The COVID-19 epidemic has now entered its third year with its effects still being felt across the world. In many countries, there have been an alarming trend of waning vaccine efficacy paired with the emergence of variants with stronger immune escape and transmission ability. This consistent challenging of our pre-established immune barriers has driven the need for new, innovative vaccine modalities that overcome the hurdles of existing vaccination programs.
A recent breakthrough in COVID vaccine research is the regulatory approval of CovidenciaTM Air from CanSinoBio, a first-in-class inhaled vaccine described to ‘effectively induce comprehensive immune protection in response to SARS-CoV-2 after just one breath’. This was swiftly followed by another inhaled aerosol vaccine by Bharat Biotech in India, indicated for ‘restricted use in emergency situations.’ With these new, innovative vaccine breakthroughs, what does this mean for the future of vaccine research?
Routes of Administration: Inhalation vs Intramuscular
The advent of this new administration modality directs our attention to the comparison between inhaled vaccines and conventional intramuscular vaccines. On one hand, intramuscular vaccines are designed to stimulate the systemic immune response, triggering the production of neutralizing antibodies such as IgGs. Contrary to this, aerosolized inhaled vaccines focus on simulating respiratory viral infection, leading to increased surface-level immune response and a quicker response to viral invaders.
It is important to note that aerosol-based vaccines have been introduced previously in the form of nasal vaccines. However, questions and concerns have been raised regarding its limited efficacy in initial studies. With these new, inhaled aerosol vaccines, these vaccines have been shown to have improved biodistribution deeper into the respiratory tract in comparison to nasal vaccines.
This increased biodistribution has shown to be induce a higher immune response and confer improved protective effects in preliminary studies.
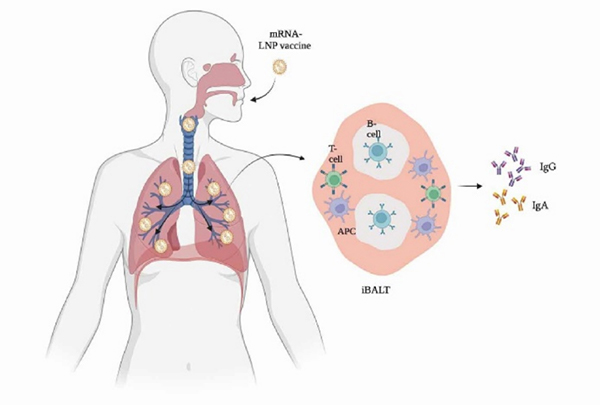
Figure 1. Mucosal immune response in the lung after vaccination through novel mRNA inhaled vaccine. 1
Evaluating the Safety and Efficacy of Inhaled Vaccines
The advantages of an inhaled vaccines are undeniable, especially logistically, where these vaccines have lower dosages, conventional storage conditions, and have a wider distribution availability. This is heavily advantageous in resource-limited countries that may struggle with establishing and distributing newer, urgent vaccines. However, the evaluation of new vaccine modalities is incomplete, especially in regulatory settings. For intramuscular COVID-19 vaccines, the standard method in predicting vaccine efficacy is through the evaluation of neutralizing-antibody levels, while cellular immunity is evaluated by antigen-specific T cell response and cytokine secretion. Conversely, the proposed efficacy of inhaled vaccines stems from the stimulation of mucosal immune response alongside humoral and cellular responses. As such, the mucosal immune response has been highlighted as a critical immune response that could play a role in combating initial infections and should be evaluated. This is evidenced by the stimulation of the mucosal immune system, triggering the production of both IgGs and local IgAs. Produced by mucosal tissue, IgAs are responsible for pathogen neutralization and prevention of binding to mucosal tissue. Thus, when combating respiratory diseases such as COVID-19, IgA levels are increasingly of-interest when evaluating vaccine efficacy.
The Next Generation of Vaccines?
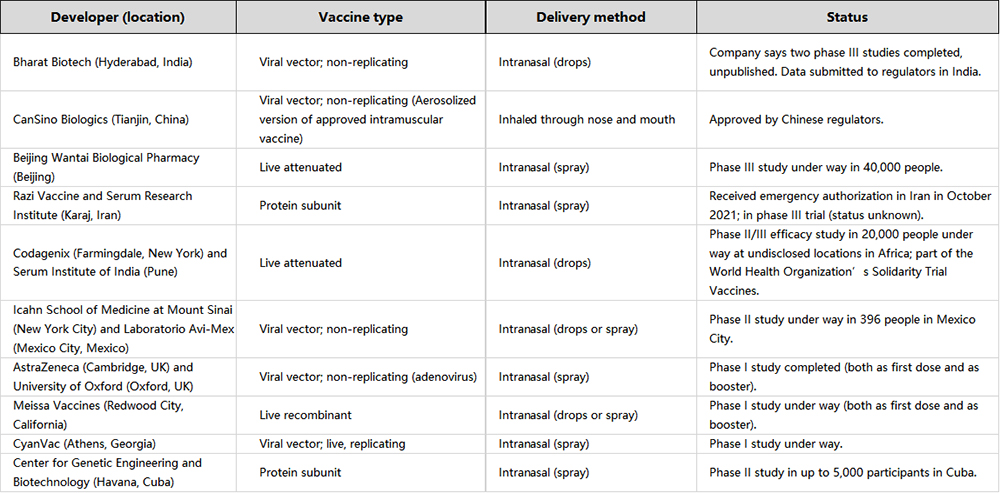
Overall, it might be easy to jump to the conclusion that inhaled vaccines will be the future route of administration for vaccines. Without the need for medical professionals, needles, and lower vaccine dosages, these inhaled and other aerosol-based vaccines are undoubtedly a significant breakthrough. According to a health-analytics company in London, there are currently around 100 aerosol-based COVID-19 vaccines are being developed in the world with around 20 of them reaching human clinical trials.2
Despite the potential, conventional intramuscular vaccines are projected to retain its role as the front-line defense in vaccination. As the more mature method, intramuscular vaccines still provide strong immune responses to invading viruses. Most companies are developing inhaled vaccines as a complement or enhanced vaccine booster to improve the current state of immunity. This is supported by various studies that proposes a ‘prime-pull’ vaccination strategy which utilizes intramuscular vaccines to ‘prime’ the immune system with an inhaled booster to increase the immune defense.
Moreover, the effectiveness and potential of these inhaled vaccines needs to be further evaluated, especially as more inhaled vaccines obtain approval and widespread use. In theory, if these type of vaccines can help prevent infections and transmission, they could greatly impact the COVID-19 pandemic. Inhaled vaccines could boost a person’s “first line of defense” against the virus and have the potential to reduce onward transmission, Mike Ryan, the executive director of WHO Health Emergencies Programme, said at a press briefing. “But it remains to be seen.”
News
Scientists Discover Why Some COVID Survivors Still Can’t Taste Food Years Later
A new study provides the first direct biological evidence explaining why some people continue to experience taste loss long after recovering from COVID-19. Researchers have uncovered specific biological changes in taste buds that could help [...]
Catching COVID significantly raises the risk of developing kidney disease, researchers find
Catching Covid significantly raises the risk of developing deadly kidney disease, research has shown. The virus was found to increase the chances that patients will develop the incurable condition by around 50 per cent. [...]
New Toothpaste Stops Gum Disease Without Harming Healthy Bacteria
Researchers have developed a targeted approach to combat periodontitis without disrupting the natural balance of the oral microbiome. The innovation could reshape how gum disease is treated while preserving beneficial bacteria. The human mouth [...]
Plastic Without End: Are We Polluting the Planet for Eternity?
The Kunming Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework calls for the elimination of plastic pollution by 2030. If that goal has been clearly set, why have meaningful measures that create real change still not been implemented? [...]
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]