A recent study reveals oscillations in the refractive index that are faster than can be explained by current theories.
A study recently published in the journal Nanophotonics reveals that by rapidly modulating the refractive index – which is the ratio of the speed of electromagnetic radiation in a medium compared to its speed in a vacuum – it’s possible to produce photonic time crystals (PTCs) in the near-visible part of the spectrum.
The study’s authors suggest that the ability to sustain PTCs in the optical domain could have profound implications for the science of light, enabling truly disruptive applications in the future.
PTCs, materials in which the refractive index rises and falls rapidly in time, are the temporal equivalent of photonic crystals in which the refractive index oscillates periodically in space causing, for example, the iridescence of precious minerals and insect wings.
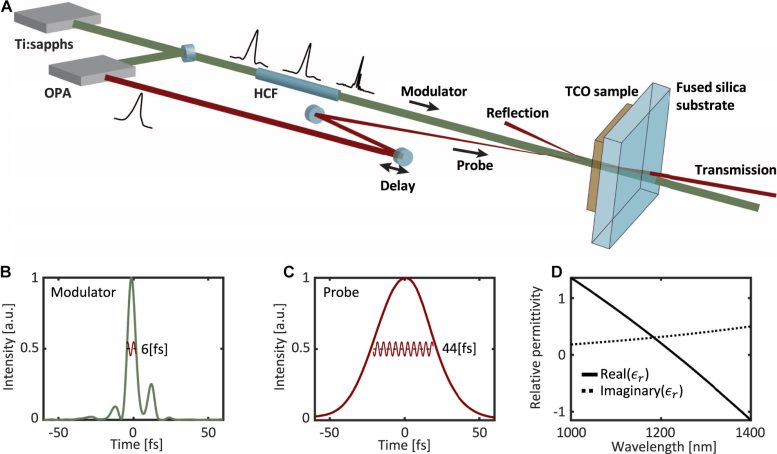
Experimental setup for measuring time-refraction in the single-cycle regime. Credit: Eran Lustig et al.
A PTC is only stable if the refractive index can be made to rise and fall in line with a single cycle of electromagnetic waves at the frequency concerned so, unsurprisingly, PTCs have thus far been observed at the lowest-frequency end of the electromagnetic spectrum: with radio waves.
In this new study, lead author Mordechai Segev of the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, Israel, with collaborators Vladimir Shalaev and AlexndraBoltasseva from Purdue University, Indiana, USA, and their teams, sent extremely short (5-6 femtosecond) pulses of laser light at a wavelength of 800 nanometers through transparent conductive oxide materials.
This caused a rapid shift in refractive index that was explored using a probe laser beam at a slightly longer (near infrared) wavelength. The probe beam was rapidly red-shifted (that is, its wavelength increased) and then blue-shifted (wavelength decreased) as the material’s refractive index relaxed back to its normal value.
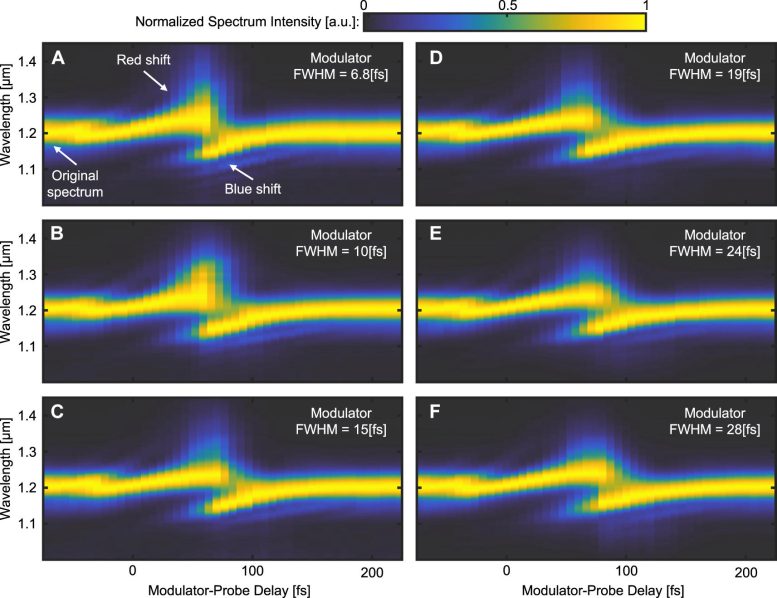
Transmission spectrograms of 44 fs probe pulses that have passed through the ITO sample, for modulator pulses of different temporal widths. Credit: Eran Lustig et al.
The time taken for each of these refractive index changes was minuscule – less than 10 femtoseconds – and, therefore, within the single cycle necessary to form a stable PTC.
“Electrons excited to high energy in crystals generally need over ten times as long to relax back to their ground states, and many researchers thought that the ultra-fast relaxation we observe here would be impossible,” Segev said. “We don’t yet understand exactly how it happens.”
Co-author Shalaev further suggests that the ability to sustain PTCs in the optical domain, as demonstrated here, will “open a new chapter in the science of light and enable truly disruptive applications”. However, we know as little of what these might be as physicists in the 1960s knew of the possible applications of lasers.
Reference: “Time-refraction optics with single cycle modulation” by Eran Lustig, Ohad Segal, Soham Saha, Eliyahu Bordo, Sarah N. Chowdhury, Yonatan Sharabi, Avner Fleischer, Alexandra Boltasseva, Oren Cohen, Vladimir M. Shalaev and Mordechai Segev, 31 May 2023, Nanophotonics.
DOI: 10.1515/nanoph-2023-0126
The research was funded by the German Research Foundation.
News
Global Nanomaterial Regulation: A Country-by-Country Comparison
Nanomaterials are materials with at least one dimension smaller than 100 nanometres (about 100,000 times thinner than a human hair). Because of their tiny size, they have unique properties that can be useful in [...]
Pandemic Potential: Scientists Discover 3 Hotspots of Deadly Emerging Disease in the US
Virginia Tech researchers discovered six new rodent carriers of hantavirus and identified U.S. hotspots, highlighting the virus’s adaptability and the impact of climate and ecology on its spread. Hantavirus recently drew public attention following reports [...]
Studies detail high rates of long COVID among healthcare, dental workers
Researchers have estimated approximately 8% of Americas have ever experienced long COVID, or lasting symptoms, following an acute COVID-19 infection. Now two recent international studies suggest that the percentage is much higher among healthcare workers [...]
Melting Arctic Ice May Unleash Ancient Deadly Diseases, Scientists Warn
Melting Arctic ice increases human and animal interactions, raising the risk of infectious disease spread. Researchers urge early intervention and surveillance. Climate change is opening new pathways for the spread of infectious diseases such [...]
Scientists May Have Found a Secret Weapon To Stop Pancreatic Cancer Before It Starts
Researchers at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory have found that blocking the FGFR2 and EGFR genes can stop early-stage pancreatic cancer from progressing, offering a promising path toward prevention. Pancreatic cancer is expected to become [...]
Breakthrough Drug Restores Vision: Researchers Successfully Reverse Retinal Damage
Blocking the PROX1 protein allowed KAIST researchers to regenerate damaged retinas and restore vision in mice. Vision is one of the most important human senses, yet more than 300 million people around the world are at [...]
Differentiating cancerous and healthy cells through motion analysis
Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have found that the motion of unlabeled cells can be used to tell whether they are cancerous or healthy. They observed malignant fibrosarcoma [...]
This Tiny Cellular Gate Could Be the Key to Curing Cancer – And Regrowing Hair
After more than five decades of mystery, scientists have finally unveiled the detailed structure and function of a long-theorized molecular machine in our mitochondria — the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier. This microscopic gatekeeper controls how [...]
Unlocking Vision’s Secrets: Researchers Reveal 3D Structure of Key Eye Protein
Researchers have uncovered the 3D structure of RBP3, a key protein in vision, revealing how it transports retinoids and fatty acids and how its dysfunction may lead to retinal diseases. Proteins play a critical [...]
5 Key Facts About Nanoplastics and How They Affect the Human Body
Nanoplastics are typically defined as plastic particles smaller than 1000 nanometers. These particles are increasingly being detected in human tissues: they can bypass biological barriers, accumulate in organs, and may influence health in ways [...]
Measles Is Back: Doctors Warn of Dangerous Surge Across the U.S.
Parents are encouraged to contact their pediatrician if their child has been exposed to measles or is showing symptoms. Pediatric infectious disease experts are emphasizing the critical importance of measles vaccination, as the highly [...]
AI at the Speed of Light: How Silicon Photonics Are Reinventing Hardware
A cutting-edge AI acceleration platform powered by light rather than electricity could revolutionize how AI is trained and deployed. Using photonic integrated circuits made from advanced III-V semiconductors, researchers have developed a system that vastly [...]
A Grain of Brain, 523 Million Synapses, Most Complicated Neuroscience Experiment Ever Attempted
A team of over 150 scientists has achieved what once seemed impossible: a complete wiring and activity map of a tiny section of a mammalian brain. This feat, part of the MICrONS Project, rivals [...]
The Secret “Radar” Bacteria Use To Outsmart Their Enemies
A chemical radar allows bacteria to sense and eliminate predators. Investigating how microorganisms communicate deepens our understanding of the complex ecological interactions that shape our environment is an area of key focus for the [...]
Psychologists explore ethical issues associated with human-AI relationships
It's becoming increasingly commonplace for people to develop intimate, long-term relationships with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. At their extreme, people have "married" their AI companions in non-legally binding ceremonies, and at least two people [...]
When You Lose Weight, Where Does It Actually Go?
Most health professionals lack a clear understanding of how body fat is lost, often subscribing to misconceptions like fat converting to energy or muscle. The truth is, fat is actually broken down into carbon [...]