An enormous meteor spelled doom for most dinosaurs 65 million years ago. But not all. In the aftermath of the extinction event, birds — technically dinosaurs themselves — flourished.
Scientists have spent centuries trying to organize and sort some 10,000 species of birds into one clear family tree to understand how the last surviving dinosaurs filled the skies. Cheap DNA sequencing should have made this simple, as it has for countless other species.
But birds were prepared to deceive us.
In a pair of new research papers released today, April 1, scientists reveal that another event 65 million years ago misled them about the true family history of birds. They discovered that a section of one chromosome spent millions of years frozen in time, and it refused to mix together with nearby DNA as it should have.
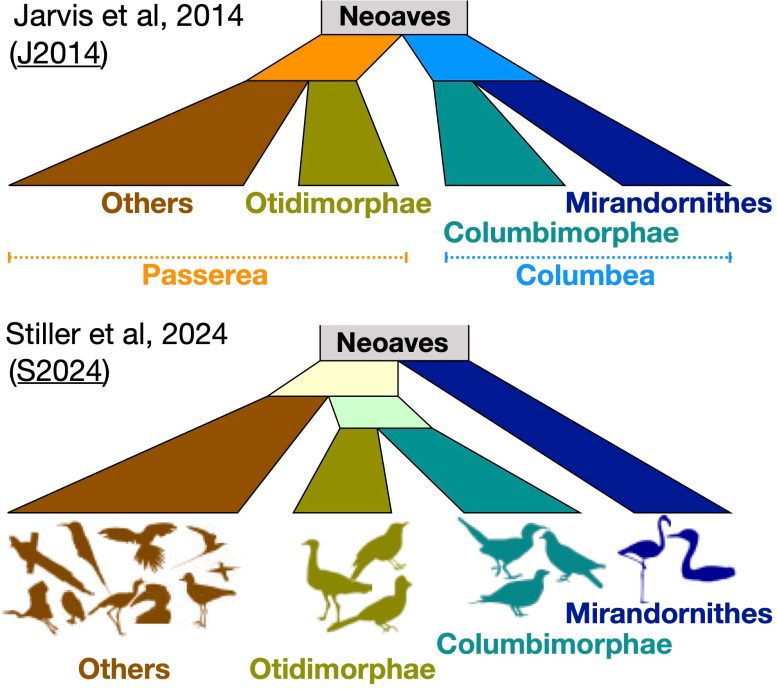
This section, just two percent of the bird genome, convinced scientists that most birds could be grouped into two major categories, with flamingos and doves as evolutionary cousins. The more accurate family tree, which accounts for the misleading section of the genome, identifies four main groups and identifies flamingos and doves as more distantly related.
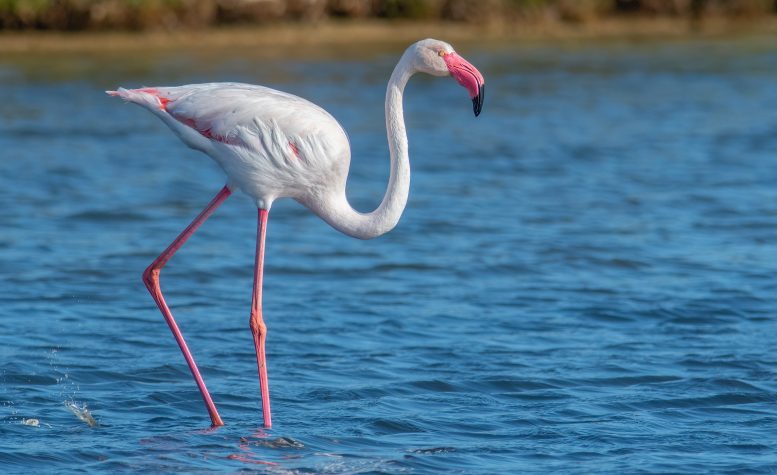
A greater flamingo in Mallorca, Spain. Unraveling a genetic mystery revealed that flamingos and doves are more distantly related than previously thought. Credit: Daniel J. Field
Breakthrough in Bird Evolution Research
"My lab has been chipping away at this problem of bird evolution for longer than I want to think about," said Edward Braun, Ph.D., the senior author of the paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences and a professor of biology at the University of Florida. "We had no idea there would be a big chunk of the genome that behaved unusually. We kind of stumbled onto it."
Braun supervised an international team of collaborators led by Siavash Mirarab, a professor of computer engineering at the University of California San Diego, to publish their evidence that this sticky chunk of DNA muddied the true history of bird evolution. Mirarab and Braun also contributed to a companion paper published in Nature that outlines the updated bird family tree, which was led by Josefin Stiller at the University of Copenhagen.
Both papers are part of the B10K avian genomics project led by Guojie Zhang of Zhejiang University, Erich Jarvis of Rockefeller University, and Tom Gilbert of the University of Copenhagen.
Two mutually exclusive bird family trees. The top family tree lumps flamingos and doves, in blue and teal respectively, closely together, while the bottom family tree does not. The top family tree was built around distortions in bird genomes that date back to the extinction of the dinosaurs. The bottom family tree is likely more accurate, after accounting for these genomic anomalies. Credit: Edward Braun
Genetic Anomalies and Evolutionary Insights
Ten years ago, Braun and his collaborators pieced together a family tree for the Neoaves, a group that includes the vast majority of bird species. Based on the genomes of 48 species, they split the Neoaves into two big categories: doves and flamingos in one group, all the rest in the other. When repeating a similar analysis this year using 363 species, a different family tree emerged that split up doves and flamingos into two distinct groups.
With two mutually exclusive family trees in hand, the scientists went hunting for explanations that could tell them which tree was correct.
"When we looked at the individual genes and what tree they supported, all of a sudden it popped out that all the genes that support the older tree, they're all in one spot. That's what started the whole thing," Braun said.
Investigating this spot, Braun's team noticed it was not as mixed together as it should have been over millions of years of sexual reproduction. Like humans, birds combine genes from a father and a mother into the next generation. But birds and humans alike first mix the genes they inherited from their parents when creating sperm and eggs. This process is called recombination, and it maximizes a species' genetic diversity by making sure no two siblings are quite the same.
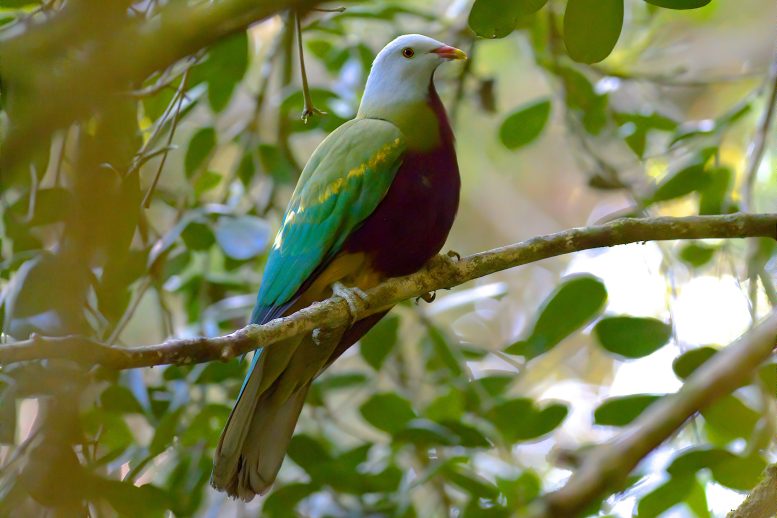
A wompoo fruit-dove in Queensland, Australia. Unraveling a genetic mystery revealed that flamingos and doves are more distantly related than previously thought. Credit: Daniel J. Field
Braun's team found evidence that one section of one bird chromosome had suppressed this recombination process for a few million years around the time the dinosaurs disappeared. Whether the extinction event and the genomic anomalies are related is unclear.
The result was that the flamingos and doves looked similar to one another in this chunk of frozen DNA. But taking into account the full genome, it became clear that the two groups are more distantly related.
"What's surprising is that this period of suppressed recombination could mislead the analysis," Braun said. "And because it could mislead the analysis, it was actually detectable more than 60 million years in the future. That's the cool part."
Such a mystery could be lurking in the genomes of other organisms as well.
"We discovered this misleading region in birds because we put a lot of energy into sequencing birds' genomes," Braun said. "I think there are cases like this out there for other species that are just not known right now."
References:
"Complexity of avian evolution revealed by family-level genomes" by Josefin Stiller, Shaohong Feng, Al-Aabid Chowdhury, Iker Rivas-González, David A. Duchêne, Qi Fang, Yuan Deng, Alexey Kozlov, Alexandros Stamatakis, Santiago Claramunt, Jacqueline M. T. Nguyen, Simon Y. W. Ho, Brant C. Faircloth, Julia Haag, Peter Houde, Joel Cracraft, Metin Balaban, Uyen Mai, Guangji Chen, Rongsheng Gao, Chengran Zhou, Yulong Xie, Zijian Huang, Zhen Cao, Zhi Yan, Huw A. Ogilvie, Luay Nakhleh, Bent Lindow, Benoit Morel, Jon Fjeldså, Peter A. Hosner, Rute R. da Fonseca, Bent Petersen, Joseph A. Tobias, Tamás Székely, Jonathan David Kennedy, Andrew Hart Reeve, Andras Liker, Martin Stervander, Agostinho Antunes, Dieter Thomas Tietze, Mads Bertelsen, Fumin Lei, Carsten Rahbek, Gary R. Graves, Mikkel H. Schierup, Tandy Warnow, Edward L. Braun, M. Thomas P. Gilbert, Erich D. Jarvis, Siavash Mirarab and Guojie Zhang, 32 March 2024, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07323-1
"A region of suppressed recombination misleads neoavian phylogenomics" by Siavash Mirarab, Iker Rivas-González, Shaohong Feng, Josefin Stiller, Qi Fang, Uyen Mai, Glenn Hickey, Guangji Chen, Nadolina Brajuka, Olivier Fedrigo, Giulio Formenti, Jochen B. W. Wolf, Kerstin Howe, Agostinho Antunes, Mikkel H. Schierup, Benedict Paten, Erich D. Jarvis, Guojie Zhang and Edward L. Braun, 1 April 2024, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2319506121
This work was supported in part by the National Science Foundation.
News
Cell Membranes May Act Like Tiny Power Generators
Living cells may generate electricity through the natural motion of their membranes. These fast electrical signals could play a role in how cells communicate and sense their surroundings. Scientists have proposed a new theoretical [...]
This Viral RNA Structure Could Lead to a Universal Antiviral Drug
Researchers identify a shared RNA-protein interaction that could lead to broad-spectrum antiviral treatments for enteroviruses. A new study from the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC), published in Nature Communications, explains how enteroviruses begin reproducing [...]
New study suggests a way to rejuvenate the immune system
Stimulating the liver to produce some of the signals of the thymus can reverse age-related declines in T-cell populations and enhance response to vaccination. As people age, their immune system function declines. T cell [...]
Nerve Damage Can Disrupt Immunity Across the Entire Body
A single nerve injury can quietly reshape the immune system across the entire body. Preclinical research from McGill University suggests that nerve injuries may lead to long-lasting changes in the immune system, and these [...]
Fake Science Is Growing Faster Than Legitimate Research, New Study Warns
New research reveals organized networks linking paper mills, intermediaries, and compromised academic journals Organized scientific fraud is becoming increasingly common, ranging from fabricated research to the buying and selling of authorship and citations, according [...]
Scientists Unlock a New Way to Hear the Brain’s Hidden Language
Scientists can finally hear the brain’s quietest messages—unlocking the hidden code behind how neurons think, decide, and remember. Scientists have created a new protein that can capture the incoming chemical signals received by brain [...]
Does being infected or vaccinated first influence COVID-19 immunity?
A new study analyzing the immune response to COVID-19 in a Catalan cohort of health workers sheds light on an important question: does it matter whether a person was first infected or first vaccinated? [...]
We May Never Know if AI Is Conscious, Says Cambridge Philosopher
As claims about conscious AI grow louder, a Cambridge philosopher argues that we lack the evidence to know whether machines can truly be conscious, let alone morally significant. A philosopher at the University of [...]
AI Helped Scientists Stop a Virus With One Tiny Change
Using AI, researchers identified one tiny molecular interaction that viruses need to infect cells. Disrupting it stopped the virus before infection could begin. Washington State University scientists have uncovered a method to interfere with a key [...]
Deadly Hospital Fungus May Finally Have a Weakness
A deadly, drug-resistant hospital fungus may finally have a weakness—and scientists think they’ve found it. Researchers have identified a genetic process that could open the door to new treatments for a dangerous fungal infection [...]
Fever-Proof Bird Flu Variant Could Fuel the Next Pandemic
Bird flu viruses present a significant risk to humans because they can continue replicating at temperatures higher than a typical fever. Fever is one of the body’s main tools for slowing or stopping viral [...]
What could the future of nanoscience look like?
Society has a lot to thank for nanoscience. From improved health monitoring to reducing the size of electronics, scientists’ ability to delve deeper and better understand chemistry at the nanoscale has opened up numerous [...]
Scientists Melt Cancer’s Hidden “Power Hubs” and Stop Tumor Growth
Researchers discovered that in a rare kidney cancer, RNA builds droplet-like hubs that act as growth control centers inside tumor cells. By engineering a molecular switch to dissolve these hubs, they were able to halt cancer [...]
Platelet-inspired nanoparticles could improve treatment of inflammatory diseases
Scientists have developed platelet-inspired nanoparticles that deliver anti-inflammatory drugs directly to brain-computer interface implants, doubling their effectiveness. Scientists have found a way to improve the performance of brain-computer interface (BCI) electrodes by delivering anti-inflammatory drugs directly [...]
After 150 years, a new chapter in cancer therapy is finally beginning
For decades, researchers have been looking for ways to destroy cancer cells in a targeted manner without further weakening the body. But for many patients whose immune system is severely impaired by chemotherapy or radiation, [...]
Older chemical libraries show promise for fighting resistant strains of COVID-19 virus
SARS‑CoV‑2, the virus that causes COVID-19, continues to mutate, with some newer strains becoming less responsive to current antiviral treatments like Paxlovid. Now, University of California San Diego scientists and an international team of [...]