Most drugs are small molecules that bind firmly to a specific target—some molecule in human cells that is involved in a disease—in order to work. For example, a cancer drug’s target might be a molecule that is abundant inside of cancer cells. The drug should hypothetically travel freely throughout the cell until it comes to its target and then lock onto it, leading to a therapeutic action.
However, small molecule drugs do not travel in such an unrestricted manner; instead, they tend to concentrate in specific regions of the cell. This is because each drug is capable of interacting with many more molecules than its target.
These other interactions tend to be weaker, like static cling versus the pull of a powerful magnet, but they can accumulate when molecules are concentrated together in cellular compartments called condensates. In these compartments, collective weak interactions may detain a significant percentage of drug molecules, keeping them localized either in the same neighborhood as their target or far away from it.
Researchers in Whitehead Institute Member Richard Young’s lab are working to understand the chemical environments inside of different condensates and how these chemistries interact with those of small molecules. In research published in Nature Chemical Biology on September 28, Young and colleagues—including Regina Barzilay, the School of Engineering Distinguished Professor for AI and Health in the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab—trained a machine learning model to predict in which condensates a drug will concentrate based on their chemical features.
This work shows that interactions between condensates and small molecules help to determine where in the cell a small molecule will end up and what it will interact with, which may be relevant to understanding many cellular processes and to the design of safe and effective drugs.
If a large percentage of a small molecule drug, for instance, ends up in a condensate that does not contain the drug’s target, then much higher doses of the drug may be required for it to work, increasing the likelihood of toxicity and unintended side effects. Conversely, a drug designed to frequent the same condensate as its target would likely be more effective at lower—and so, typically, safer—doses.
“Our work suggests that if you want to develop a very efficacious drug, then you should know where the target of the drug is in the cell with respect to these compartments,” says Young, who is also a professor of biology at MIT. “This would inform researchers and companies of the best way to develop a drug so that it is optimally concentrated near its target.”
Decoding condensate chemistry
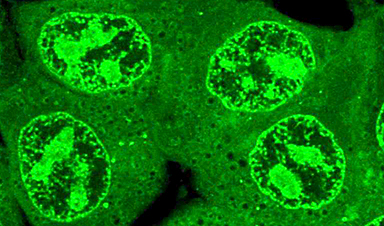
Young lab researchers have spent years dedicated to the study of condensates, membrane-less cellular compartments that form when certain molecules tangle together to make a droplet within the cell, like a bead of oil suspended in water. These droplets function as organizational spaces in which the cell can gather together the right combination of molecules in the right location to perform their functions.
Young and others have found evidence that condensates play this organizational role in many different cellular processes. They have also found evidence that drugs can concentrate in condensates, and that this may affect their efficacy. In 2020, Young and colleagues published a Science paper showing that the commonly used cancer drug cisplatin concentrates in transcriptional condensates, which keep the drug near the cancer-causing genes that it acts on.
Young lab postdoc Henry Kilgore and graduate student Kalon Overholt, co-first authors on the new paper, wondered what they would learn if they systematically tested whether and how different drugs concentrate in different condensates. First, they tested a large swathe of drugs to confirm that it is a common occurrence for drugs to concentrate in specific compartments rather than dispersing freely throughout the whole cell: they found that it is.
Next, they devised a system to study what might be causing drugs to concentrate in one condensate over another. They created models of three important types of condensates: one involved in gene transcription, one involved in gene repression, and the nucleolus—a large condensate inside of the nucleus that produces ribosomes. The researchers isolated the dominant type of protein that forms the framework of each of these three types of condensates, and formed simplified condensates made solely of each dominant protein.
Then the researchers assembled a library of more than 1,500 small molecules with a wide variety of chemical features, and tested to see how strongly they would concentrate in each of the three model condensates. Most of the small molecules did favor one condensate over the others. Co-first author Peter Mikhael, a graduate student in Barzilay’s lab, trained a machine learning model on this data to identify patterns in how the small molecules sorted into different condensates.
The model found that the molecules that favored each type of condensate tended to have shared chemical features, and were more like each other than like molecules that favored other condensate types. It identified a number of features that seem to affect where molecules end up. For example, transcriptional condensates tended to attract small molecules containing electron-rich aromatic rings (a certain type of ring structure). Using these patterns, the model was very good at predicting in which of the simple condensates additional drugs would concentrate.
Next, the researchers tested how well the model could predict where drugs would concentrate in live cells. It had moderate success. The lower accuracy reflects that the model was trained on simplified cases of single-protein condensates. In a cell, condensates contain hundreds of proteins, each of which may influence the local chemical environment, and condensates and other cellular compartments don’t exist in isolation: they compete to accumulate a drug.
The researchers are now working to understand the physical and chemical properties of these many proteins, so that they can improve their models. They also intend to narrow in on the specific mechanisms by which condensates create a favorable chemical environment for some molecules over others.
“In order for us to make use of condensate biochemistry, we would really like to have predictive power over where different molecules concentrate. While we’re still at the early stages, it’s exciting to envision a world where we have much finer control over where exactly drugs that we synthesize will go, such that they have maximum efficacy and minimal unwanted side-effects,” Mikhael says.
In the meantime, the researchers hope that this work demonstrates the importance of re-thinking how cells are organized, and considering where molecules concentrate based on their chemical features.
“The inside of the cell has evolved to be highly compartmentalized, and that means the small molecules inside the cell are not distributed homogeneously,” Overholt says. “It has been exciting to talk to experts from different fields and realize how many disciplines could potentially draw from our work on how molecules actually distribute in the cell.”
The researchers anticipate that their work will be very useful to drug developers, but they also expect it to prove relevant to a number of other processes that occur within cells. More and more critical cellular processes are being found to rely on condensates to organize when and where relevant molecules concentrate. The better that researchers understand the chemical coding that regulates this organization, the better they will understand how essential cellular processes take place—and what may be going awry with them in disease.
“Everything we’ve learned about condensates in this study suggests that condensates and other cellular organelles have a powerful effect on the distribution of small molecules,” Kilgore says. “I’m convinced at this point that condensate small molecule selectivity has fundamental implications for biology and drug discovery.”
News
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]
AI tool detects 9 types of dementia from a single brain scan
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that helps clinicians identify brain activity patterns linked to nine types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, using a single, widely available scan—a transformative [...]
Is plastic packaging putting more than just food on your plate?
New research reveals that common food packaging and utensils can shed microscopic plastics into our food, prompting urgent calls for stricter testing and updated regulations to protect public health. Beyond microplastics: The analysis intentionally [...]
Aging Spreads Through the Bloodstream
Summary: New research reveals that aging isn’t just a local cellular process—it can spread throughout the body via the bloodstream. A redox-sensitive protein called ReHMGB1, secreted by senescent cells, was found to trigger aging features [...]
AI and nanomedicine find rare biomarkers for prostrate cancer and atherosclerosis
Imagine a stadium packed with 75,000 fans, all wearing green and white jerseys—except one person in a solid green shirt. Finding that person would be tough. That's how hard it is for scientists to [...]
Are Pesticides Breeding the Next Pandemic? Experts Warn of Fungal Superbugs
Fungicides used in agriculture have been linked to an increase in resistance to antifungal drugs in both humans and animals. Fungal infections are on the rise, and two UC Davis infectious disease experts, Dr. George Thompson [...]
Scientists Crack the 500-Million-Year-Old Code That Controls Your Immune System
A collaborative team from Penn Medicine and Penn Engineering has uncovered the mathematical principles behind a 500-million-year-old protein network that determines whether foreign materials are recognized as friend or foe. How does your body [...]
Team discovers how tiny parts of cells stay organized, new insights for blocking cancer growth
A team of international researchers led by scientists at City of Hope provides the most thorough account yet of an elusive target for cancer treatment. Published in Science Advances, the study suggests a complex signaling [...]
Nanomaterials in Ophthalmology: A Review
Eye diseases are becoming more common. In 2020, over 250 million people had mild vision problems, and 295 million experienced moderate to severe ocular conditions. In response, researchers are turning to nanotechnology and nanomaterials—tools that are transforming [...]
Natural Plant Extract Removes up to 90% of Microplastics From Water
Researchers found that natural polymers derived from okra and fenugreek are highly effective at removing microplastics from water. The same sticky substances that make okra slimy and give fenugreek its gel-like texture could help [...]
Instant coffee may damage your eyes, genetic study finds
A new genetic study shows that just one extra cup of instant coffee a day could significantly increase your risk of developing dry AMD, shedding fresh light on how our daily beverage choices may [...]
Nanoneedle patch offers painless alternative to traditional cancer biopsies
A patch containing tens of millions of microscopic nanoneedles could soon replace traditional biopsies, scientists have found. The patch offers a painless and less invasive alternative for millions of patients worldwide who undergo biopsies [...]