The delta variant within the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) virus continued to cause devastation with high infection rates and transmissibility and this illustrated the lack of efficacy by the SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. However, novel research published in the journal, ACS Omega has reported the use of human host defense peptide-conjugated graphene quantum dots for the prevention of virus entry into host cells.
The severe acute respiratory coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) caused a global health crisis, which the World Health Organization (WHO) named to be a pandemic in March 2019. This virus was responsible for over 5.4 million deaths worldwide and has become a very intriguing research point for researchers studying its many emerging variants.
Research on this evolving virus mainly focuses on the spike protein (S1) which contains the receptor-binding domain (RBD) and the binding of this to the angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor within epithelial cells enables the virus to enter host cells in humans. This research resulted in the spike protein becoming a target for vaccines that aimed to produce neutralizing antibodies against the S-RBD.
While this concept seemed useful, recent reports have suggested the mutations on the SARS-CoV-2 virus and specifically in the S-RBD, can cause a decline in the level of neutralizing antibodies against the delta (B.1.617.2) variant that may have been produced during a previous infection or from immunization via a vaccine.
With these reports coming to light, researchers have strategized a novel and innovative solution for blocking the interaction between the spike protein and the ACE2 receptor to prevent infections from mutating variants.
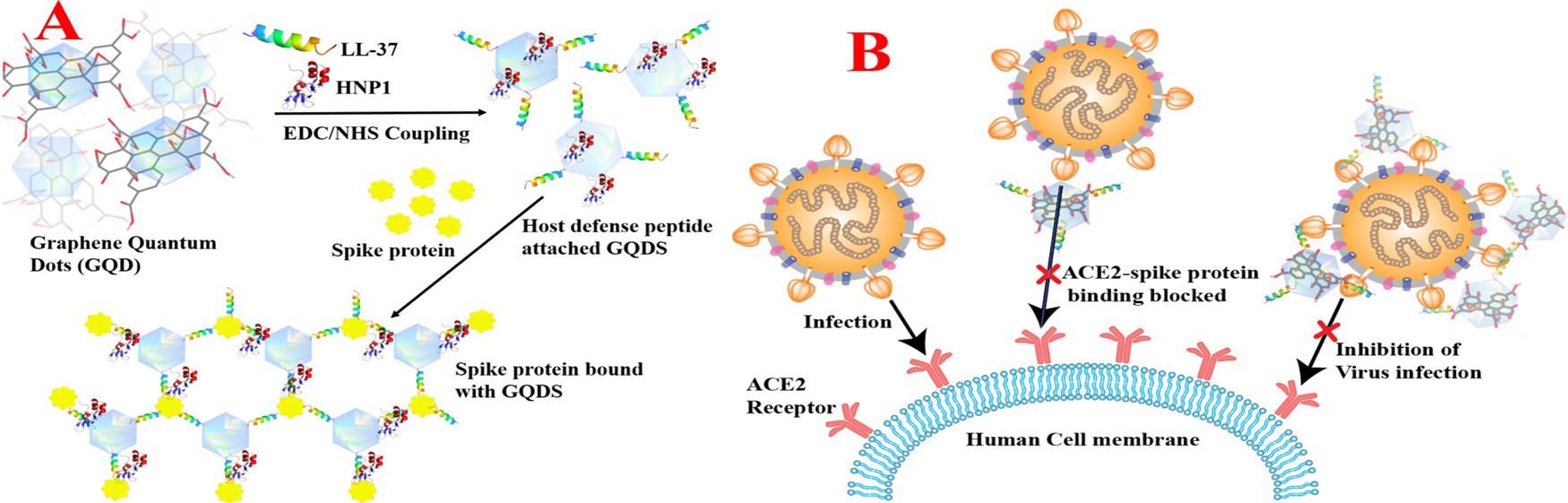
Figure 1. (A) Scheme showing the design of HNP1 and LL-37 human host defense peptide-conjugated GQDs and binding of HNP1 and LL-37 peptide-conjugated GQDs in the presence of the SARS-CoV-2 delta variant (B.1.617.2) spike protein RBD. (B) Scheme showing the blocking of the S-RBD interaction with ACE2 on a human cell membrane and preventing the SARS-CoV-2 virus entry. © Pramanik, A., et al. (2022)
Quantum Dot Solution to COVID-19
This novel research is premised on the fact that approximately 42% of the infected population are asymptomatic, which can suggest that the COVID-19 infection can be effectively controlled by the innate immune system.
This system is the first defense against pathogens coming into the body such as viruses and bacteria; this activates an immune response to destroy the pathogen while the adaptive immune response is modulated which causes immune cells to multiply and fight against the infection and ultimately, result in recovery.
Critical components of the innate immune system consist of peptides such as α-Defensin human neutrophil peptides (HNP1, HNP2, HNP3, and HNP4) and human β-defensins (HBD1, HBD2, and HBD3) as well as LL-37 (leucine-leucine-37) cathelicidin family peptides.
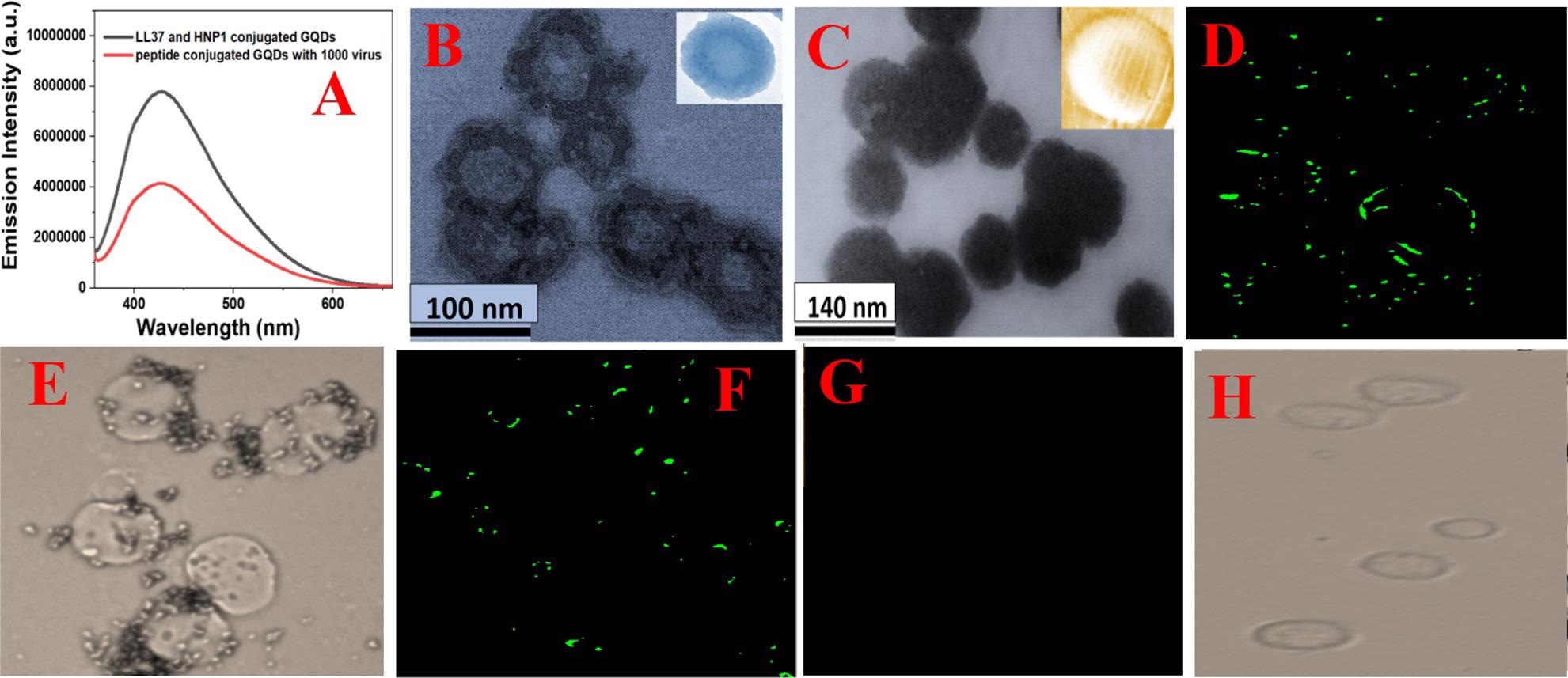
Figure 2. (A) Fluorescence spectra from HNP1 and LL-37 peptide-conjugated GQDs in the presence and absence of GFP-tagged Baculovirus pseudotyped with a SARS-CoV-2 delta variant (B.1.617.2) spike protein. (B) TEM image of Baculovirus pseudotyped after they are treated with HNP1 human host defense peptide-attached GQDs for 30 min. (C) TEM image of Baculovirus pseudotyped after they are treated with HNP1 and LL-37 human host defense peptide-attached GQDs for 30 min. (D–H) Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein binding to the surface of HEK-293T cells expressing ACE2. The green fluorescence is due to the presence of GFP-tagged Baculovirus pseudotyped with a SARS-CoV-2 delta variant (B.1.617.2) spike protein on the surface of HEK-293T cells expressing ACE2. (D) Fluorescence image of HEK-293T cells in the presence of GFP-tagged pseudotyped delta virus without GQDs. (E) Bright-field image of HEK-293T cells in the presence of GFP-tagged Baculovirus pseudotyped without GQDs. (F) Fluorescence image of HEK-293T cells in the presence of GFP-tagged virus bound with LL-37 human host defense peptide-attached GQDs. (G) Fluorescence image of HEK-293T cells in the presence of GFP-tagged virus bound with LL-37 & HNP1 human host defense peptide-attached GQDs. (H) Bright-field image of HEK-293T cells in the presence of GFP-tagged virus bound with LL-37 & HNP1 human host defense peptide-attached GQDs. © Pramanik, A., et al. (2022)
Defensins and cathelicidin peptides hold an important function in viral inhibition through binding and destabilization.
Researchers of this study aimed to block the delta variant and the subsequent infection from the SARS-CoV-2 virus through the use of an innovative design of HNP1 and LL-37 peptide-conjugated graphene quantum dots (GQDs). This novel development has the ability to bind to the delta variant S-RBD and block the binding to the ACE2 receptor in host cells, preventing the virus from entering the host cell, and therefore prevent COVID-19 infection.
The development of graphene quantum dots is a novel innovation that comprises a graphene lattice as well as graphene sheets that exhibit size-dependent luminescence properties due to quantum confinement and edge effects. These GQDs consist of surface groups including, carboxy, epoxy, and hydroxyl which illustrate high water solubility, high surface area as well as high photostability.
The unique optical properties of GQDs allow this candidate to be highly useful in applications such as bioimaging and biosensing; however, it can also be used innovatively to monitor the status of the delta variant of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
The bioconjugated GQD fluorescence in this research study has been used to monitor the spike RBD and ACE2 receptor interaction to determine the effective binding affinity. Additionally, the functional groups on the GQDs have also been used to inactivate the virus through decomposing the lipid membrane of the virus and removing the spike proteins attached to the lipid membrane.
Translational Significance
This research illustrates the double usage of this quantum dot strategy which would first be used to monitor the delta variant and compete for the S-RBD-ACE2 interaction to prevent this critical attachment, as well as attempt to remove the spike proteins from the lipid membrane to also prevent this interaction.
The binding affinity for the delta variant in comparison to the alpha, beta, and gamma variant spike-RBD was shown to be higher using this innovative strategy. This can be useful as this advancement would enable the complete inhibition of the delta variant from the host cell.
This research would enhance the defense against the coronavirus and its emerging variants, with the possibility of modification for other emerging variants of concern. Additionally, this could also be translated for use against other viruses in order to increase protection against pathogens.
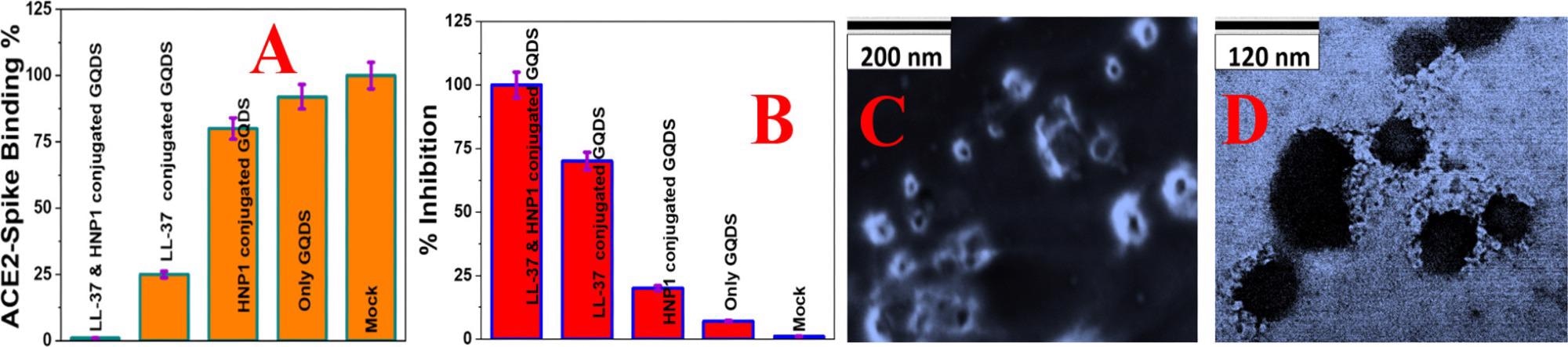
Figure 3. (A) Interaction of Baculovirus pseudotyped with a SARS-CoV-2 delta variant (B.1.617.2) spike protein and ACE2 on HEK-293T cells, measured using fluorescence imaging. (B) Inhibition efficiency of Baculovirus pseudotyped with the delta variant spike protein in infected HEK293T cells in the presence of buffer (Mock), GQDs (30 μg/mL), HNP1 (4 μg/mL)-attached GQDs (30 μg/mL), LL-37 (4 μg/mL)-attached GQDs (30 μg/mL), and LL-37 (4 μg/mL) and HNP1 (4 μg/mL)-attached GQDs (30 μg/mL). (C) SEM image of Baculovirus pseudotyped with a SARS-CoV-2 delta variant (B.1.617.2) spike protein when they are treated with peptide-attached GQDs for 6 h. (D) TEM image of Baculovirus pseudotyped with a SARS-CoV-2 delta variant (B.1.617.2) spike protein when they are treated with peptide-attached GQDs for 12 h. © Pramanik, A., et al. (2022)
News
Nanomedicine in 2026: Experts Predict the Year Ahead
Progress in nanomedicine is almost as fast as the science is small. Over the last year, we've seen an abundance of headlines covering medical R&D at the nanoscale: polymer-coated nanoparticles targeting ovarian cancer, Albumin recruiting nanoparticles for [...]
Lipid nanoparticles could unlock access for millions of autoimmune patients
Capstan Therapeutics scientists demonstrate that lipid nanoparticles can engineer CAR T cells within the body without laboratory cell manufacturing and ex vivo expansion. The method using targeted lipid nanoparticles (tLNPs) is designed to deliver [...]
The Brain’s Strange Way of Computing Could Explain Consciousness
Consciousness may emerge not from code, but from the way living brains physically compute. Discussions about consciousness often stall between two deeply rooted viewpoints. One is computational functionalism, which holds that cognition can be [...]
First breathing ‘lung-on-chip’ developed using genetically identical cells
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and AlveoliX have developed the first human lung-on-chip model using stem cells taken from only one person. These chips simulate breathing motions and lung disease in an individual, [...]
Cell Membranes May Act Like Tiny Power Generators
Living cells may generate electricity through the natural motion of their membranes. These fast electrical signals could play a role in how cells communicate and sense their surroundings. Scientists have proposed a new theoretical [...]
This Viral RNA Structure Could Lead to a Universal Antiviral Drug
Researchers identify a shared RNA-protein interaction that could lead to broad-spectrum antiviral treatments for enteroviruses. A new study from the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC), published in Nature Communications, explains how enteroviruses begin reproducing [...]
New study suggests a way to rejuvenate the immune system
Stimulating the liver to produce some of the signals of the thymus can reverse age-related declines in T-cell populations and enhance response to vaccination. As people age, their immune system function declines. T cell [...]
Nerve Damage Can Disrupt Immunity Across the Entire Body
A single nerve injury can quietly reshape the immune system across the entire body. Preclinical research from McGill University suggests that nerve injuries may lead to long-lasting changes in the immune system, and these [...]
Fake Science Is Growing Faster Than Legitimate Research, New Study Warns
New research reveals organized networks linking paper mills, intermediaries, and compromised academic journals Organized scientific fraud is becoming increasingly common, ranging from fabricated research to the buying and selling of authorship and citations, according [...]
Scientists Unlock a New Way to Hear the Brain’s Hidden Language
Scientists can finally hear the brain’s quietest messages—unlocking the hidden code behind how neurons think, decide, and remember. Scientists have created a new protein that can capture the incoming chemical signals received by brain [...]
Does being infected or vaccinated first influence COVID-19 immunity?
A new study analyzing the immune response to COVID-19 in a Catalan cohort of health workers sheds light on an important question: does it matter whether a person was first infected or first vaccinated? [...]
We May Never Know if AI Is Conscious, Says Cambridge Philosopher
As claims about conscious AI grow louder, a Cambridge philosopher argues that we lack the evidence to know whether machines can truly be conscious, let alone morally significant. A philosopher at the University of [...]
AI Helped Scientists Stop a Virus With One Tiny Change
Using AI, researchers identified one tiny molecular interaction that viruses need to infect cells. Disrupting it stopped the virus before infection could begin. Washington State University scientists have uncovered a method to interfere with a key [...]
Deadly Hospital Fungus May Finally Have a Weakness
A deadly, drug-resistant hospital fungus may finally have a weakness—and scientists think they’ve found it. Researchers have identified a genetic process that could open the door to new treatments for a dangerous fungal infection [...]
Fever-Proof Bird Flu Variant Could Fuel the Next Pandemic
Bird flu viruses present a significant risk to humans because they can continue replicating at temperatures higher than a typical fever. Fever is one of the body’s main tools for slowing or stopping viral [...]
What could the future of nanoscience look like?
Society has a lot to thank for nanoscience. From improved health monitoring to reducing the size of electronics, scientists’ ability to delve deeper and better understand chemistry at the nanoscale has opened up numerous [...]