes COVID-19, continues to mutate, with some newer strains becoming less responsive to current antiviral treatments like Paxlovid. Now, University of California San Diego scientists and an international team of [...]
Lower doses of immunotherapy for skin cancer give better results, study suggests
According to a new study, lower doses of approved immunotherapy for malignant melanoma can give better results against tumors, while reducing side effects. This is reported by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in the Journal of the National [...]
Researchers highlight five pathways through which microplastics can harm the brain
Microplastics could be fueling neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, with a new study highlighting five ways microplastics can trigger inflammation and damage in the brain. More than 57 million people live with dementia, [...]