In a research study published recently in the journal Agriculture, an electrolytic sensor based on the concentration of floral nano-ZnO and the identification of immune reaction was created for the high-sensitivity monitoring of Tenuazonic acid (TeA) in fruit and vegetables.
When comparing various morphologies, dimensions, and crystalline structures of nano-ZnO, the researchers discovered that floral nano-ZnO (ZnO NFs) with a hexagonal phase had the best surface area and conductance.
What is Tenuazonic Acid (TeA)?
When compared to other Alternaria chemicals, tenuazonic acid (TeA) exhibits a high level of toxic effects, including neurotoxicity and probable carcinogenic effects.
It may also cause cumulative harm when combined with other toxins, leading to acute poisoning.
TeA can be found in a variety of foods, including grains, peppercorns, vegetables, fruits, and even animal proteins, with levels of contamination varying from a few milligrams to thousands of milligrams.
TeA was included by the United States National Council for Occupational Health & Safety in 1979 due to its high contamination of farm products.
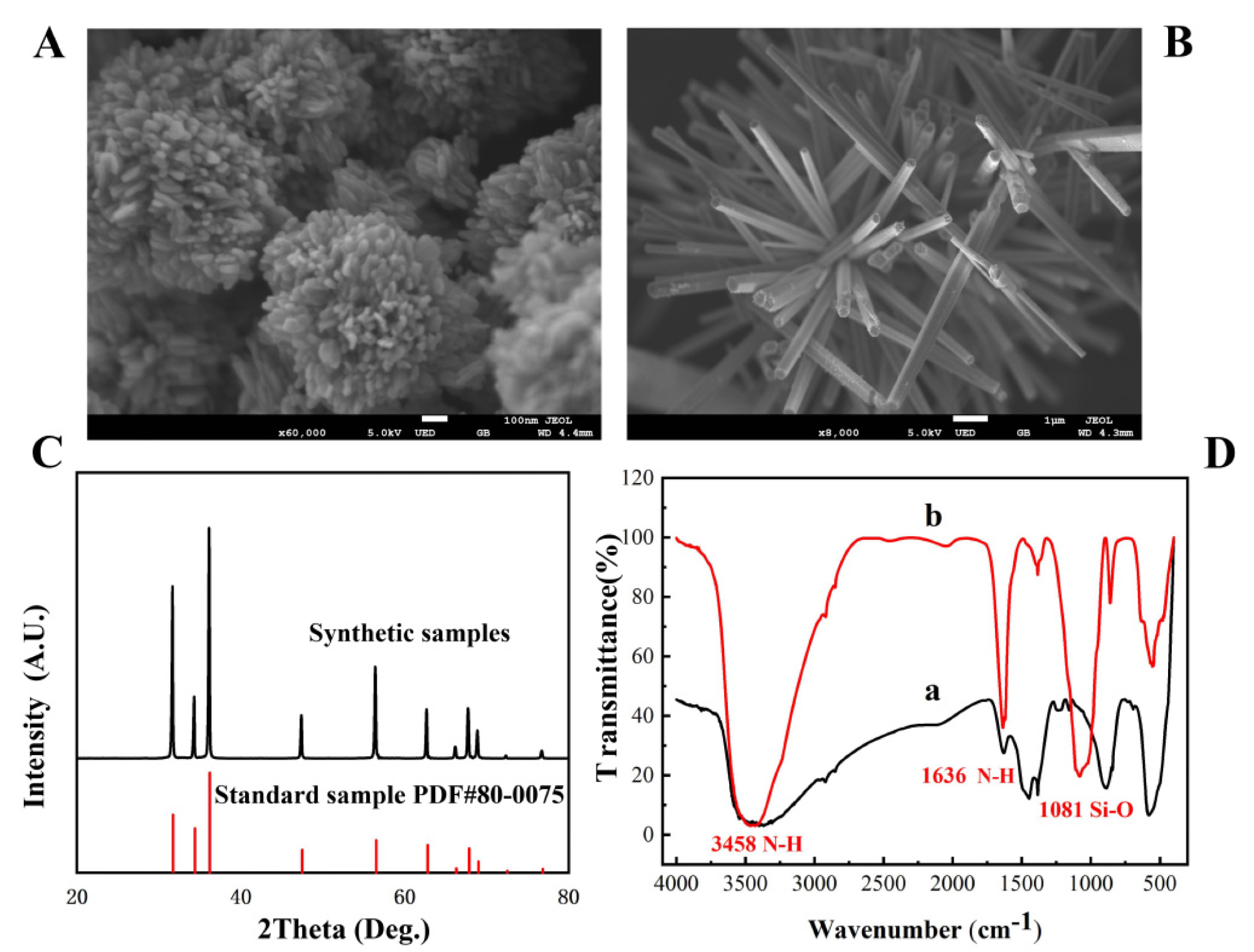
Figure 1. The SEM image of flower-shaped nano-ZnO (A) and brush-shaped nano-ZnO (B); XRD patterns of ZnO (C); FT-IR spectrum of amino-modified nano-ZnO (D). © Zhang, C. et al. (2022)
To date, enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) and column chromatography spectroscopy have been the primary methods for detecting the carcinogen TeA.
However, since these traditional detection systems have significant drawbacks, such as being inconvenient, time-consuming, and having low susceptibility, enhancements in sensing methods of TeA are still needed.
Importance of ZnO Based Electrochemical Biosensors
In comparison to the approaches mentioned above, the electrochemical biosensor has been commonly regarded as a potent assessment technique with several advantages, including quick detection rate and mobile devices.
Recent research has focused on increasing its high specificity using a nanocomposite with a large surface area, great conductance, and superior photocatalytic characteristics.
Zinc oxide (ZnO) is a global semiconductor that may function as both a nanocomposite and a transistor. Because of its huge surface area, excellent durability, and superior cytocompatibility, it can offer much more redox potential for biorecognition components such as nucleic acid aptamers and monoclonal antibodies.
Since numerous microstructures of ZnO have been effectively implemented to biosensors to identify different bioactive molecules, it is essential to measure the impact of varying morphological features of ZnO on surface area and permeability to widen its implementation in delicate biosensors.
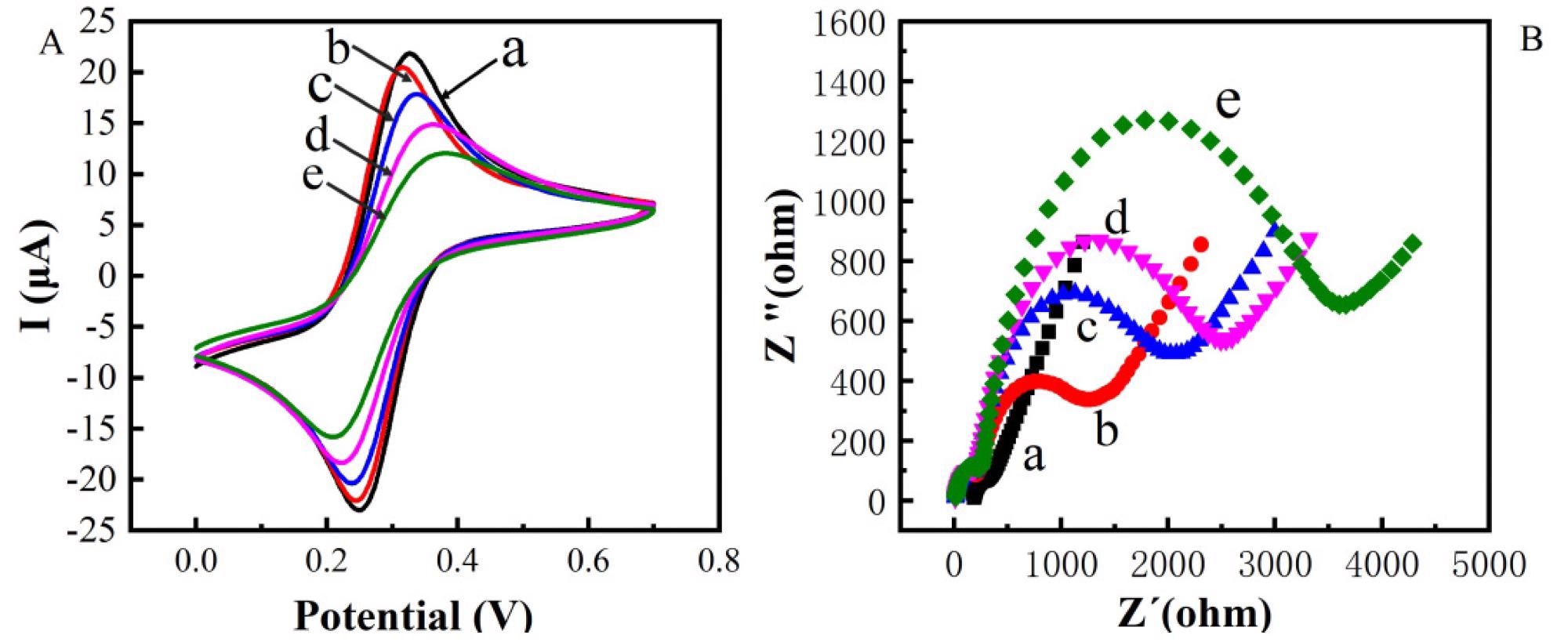
Figure 2. Cyclic voltametric characterization of constructing electrochemical immunosensor (A) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy characterization of constructing electrochemical immunosensor (B) (a: bare Au; b: bare Au/ZnO; c: bare Au/ZnO/antibody; d: bare Au/ZnO/antibody/BSA; e: bare Au/ZnO/antibody/BSA/TeA). © Zhang, C. et al. (2022)
ZnO NFs as Biosensors for Detection of TeA
In this study, by carefully adjusting pH, response duration, activation time, and precipitator, ZnO with various morphologies, dimensions, and crystallinity was manufactured.
Because of the hard surface, three-dimensional structure, and numerous gaps on each nucleotide surface, the floral nanoscale ZnO has the highest load-bearing capacity.
Through an amidation process between the amino group of antigens and the carboxylate, the ZnO NFs were covalently bonded with TeA specific antibodies and subsequently anchored on a gold working electrode altered with 2-mercaptobenzoic acid (MBA).
Construction of Electrochemical TeA Sensor
A traditional three-electrode cell arrangement was used in which a gold wire acted as the electrode material, an Ag/AgCl electrode functioned as the reference electrode, and a Pt cable worked as the counter electrode.
The gold electrode was first soaked in a 1 percent MBA absolute ethanol, then maintained at 37 °C for 2 hours before being washed with distilled water and air-dried.
CV imaging and electrical resistance spectrometry were performed after each of the layers above had been modified.
The electrochemical behavior was investigated using a differentiated pulse voltammetry (DPV) test with a phase voltage of 4 mV, a frequency of 25 Hz, and an intensity of 25 mV.
Research Conclusion and Prospects
In conclusion, to overcome the high-loading issue of specific antibodies, the researchers created altered ZnO and floral nano-ZnO.
The effective production of Au/ZnO/antibody/BSA/TeA was validated by CV and EIS studies. Moreover, the electrolytic biosensor has good specificity and low resistance.
Sensitivity experiments revealed that it has a unique anti-interference capability against pollutants with a composition comparable to TeA.
TeA was effectively determined with a low detection limit using a straightforward, cost-effective, and pollution-free nano-ZnO, paving the way for the development of more economical and accurate biosensors for the identification of additional substances.
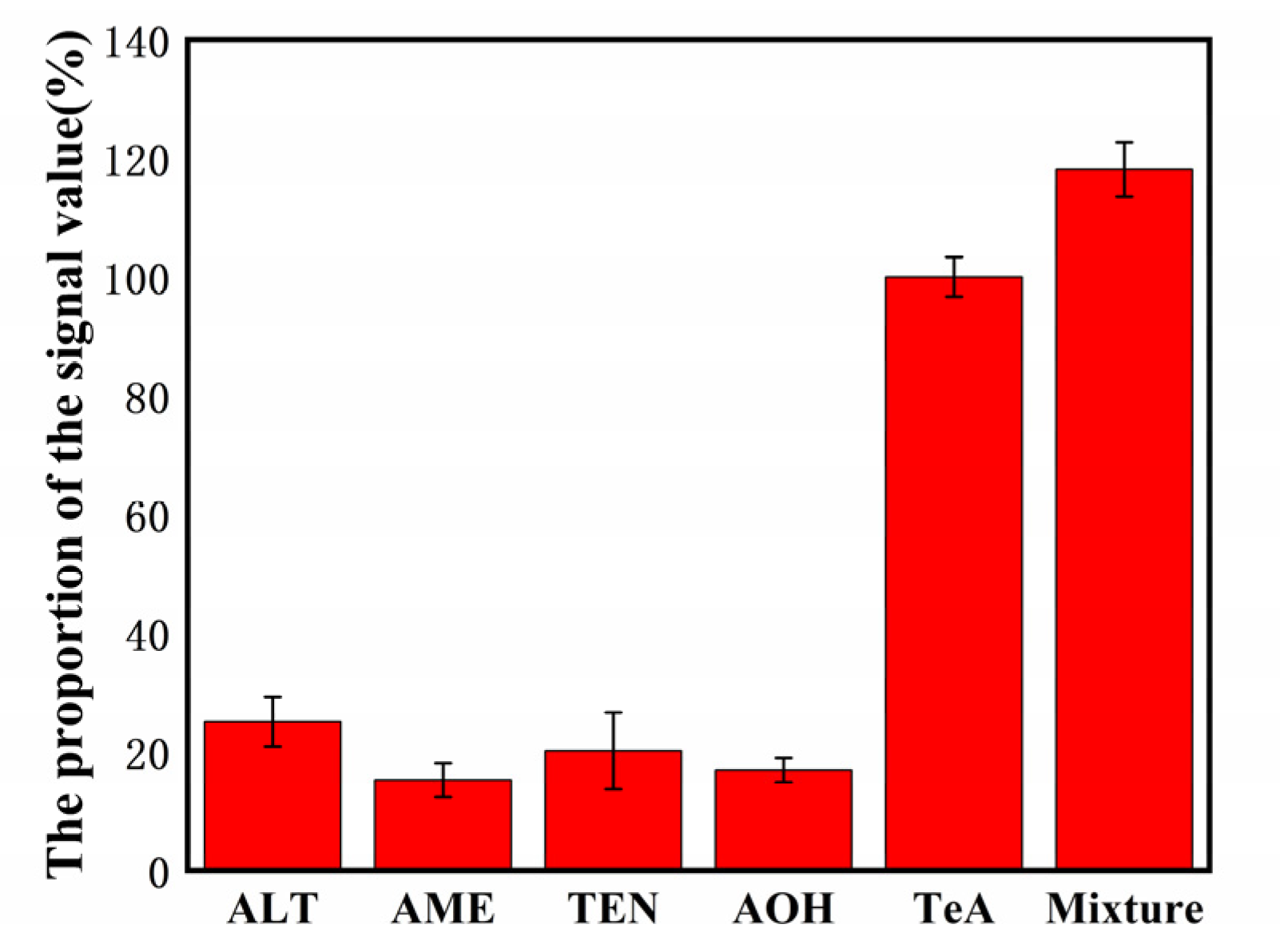
Figure 3. Selectivity of the biosensor detection of TeA (500 pg/mL) against the interference proteins: 50 ng/mL ALT, 50 ng/mL AME, 50 ng/mL TEN, and 50 ng/mL AOH. © Zhang, C. et al. (2022)
News
AI Helped Scientists Stop a Virus With One Tiny Change
Using AI, researchers identified one tiny molecular interaction that viruses need to infect cells. Disrupting it stopped the virus before infection could begin. Washington State University scientists have uncovered a method to interfere with a key [...]
Deadly Hospital Fungus May Finally Have a Weakness
A deadly, drug-resistant hospital fungus may finally have a weakness—and scientists think they’ve found it. Researchers have identified a genetic process that could open the door to new treatments for a dangerous fungal infection [...]
Fever-Proof Bird Flu Variant Could Fuel the Next Pandemic
Bird flu viruses present a significant risk to humans because they can continue replicating at temperatures higher than a typical fever. Fever is one of the body’s main tools for slowing or stopping viral [...]
What could the future of nanoscience look like?
Society has a lot to thank for nanoscience. From improved health monitoring to reducing the size of electronics, scientists’ ability to delve deeper and better understand chemistry at the nanoscale has opened up numerous [...]
Scientists Melt Cancer’s Hidden “Power Hubs” and Stop Tumor Growth
Researchers discovered that in a rare kidney cancer, RNA builds droplet-like hubs that act as growth control centers inside tumor cells. By engineering a molecular switch to dissolve these hubs, they were able to halt cancer [...]
Platelet-inspired nanoparticles could improve treatment of inflammatory diseases
Scientists have developed platelet-inspired nanoparticles that deliver anti-inflammatory drugs directly to brain-computer interface implants, doubling their effectiveness. Scientists have found a way to improve the performance of brain-computer interface (BCI) electrodes by delivering anti-inflammatory drugs directly [...]
After 150 years, a new chapter in cancer therapy is finally beginning
For decades, researchers have been looking for ways to destroy cancer cells in a targeted manner without further weakening the body. But for many patients whose immune system is severely impaired by chemotherapy or radiation, [...]
Older chemical libraries show promise for fighting resistant strains of COVID-19 virus
SARS‑CoV‑2, the virus that causes COVID-19, continues to mutate, with some newer strains becoming less responsive to current antiviral treatments like Paxlovid. Now, University of California San Diego scientists and an international team of [...]
Lower doses of immunotherapy for skin cancer give better results, study suggests
According to a new study, lower doses of approved immunotherapy for malignant melanoma can give better results against tumors, while reducing side effects. This is reported by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in the Journal of the National [...]
Researchers highlight five pathways through which microplastics can harm the brain
Microplastics could be fueling neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, with a new study highlighting five ways microplastics can trigger inflammation and damage in the brain. More than 57 million people live with dementia, [...]
Tiny Metal Nanodots Obliterate Cancer Cells While Largely Sparing Healthy Tissue
Scientists have developed tiny metal-oxide particles that push cancer cells past their stress limits while sparing healthy tissue. An international team led by RMIT University has developed tiny particles called nanodots, crafted from a metallic compound, [...]
Gold Nanoclusters Could Supercharge Quantum Computers
Researchers found that gold “super atoms” can behave like the atoms in top-tier quantum systems—only far easier to scale. These tiny clusters can be customized at the molecular level, offering a powerful, tunable foundation [...]
A single shot of HPV vaccine may be enough to fight cervical cancer, study finds
WASHINGTON -- A single HPV vaccination appears just as effective as two doses at preventing the viral infection that causes cervical cancer, researchers reported Wednesday. HPV, or human papillomavirus, is very common and spread [...]
New technique overcomes technological barrier in 3D brain imaging
Scientists at the Swiss Light Source SLS have succeeded in mapping a piece of brain tissue in 3D at unprecedented resolution using X-rays, non-destructively. The breakthrough overcomes a long-standing technological barrier that had limited [...]
Scientists Uncover Hidden Blood Pattern in Long COVID
Researchers found persistent microclot and NET structures in Long COVID blood that may explain long-lasting symptoms. Researchers examining Long COVID have identified a structural connection between circulating microclots and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). The [...]
This Cellular Trick Helps Cancer Spread, but Could Also Stop It
Groups of normal cbiells can sense far into their surroundings, helping explain cancer cell migration. Understanding this ability could lead to new ways to limit tumor spread. The tale of the princess and the [...]





















