The findings could potentially improve the success rate of cancer drug development.
Approximately 90% of drugs don't reach the market, highlighting the clear need for increased efficiency in drug development. The story isn't different for drugs aimed at treating cancer, with many failing due to various reasons. Now, researchers have revealed one reason why certain anti-cancer compounds can cause unexpected side effects. This research could help guide an understanding of why some drugs show more promise than others, providing a new tool that can be used to identify those drugs and drug candidates.
One of the most essential and energy-consuming cellular processes is ribosome biogenesis, the formation of the cellular machines that manufacture all proteins. For cancer cells, this process is paramount. A recent study published in the journal eLife from the Stowers Institute for Medical Research screened over 1,000 existing anti-cancer drugs to assess how they impact the structure and function of the nucleolus, the ubiquitous cellular organelle where ribosomes are made.
"All cells must make proteins to function, so they have to make ribosomes, which are also protein complexes themselves," said lead author Tamara Potapova, Ph.D., a research specialist in the lab of Investigator Jennifer Gerton, Ph.D. "In cancer cells, ribosome production must be in overdrive to compensate for high proliferation rates requiring even more proteins."
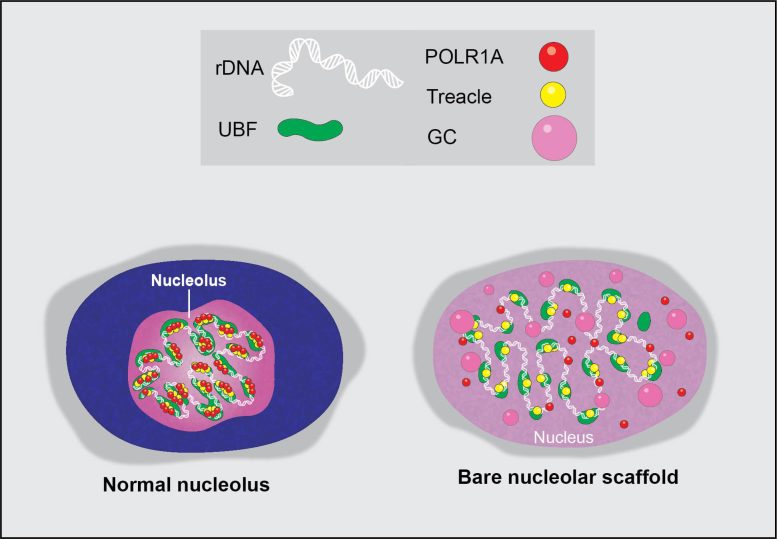
Graphical illustration of a normal nucleolus and its extreme stress state following transcriptional cyclin-dependent kinase inhibition by chemotherapy agents. Credit: Image courtesy of Mark Miller and Tamara Potapova, Stowers Institute for Medical Research
The nucleolus is a special part of the cell nucleus that houses ribosomal DNA, and where ribosomal RNA production and ribosome assembly largely takes place. Nucleoli can vary greatly in appearance, serving as visual indicators of the overall health of this process. Thus, the team found a way to capitalize on this variation and asked how chemotherapy drugs impact the nucleolus, causing nucleolar stress.
"In this study, we not only evaluated how anti-cancer drugs alter the appearance of nucleoli but also identified categories of drugs that cause distinct nucleolar shapes," said Gerton. "This enabled us to create a classification system for nucleoli based on their appearance that is a resource other researchers can use."
Because cancer's hallmark is unchecked proliferation, most existing chemotherapeutic agents are designed to slow this down. "The logic was to see whether these drugs, intentionally or unintentionally, are affecting ribosome biogenesis and to what degree," said Potapova. "Hitting ribosome biogenesis could be a double-edged sword—it would impair the viability of cancer cells while simultaneously altering protein production in normal cells."
Different drugs impact different pathways involved in cancer growth. Those that influence ribosome production can induce distinct states of nucleolar stress that manifest in easily seen morphological changes. However, nucleolar stress can be difficult to measure.
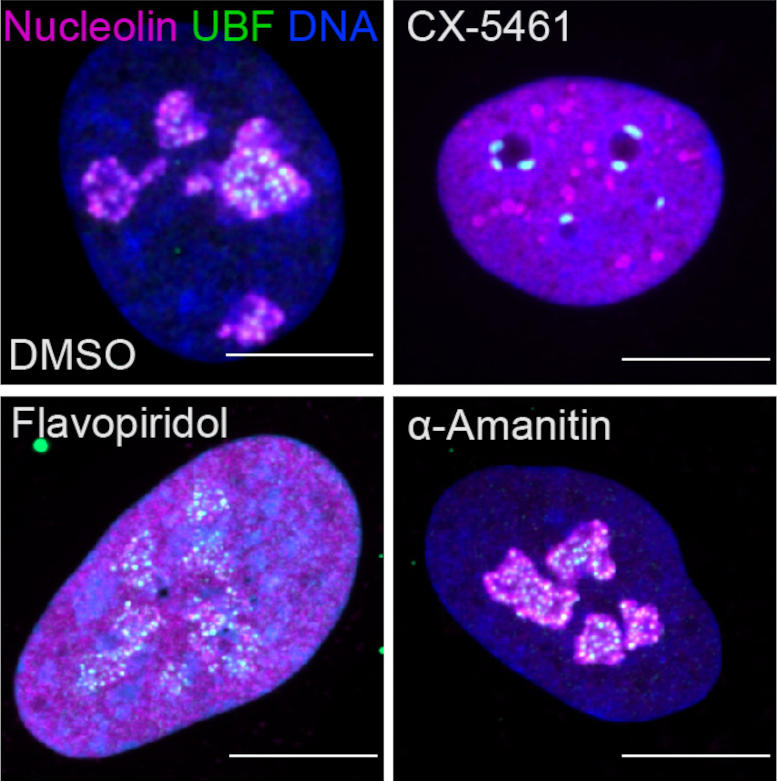
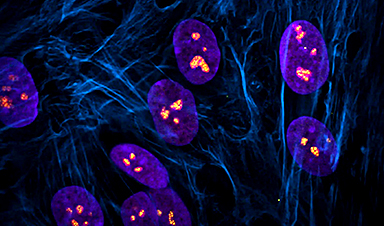
Fluorescent images showing nucleolar stress induced by drugs that inhibit transcriptional enzymes, or cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK). The upper left panel shows a normal cell with two important nucleolar proteins stained (magenta and green) and DNA (blue). The remaining panels show the impact of CDK or transcription-inhibitory drugs on nucleoli. Credit: Image courtesy of Tamara Potapova, Gerton Lab, Stowers Institute for Medical Research
"This was one of the issues that impeded this field," said Potapova. "Cells can have different numbers of nucleoli with different sizes and shapes, and it has been challenging to find a single parameter that can fully describe a "normal" nucleolus. Developing this tool, which we termed "nucleolar normality score," allowed us to measure nucleolar stress precisely, and it can be used by other labs to measure nucleolar stress in their experimental models."
Through the comprehensive screening of anti-cancer compounds on nucleolar stress, the team identified one class of enzymes in particular, cyclin-dependent kinases, whose inhibition destroys the nucleolus almost completely. Many of these inhibitors failed in clinical trials, and their detrimental impact on the nucleolus was not fully appreciated previously.
Drugs often fail in clinical trials due to excessive and unintended toxicity that can be caused by their off-target effects. This means that a molecule designed to target one pathway may also be impacting a different pathway or inhibiting an enzyme required for cellular function. In this study, the team found an effect on an entire organelle.
"I hope at a minimum this study increases awareness that some anti-cancer drugs can cause unintended disruption of the nucleolus, which can be very prominent," said Potapova. "This possibility should be considered during new drug development."
News
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]
Analyzing Darwin’s specimens without opening 200-year-old jars
Scientists have successfully analyzed Charles Darwin's original specimens from his HMS Beagle voyage (1831 to 1836) to the Galapagos Islands. Remarkably, the specimens have been analyzed without opening their 200-year-old preservation jars. Examining 46 [...]
Scientists discover natural ‘brake’ that could stop harmful inflammation
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have uncovered a key mechanism that helps the body switch off inflammation—a breakthrough that could lead to new treatments for chronic diseases affecting millions worldwide. Inflammation is the [...]
A Forgotten Molecule Could Revive Failing Antifungal Drugs and Save Millions of Lives
Scientists have uncovered a way to make existing antifungal drugs work again against deadly, drug-resistant fungi. Fungal infections claim millions of lives worldwide each year, and current medical treatments are failing to keep pace. [...]
Scientists Trap Thyme’s Healing Power in Tiny Capsules
A new micro-encapsulation breakthrough could turn thyme’s powerful health benefits into safer, smarter nanodoses. Thyme extract is often praised for its wide range of health benefits, giving it a reputation as a natural medicinal [...]
Scientists Develop Spray-On Powder That Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds
KAIST scientists have created a fast-acting, stable powder hemostat that stops bleeding in one second and could significantly improve survival in combat and emergency medicine. Severe blood loss remains the primary cause of death from [...]
Oceans Are Struggling To Absorb Carbon As Microplastics Flood Their Waters
New research points to an unexpected way plastic pollution may be influencing Earth’s climate system. A recent study suggests that microscopic plastic pollution is reducing the ocean’s capacity to take in carbon dioxide, a [...]
Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine – New book from Frank Boehm
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
New Book! NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Global Health Care Equivalency in the Age of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine and Artificial Intelligence
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
Miller School Researchers Pioneer Nanovanilloid-Based Brain Cooling for Traumatic Injury
A multidisciplinary team at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine has developed a breakthrough nanodrug platform that may prove beneficial for rapid, targeted therapeutic hypothermia after traumatic brain injury (TBI). Their work, published in ACS [...]
COVID-19 still claims more than 100,000 US lives each year
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention researchers report national estimates of 43.6 million COVID-19-associated illnesses and 101,300 deaths in the US during October 2022 to September 2023, plus 33.0 million illnesses and 100,800 deaths [...]
Nanomedicine in 2026: Experts Predict the Year Ahead
Progress in nanomedicine is almost as fast as the science is small. Over the last year, we've seen an abundance of headlines covering medical R&D at the nanoscale: polymer-coated nanoparticles targeting ovarian cancer, Albumin recruiting nanoparticles for [...]
Lipid nanoparticles could unlock access for millions of autoimmune patients
Capstan Therapeutics scientists demonstrate that lipid nanoparticles can engineer CAR T cells within the body without laboratory cell manufacturing and ex vivo expansion. The method using targeted lipid nanoparticles (tLNPs) is designed to deliver [...]
The Brain’s Strange Way of Computing Could Explain Consciousness
Consciousness may emerge not from code, but from the way living brains physically compute. Discussions about consciousness often stall between two deeply rooted viewpoints. One is computational functionalism, which holds that cognition can be [...]
First breathing ‘lung-on-chip’ developed using genetically identical cells
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and AlveoliX have developed the first human lung-on-chip model using stem cells taken from only one person. These chips simulate breathing motions and lung disease in an individual, [...]