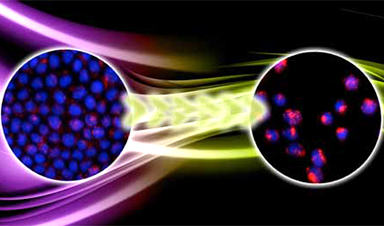
| Diseased cells such as metastatic cancer cells have markedly different mechanical properties that can be used to improve targeted drug uptake, according to a team of researchers at Penn State. | |
| Many labs around the world are developing nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems to selectively target tumors. They rely on a key-and-lock system in which protein keys on the surface of the nanoparticle click into the locks of a highly expressed protein on the surface of the cancer cell. The cell membrane then wraps around the nanoparticle and ingests it. If enough of the nanoparticles and their drug cargo is ingested, the cancer cell will die. | |
| The adhesive force of the lock and key is what drives the nanoparticle into the cell, says Sulin Zhang, professor of engineering science and mechanics. “It is almost universal that whenever there is a driving force for a process, there always is a resistive force. Here, the driving force is biochemical – the protein-protein interaction.” | |
| The resistive force is mechanical, the energy cost of the membrane wrapping around the nanoparticle. Until now, bioengineers only considered the driving force and designed nanoparticles to optimize the chemical interactions, a targeting strategy called “chemotargeting.” Zhang believes they should also take into account the mechanics of the cells to design nanoparticles to achieve enhanced targeting, which forms a new targeting strategy called “mechanotargeting.” |
Image Credit: Zhang lab/vecteezy.com
News This Week
According to Researchers, Your Breathing Patterns Could Hold the Key to Better Memory
Breathing synchronizes brain waves that support memory consolidation. A new study from Northwestern Medicine reports that, much like a conductor harmonizes various instruments in an orchestra to create a symphony, breathing synchronizes hippocampal brain waves to [...]
The Hidden Culprit Behind Alzheimer’s Revealed: Microglia Under the Microscope
Researchers at the CUNY Graduate Center have made a groundbreaking discovery in Alzheimer’s disease research, identifying a critical link between cellular stress in the brain and disease progression. Their study focuses on microglia, the brain’s immune [...]
“Mirror Bacteria” Warning: A New Kind of Life Could Pose a Global Threat
Mirror life, a concept involving synthetic organisms with reversed molecular structures, carries significant risks despite its potential for medical advancements. Experts warn that mirror bacteria could escape natural biological controls, potentially evolving to exploit [...]
Lingering Viral Fragments: The Hidden Cause of Long COVID
Long COVID, affecting 5-10% of COVID-19 patients, might be caused by the enduring presence of the virus in the body. Research suggests that viral fragments, possibly live, linger and lead to symptoms. Addressing this involves antiviral treatments, enhanced [...]
Hidden Scars: How COVID Lockdowns Altered Teen Brains Forever
Research from the University of Washington revealed that COVID-19 lockdowns led to accelerated cortical thinning in adolescents, impacting brain development significantly. This effect was more pronounced in females than males, raising concerns about long-term brain health. The study [...]
Simple Blood Test To Detect Dementia Before Symptoms Appear
UCLA researchers have identified placental growth factor (PlGF) as a potential blood biomarker for early detection of cognitive impairment and dementia. High PlGF levels correlate with increased vascular permeability, suggesting its role in the development [...]
Investing Goldman Sachs asks ‘Is curing patients a sustainable business model?’
Goldman Sachs analysts attempted to address a touchy subject for biotech companies, especially those involved in the pioneering “gene therapy” treatment: cures could be bad for business in the long run. “Is curing patients [...]
The risks of reversed chirality: Study highlights dangers of mirror organisms
A groundbreaking study evaluates the feasibility, risks, and ethical considerations of creating mirror bacteria with reversed chirality, highlighting potential threats to health and ecosystems. In a recent study published in Science, a team of researchers [...]










Leave A Comment