Researchers from CIC-nanoGUNE (San Sebastián, Spain), in collaboration with the Donostia International Physics Center (San Sebastián, Spain), Materials Physics Center (CFM, CSIC-UPV/EHU, San Sebastián, Spain) and University of Oviedo demonstrate a new way to strongly couple infrared light and molecular vibrations, by utilizing phonon polariton nanoresonators made of hexagonal boron nitride, a Van der Waals material.
The results published in Light: Science & Applications (“Boron nitride nanoresonators for phonon-enhanced molecular vibrational spectroscopy at the strong coupling limit”) open new avenues for fundamental studies of vibrational strong coupling, as well as for the development of novel infrared sensors for chemical recognition of very small amounts of molecules.
The interaction of light and matter at the nanoscale is a key element for many fundamental studies and technological applications, ranging from light harvesting to the detection of small amounts of molecules.
During the last decades, many strategies have been implemented in order to enhance nanoscale light-matter interactions. One approach is based on concentrating light with the help of propagating and localized surface plasmon polaritons, which are collective electron oscillations in metals or semiconductors that are coupled to light. These electromagnetic excitations can concentrate light into nanoscale spots, so-called hotspots. At mid-infrared frequencies, they enable, for example, the detection of tiny amounts of molecules. This method is called surface-enhanced infrared absorption (SEIRA) spectroscopy. However, typical mid-infrared plasmonic structures suffer from large losses and do not achieve ultimate light concentration.
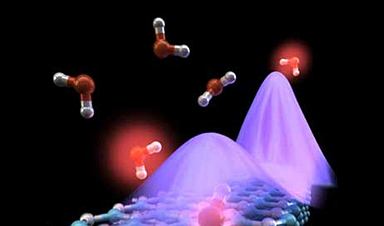
An interesting but much less explored approach for enhancing nanoscale light-matter interaction is based on infrared-phononic materials, in which light couples to crystal lattice vibrations to form so-called phonon polaritons. “Phonon-polariton resonators offer much lower losses and field confinement than their mid-infrared plasmonic counterparts. For that reason, we decided to develop and apply infrared-phononic resonators to enhance the coupling of infrared light to molecular vibrations” says postdoc Marta Autore, first author of the paper.
Image Credit: Ella Maru Studio
News This Week
AI Helped Scientists Stop a Virus With One Tiny Change
Using AI, researchers identified one tiny molecular interaction that viruses need to infect cells. Disrupting it stopped the virus before infection could begin. Washington State University scientists have uncovered a method to interfere with a key [...]
Deadly Hospital Fungus May Finally Have a Weakness
A deadly, drug-resistant hospital fungus may finally have a weakness—and scientists think they’ve found it. Researchers have identified a genetic process that could open the door to new treatments for a dangerous fungal infection [...]
Fever-Proof Bird Flu Variant Could Fuel the Next Pandemic
Bird flu viruses present a significant risk to humans because they can continue replicating at temperatures higher than a typical fever. Fever is one of the body’s main tools for slowing or stopping viral [...]
What could the future of nanoscience look like?
Society has a lot to thank for nanoscience. From improved health monitoring to reducing the size of electronics, scientists’ ability to delve deeper and better understand chemistry at the nanoscale has opened up numerous [...]
Scientists Melt Cancer’s Hidden “Power Hubs” and Stop Tumor Growth
Researchers discovered that in a rare kidney cancer, RNA builds droplet-like hubs that act as growth control centers inside tumor cells. By engineering a molecular switch to dissolve these hubs, they were able to halt cancer [...]
Platelet-inspired nanoparticles could improve treatment of inflammatory diseases
Scientists have developed platelet-inspired nanoparticles that deliver anti-inflammatory drugs directly to brain-computer interface implants, doubling their effectiveness. Scientists have found a way to improve the performance of brain-computer interface (BCI) electrodes by delivering anti-inflammatory drugs directly [...]
After 150 years, a new chapter in cancer therapy is finally beginning
For decades, researchers have been looking for ways to destroy cancer cells in a targeted manner without further weakening the body. But for many patients whose immune system is severely impaired by chemotherapy or radiation, [...]
Older chemical libraries show promise for fighting resistant strains of COVID-19 virus
SARS‑CoV‑2, the virus that causes COVID-19, continues to mutate, with some newer strains becoming less responsive to current antiviral treatments like Paxlovid. Now, University of California San Diego scientists and an international team of [...]













Leave A Comment