A group of researchers recently published a paper in the journal Materials that demonstrated the viability of using vancomycin-functionalized gold nanoparticles (V-GNPs) against pathogenic bacterial strains.
Background
Antibiotic resistance among pathogenic bacteria is rising at a remarkable rate, which poses a significant risk to human health. For instance, vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, is typically used for treating bacterial infections such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). However, the excessive use of vancomycin has led to the emergence of vancomycin-resistant bacterial strains.
Innovative strategies such as the use of nanoparticles (NPs) hold the potential to combat antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections.
The characteristics of NPs, such as surface chemistry, size, and shape, can be manipulated easily, which makes them suitable for fighting bacterial infections.
Metallic NPs, such as GNPs, are specifically being evaluated in different studies for their potential in treating bacterial infections.
Several studies have shown that the antibacterial activities of antibiotics can be enhanced by conjugating GNPs with antibiotics.
In this study, researchers investigated the ability of GNPs to enhance the antibacterial efficacy of the antibiotic vancomycin against different bacterial strains.
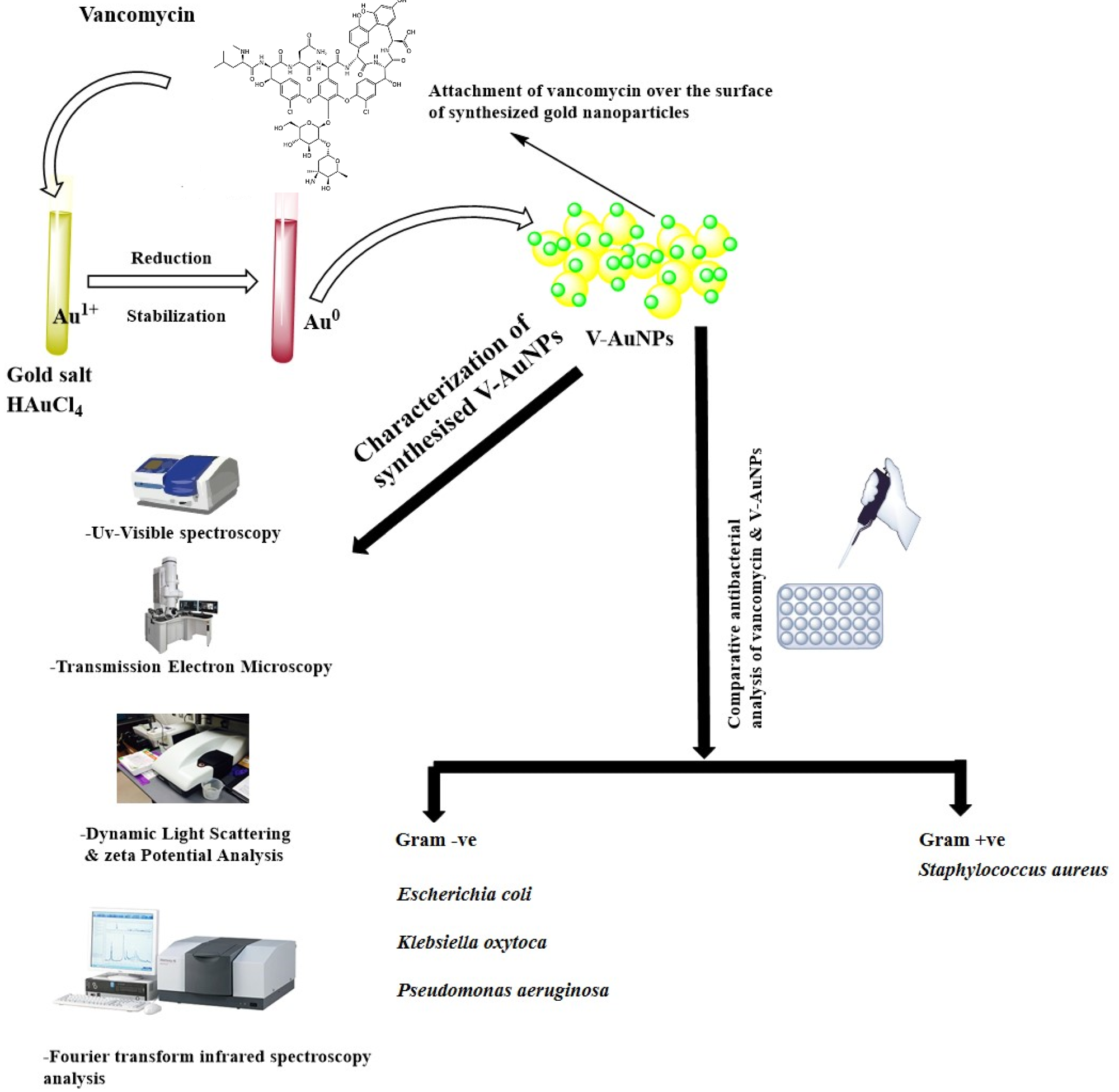
Figure 1. Schematic representation of vancomycin-mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles (V-GNPs), their characterization, and antibacterial testing. © Hagbani, T.A., Yadav, H., Moin, A. et al. (2022)
The Study
Gold (III) chloride trihydrate (HAuCl4·3H2O), phosphate buffer, and vancomycin were used for preparing V-GNPs in the study.
In the preparation, 1, 0.75, 0.50, or 0.25 mg/mL of vancomycin was mixed with a 3 mL reaction mixture containing 50 mM phosphate buffer with a pH value of 7.4 and 1 mM HAuCl4·3H2O, and the resultant mixture was incubated at 60, 50, 40, and 30 oC, respectively, for 48 h.
The synthesized V-GNPs were obtained by centrifugation of the reaction mixture for 30 min at 30,000× g and the collected NPs were treated with 50% v/v ethanol in order to eliminate unattached materials.
The Gram-positive bacterial strain of Staphylococcus aureus and the Gram-negative strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella oxytoca, and Escherichia coli were used in the study to evaluate the antibacterial efficacy of V-GNPs.
Each bacterial strain was maintained and cultivated in Mueller Hinton (MH) agar media at 37 oC.
A Shimadzu UV-1601 spectrophotometer was employed to obtain the ultraviolet ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) spectra of the prepared V-GNPs in the range of 200-800 nm at 1 nm resolution.
The average particle size of the synthesized V-GNPs was determined using a dynamic light scattering particle (DLS) size analyzer, while the zeta-potential of the synthesized NPs was measured using a Malvern Zetasizer Nano-ZS.
A transmission electron microscopy (TEM) operating at an accelerating voltage of 80 kV was used to assess the homogeneity of the prepared V-GNPs, while Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was performed to evaluate the conformational changes after vancomycin was loaded on the surface of GNPs.
The FTIR spectra were acquired using the potassium bromide (KBr) pellet method with a Shimadzu FTIR-8201 spectrometer within the range of 4000–400 cm-1 at a resolution of 4 cm-1.
The agar well diffusion methodology was utilized to evaluate the efficacy of prepared V-GNPs and pure vancomycin.
The in vitro antibacterial activity of pure vancomycin and V-GNPs was assessed using the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) method. The loading efficiency of V-GNPs was also calculated. All findings in the study were analyzed using GraphPad Prism through a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).
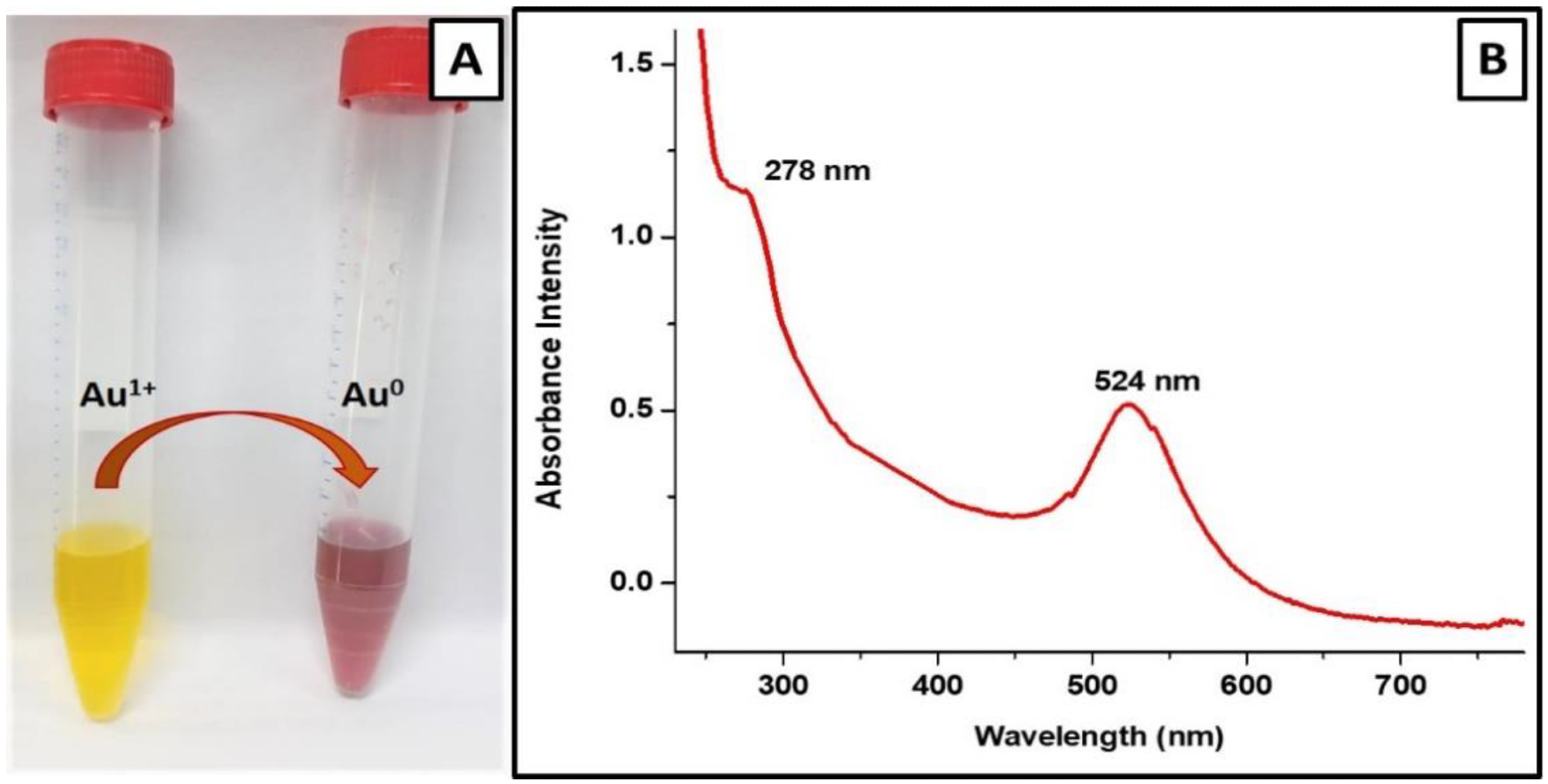
Figure 2. Characterization of V-GNPs: (A) color change from light yellow to ruby red resulted from SPR; (B) UV–Visible spectra (SPR band at 524 nm). © Hagbani, T.A., Yadav, H., Moin, A. et al. (2022)
Observations
GNPs with good physicochemical properties were synthesized at a pH of 7.4, a temperature of 40 oC, and a vancomycin concentration of 250 µg/mL.
The color of the gold salt solution changed from pale yellow to ruby red following the addition of 250 µg/mL vancomycin antibiotic, indicating the formation of V-GNPs.
The UV-Vis spectra of the prepared V-GNPs revealed the presence of a surface plasmon resonance peak at 524 nm.
The TEM micrographs showed that the synthesized V-GNPs were monodispersed, homogenous, and spherical in shape with an average size of 24 nm. No agglomeration was observed in the TEM micrographs, indicating the suitability of vancomycin as a stabilizing agent.
The hydrodynamic diameter of the V-GNPs was estimated as 77 nm by the DLS.
The zeta potential of the prepared V-GNPs was -18mV, indicating good stability of GNPs. Observations from the FTIR spectroscopy indicated that the vancomycin was efficiently loaded on the GNP surfaces, and the loading efficiency was 86.2%.
Both V-GNPs and pure vancomycin significantly inhibited bacterial growth. However, V-GNPs demonstrated more effective antibacterial activity compared to pure vancomycin even at a lower concentration of vancomycin.
The in vitro antibacterial studies demonstrated that the antibacterial activities of the synthesized V-GNPs were 1.6-, 1.8-, 1.6-, and 1,4-fold higher than pure vancomycin against Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella oxytoca, and Escherichia coli, respectively.
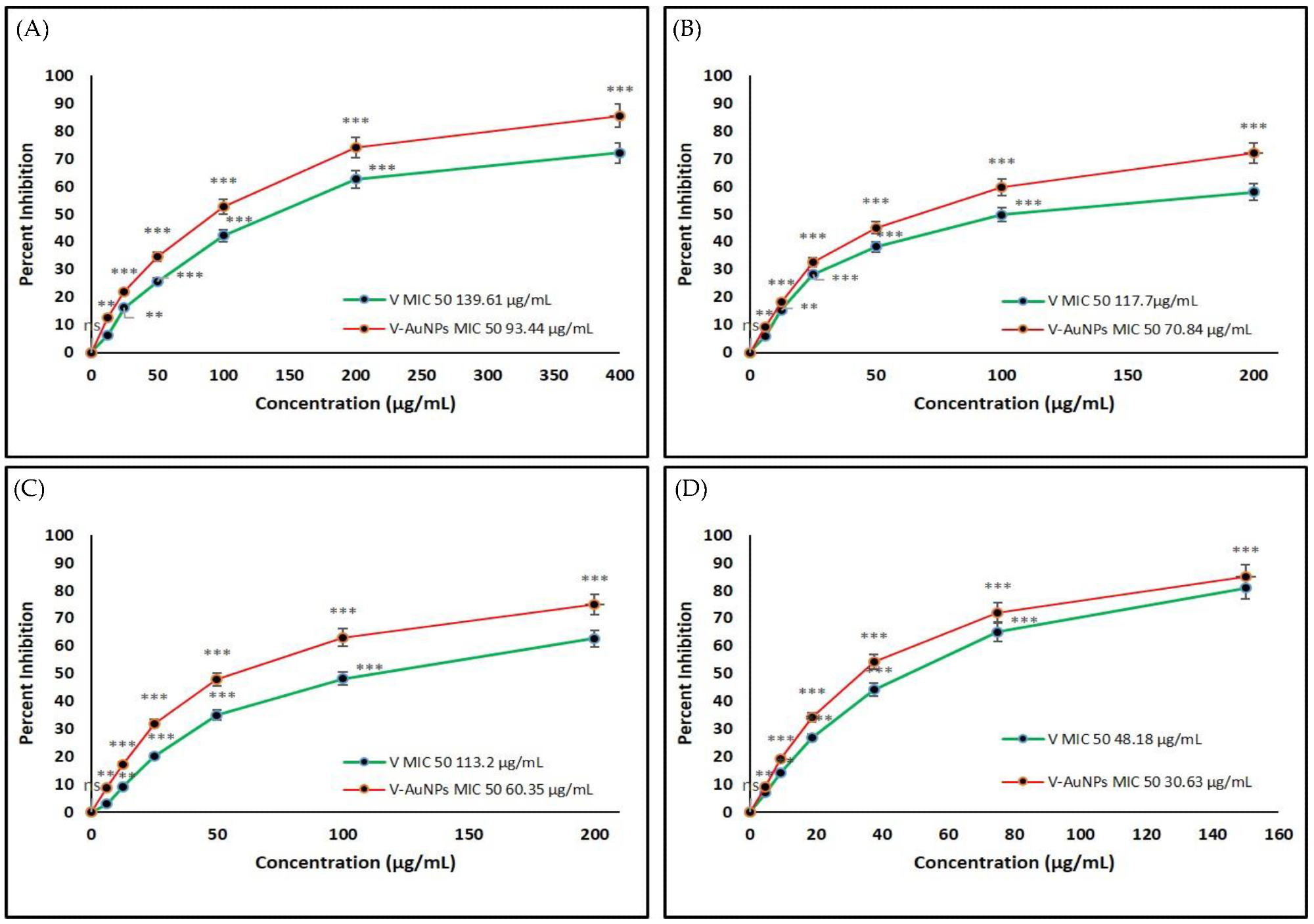
Figure 3. Determination of the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of vancomycin (V) and V-GNPs against (A) Escherichia coli; (B) Klebsiella oxytoca; (C) Pseudomonas aeruginosa; (D) Staphylococcus aureus. The experiment was repeated in triplicate, and the data shown are the means ± standard errors. Significantly different from control at ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001; non-significant from the control at ns p > 0.05. © Hagbani, T.A., Yadav, H., Moin, A. et al. (2022)
Significance of the Study
Taken together, the findings of the study demonstrated that V-GNPs represent a more suitable alternative compared to pure vancomycin against pathogenic bacterial strains.
However, in vivo investigations must be performed to assess the toxicity of V-GNPs before the synthesized vancomycin nanoformulations can be used to treat infections. Nevertheless, this study can act as a starting point for developing better antibacterial nanoformulations.
News
Study Delivers Cancer Drugs Directly to the Tumor Nucleus
A new peptide-based nanotube treatment sneaks chemo into drug-resistant cancer cells, providing a unique workaround to one of oncology’s toughest hurdles. CiQUS researchers have developed a novel molecular strategy that allows a chemotherapy drug to [...]
Scientists Begin $14.2 Million Project To Decode the Body’s “Hidden Sixth Sense”
An NIH-supported initiative seeks to unravel how the nervous system tracks and regulates the body’s internal organs. How does your brain recognize when it’s time to take a breath, when your blood pressure has [...]
Scientists Discover a New Form of Ice That Shouldn’t Exist
Researchers at the European XFEL and DESY are investigating unusual forms of ice that can exist at room temperature when subjected to extreme pressure. Ice comes in many forms, even when made of nothing but water [...]
Nobel-winning, tiny ‘sponge crystals’ with an astonishing amount of inner space
The 2025 Nobel Prize in chemistry was awarded to Richard Robson, Susumu Kitagawa and Omar Yaghi on Oct. 8, 2025, for the development of metal-organic frameworks, or MOFs, which are tunable crystal structures with extremely [...]
Harnessing Green-Synthesized Nanoparticles for Water Purification
A new review reveals how plant- and microbe-derived nanoparticles can power next-gen water disinfection, delivering cleaner, safer water without the environmental cost of traditional treatments. A recent review published in Nanomaterials highlights the potential of green-synthesized nanomaterials (GSNMs) in [...]
Brainstem damage found to be behind long-lasting effects of severe Covid-19
Damage to the brainstem - the brain's 'control center' - is behind long-lasting physical and psychiatric effects of severe Covid-19 infection, a study suggests. Using ultra-high-resolution scanners that can see the living brain in [...]
CT scan changes over one year predict outcomes in fibrotic lung disease
Researchers at National Jewish Health have shown that subtle increases in lung scarring, detected by an artificial intelligence-based tool on CT scans taken one year apart, are associated with disease progression and survival in [...]
AI Spots Hidden Signs of Disease Before Symptoms Appear
Researchers suggest that examining the inner workings of cells more closely could help physicians detect diseases earlier and more accurately match patients with effective therapies. Researchers at McGill University have created an artificial intelligence tool capable of uncovering [...]
Breakthrough Blood Test Detects Head and Neck Cancer up to 10 Years Before Symptoms
Mass General Brigham’s HPV-DeepSeek test enables much earlier cancer detection through a blood sample, creating a new opportunity for screening HPV-related head and neck cancers. Human papillomavirus (HPV) is responsible for about 70% of [...]
Study of 86 chikungunya outbreaks reveals unpredictability in size and severity
The symptoms come on quickly—acute fever, followed by debilitating joint pain that can last for months. Though rarely fatal, the chikungunya virus, a mosquito-borne illness, can be particularly severe for high-risk individuals, including newborns and older [...]
Tiny Fat Messengers May Link Obesity to Alzheimer’s Plaque Buildup
Summary: A groundbreaking study reveals how obesity may drive Alzheimer’s disease through tiny messengers called extracellular vesicles released from fat tissue. These vesicles carry lipids that alter how quickly amyloid-β plaques form, a hallmark of [...]
Ozone exposure weakens lung function and reshapes the oral microbiome
Scientists reveal that short-term ozone inhalation doesn’t just harm the lungs; it reshapes the microbes in your mouth, with men facing the greatest risks. Ozone is a toxic environmental pollutant with wide-ranging effects on [...]
New study reveals molecular basis of Long COVID brain fog
Even though many years have passed since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, the effects of infection with SARS-CoV-2 are not completely understood. This is especially true for Long COVID, a chronic condition that [...]
Scientists make huge Parkinson’s breakthrough as they discover ‘protein trigger’
Scientists have, for the first time, directly visualised the protein clusters in the brain believed to trigger Parkinson's disease, bringing them one step closer to potential treatments. Parkinson's is a progressive incurable neurological disorder [...]
Alpha amino acids’ stability may explain their role as early life’s protein building blocks
A new study from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences sheds light on one of life's greatest mysteries: why biology is based on a very specific set [...]
3D bioprinting advances enable creation of artificial blood vessels with layered structures
To explore possible treatments for various diseases, either animal models or human cell cultures are usually used first; however, animal models do not always mimic human diseases well, and cultures are far removed [...]