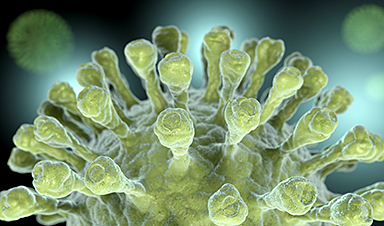
A coronavirus uses protein “spikes” to grab and infect cells. Despite their name, those spikes aren’t stiff and pointy. They’re shaped like chicken drumsticks with the meaty part facing out, and the meaty part can tilt every which way on its slender stalk. That ability to tilt, it turns out, affects how successfully the spike can infect a cell.
While the study was carried out on a much less dangerous cousin of SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that causes COVID-19, it has implications for COVID-19, too, since both viruses bind to the same receptor on a cell’s surface to initiate infection, said Jing Jin, a biologist at Vitalant Research Institute and adjunct assistant professor at the University of California, San Francisco who performed virology experiments for the study.
The results, she said, suggest that disabling the spike’s hinges could be a good way to prevent or treat a wide range of coronavirus infections.
The team also discovered that each coronavirus particle is unique, both in its underlying shape and its display of spikes. Some are spherical, some are not; some bristle with spikes while others are nearly bald.
“The spikes are floppy and move around, and we used a combination of tools to explore all their possible angles and orientations,” said Greg Pintilie, a Stanford scientist who developed detailed 3D models of the virus and its spikes. Seen up close, he said, each spike is different from all the rest, mainly in its direction and degree of tilting.
The research team reported its findings in Nature Communications.
“Since the pandemic started, most studies have looked at the structures of coronavirus spike proteins that were not attached to the virus itself,” said Wah Chiu, a professor at SLAC and Stanford and co-director of the Stanford-SLAC Cryo-EM facilities where the imaging was done. “These are the first images made of the spikes of this strain of coronavirus while they’re still attached to the virus particles.”
SARS-CoV-2’s more benign cousin
The study has roots in the early days of the pandemic, when research at SLAC shut down except for work aimed at understanding, preventing and treating COVID-19 infections.
Because experiments with the actual SARS-CoV-2 virus can only take place in high-level (BSL3) biosafety labs, many scientists chose to work with more benign members of the coronavirus family. Chiu and his colleagues selected human coronavirus NL63 as their subject. It causes up to 10% of human respiratory infections, mainly in children and immunocompromised people, with symptoms ranging from mild coughs and sniffles to bronchitis and croup.
In 2020, Chiu said, the team used cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and computational analysis to image the crowns of NL63 spikes with near-atomic resolution.
But because a spike’s stalk is much thinner than its crown, they were not able to get clear, high-resolution images of both at once.
Zooming in on spikes
This study combined information gleaned from a series of experiments to get a much more complete picture.
First, Stanford graduate student David Chmielewski used cryogenic electron tomography (cryo-ET) to combine cryo-EM images of viruses that were taken from different angles into high-resolution 3D images of more than a hundred NL63 particles.
SLAC senior scientist Michael Schmid plugged those images into a 3D visualization tool and discovered that each of a particle’s spikes was bent in a unique way. Another SLAC scientist, Muyuan Chen, used advanced image reconstruction to create maps showing the average density of the spikes’ crowns and stalks.
Zooming in on one of those spikes, biological chemist Lance Wells at the University of Georgia used a technique called mass spectrometry to pinpoint the site-specific chemical compositions of the 39 sugar chains attached to each of the spike’s three identical proteins.
Finally, Abhishek Singharoy, a computational biophysicist at Arizona State University, and his student, Eric Wilson, integrated all those measurements into atomic models of the spikes’ crowns and stalks at different bending angles, and carried out further simulations to see how far and how freely a spike can bend.
“It turns out that no matter what, the spikes have a preferred bending angle of about 50 degrees,” Chiu said, “and they can tilt up to 80 degrees in any direction in the simulation, which matches well with our cryo-ET experimental observations.”
The bending occurred at a place on the stalk, just below the crown, where a particular cluster of sugar molecules clung to the protein, forming a hinge. Computer simulations suggested that changes in the structure of this hinge would affect its ability to bend, and lab experiments went one step further: They showed that mutations in the protein part of the hinge made the spike much less infectious. This suggests that targeting the hinge could provide an avenue to fight the virus.
“People working on the more dangerous coronaviruses, including MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, have identified a region equivalent to this one and discovered antibodies targeting this region,” Jin said. “That tells us it’s a critical region that is highly conserved, meaning that it has stayed much the same over the course of evolution. So maybe by targeting this region in all coronaviruses, we can come up with a universal therapy or vaccine.”
More information: David Chmielewski et al, Structural insights into the modulation of coronavirus spike tilting and infectivity by hinge glycans, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42836-9
News
Scientists Discover Simple Saliva Test That Reveals Hidden Diabetes Risk
Researchers have identified a potential new way to assess metabolic health using saliva instead of blood. High insulin levels in the blood, known as hyperinsulinemia, can reveal metabolic problems long before obvious symptoms appear. It is [...]
One Nasal Spray Could Protect Against COVID, Flu, Pneumonia, and More
A single nasal spray vaccine may one day protect against viruses, pneumonia, and even allergies. For decades, scientists have dreamed of creating a universal vaccine capable of protecting against many different pathogens. The idea [...]
New AI Model Predicts Cancer Spread With Incredible Accuracy
Scientists have developed an AI system that analyzes complex gene-expression signatures to estimate the likelihood that a tumor will spread. Why do some tumors spread throughout the body while others remain confined to their [...]
Scientists Discover DNA “Flips” That Supercharge Evolution
In Lake Malawi, hundreds of species of cichlid fish have evolved with astonishing speed, offering scientists a rare opportunity to study how biodiversity arises. Researchers have identified segments of “flipped” DNA that may allow fish to adapt rapidly [...]
Our books now available worldwide!
Online Sellers other than Amazon, Routledge, and IOPP Indigo Global Health Care Equivalency in the Age of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine and Artifcial Intelligence Global Health Care Equivalency In The Age Of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine And Artificial [...]
Scientists Discover Why Some COVID Survivors Still Can’t Taste Food Years Later
A new study provides the first direct biological evidence explaining why some people continue to experience taste loss long after recovering from COVID-19. Researchers have uncovered specific biological changes in taste buds that could help [...]
Catching COVID significantly raises the risk of developing kidney disease, researchers find
Catching Covid significantly raises the risk of developing deadly kidney disease, research has shown. The virus was found to increase the chances that patients will develop the incurable condition by around 50 per cent. [...]
New Toothpaste Stops Gum Disease Without Harming Healthy Bacteria
Researchers have developed a targeted approach to combat periodontitis without disrupting the natural balance of the oral microbiome. The innovation could reshape how gum disease is treated while preserving beneficial bacteria. The human mouth [...]
Plastic Without End: Are We Polluting the Planet for Eternity?
The Kunming Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework calls for the elimination of plastic pollution by 2030. If that goal has been clearly set, why have meaningful measures that create real change still not been implemented? [...]
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]