Functional ultrasound (fUS) marks a significant leap in Brain-Machine Interface technology, offering a less invasive method for precise control of electronic devices by interpreting brain activity.
Brain–machine interfaces (BMIs) are devices that can read brain activity and translate that activity to control an electronic device like a prosthetic arm or computer cursor. They promise to enable people with paralysis to move prosthetic devices with their thoughts.
Many BMIs require invasive surgeries to implant electrodes into the brain in order to read neural activity. However, in 2021, Caltech researchers developed a way to read brain activity using functional ultrasound (fUS), a much less invasive technique.
Functional Ultrasound: A Game Changer for BMIs
Now, a new study is a proof-of-concept that fUS technology can be the basis for an "online" BMI—one that reads brain activity, deciphers its meaning with decoders programmed with machine learning, and consequently controls a computer that can accurately predict movement with very minimal delay time.
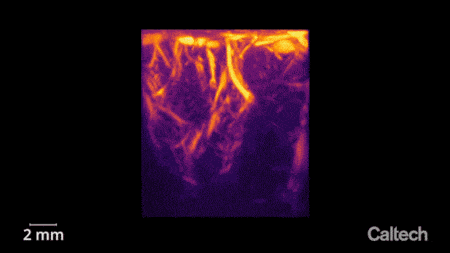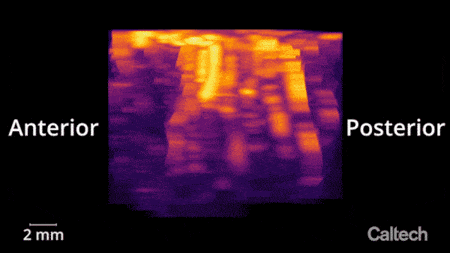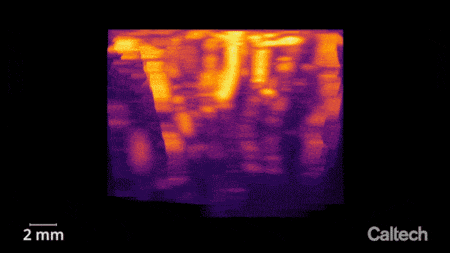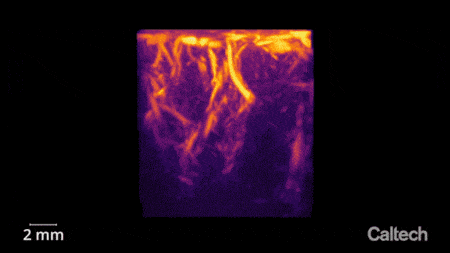
Ultrasound is used to image two-dimensional sheets of the brain, which can then be stacked together to create a 3-D image. Credit: Courtesy of W. Griggs
The study was conducted in the Caltech laboratories of Richard Andersen, James G. Boswell Professor of Neuroscience and director and leadership chair of the T&C Chen Brain–Machine Interface Center; and Mikhail Shapiro, Max Delbrück Professor of Chemical Engineering and Medical Engineering and Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator. The work was a collaboration with the laboratory of Mickael Tanter, director of physics for medicine at INSERM in Paris, France.
Advantages of Functional Ultrasound
"Functional ultrasound is a completely new modality to add to the toolbox of brain–machine interfaces that can assist people with paralysis," says Andersen. "It offers attractive options of being less invasive than brain implants and does not require constant recalibration. This technology was developed as a truly collaborative effort that could not be accomplished by one lab alone."
"In general, all tools for measuring brain activity have benefits and drawbacks," says Sumner Norman, former senior postdoctoral scholar research associate at Caltech and a co-first author on the study. "While electrodes can very precisely measure the activity of single neurons, they require implantation into the brain itself and are difficult to scale to more than a few small brain regions. Non-invasive techniques also come with tradeoffs. Functional magnetic resonance imaging [fMRI] provides whole-brain access but is restricted by limited sensitivity and resolution. Portable methods, like electroencephalography [EEG] are hampered by poor signal quality and an inability to localize deep brain function."
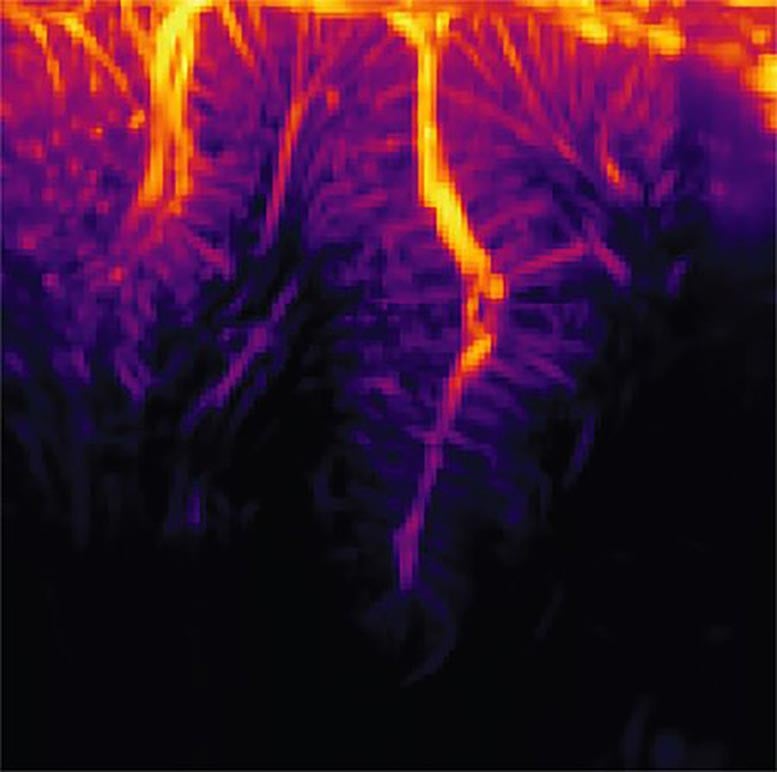
The vasculature of the posterior parietal cortex as measured by functional ultrasound neuroimaging. Credit: Courtesy of W. Griggs
Ultrasound Imaging Explained
Ultrasound imaging works by emitting pulses of high-frequency sound and measuring how those sound vibrations echo throughout a substance, such as various tissues of the human body. Sound waves travel at different speeds through these tissue types and reflect at the boundaries between them. This technique is commonly used to take images of a fetus in utero, and for other diagnostic imaging.
Because the skull itself is not permeable to sound waves, using ultrasound for brain imaging requires a transparent "window" to be installed into the skull. "Importantly, ultrasound technology does not need to be implanted into the brain itself," says Whitney Griggs (PhD '23), a co-first author on the study. "This significantly reduces the chance for infection and leaves the brain tissue and its protective dura perfectly intact."
"As neurons' activity changes, so does their use of metabolic resources like oxygen," says Norman. "Those resources are resupplied through the blood stream, which is the key to functional ultrasound." In this study, the researchers used ultrasound to measure changes in blood flow to specific brain regions. In the same way that the sound of an ambulance siren changes in pitch as it moves closer and then farther away from you, red blood cells will increase the pitch of the reflected ultrasound waves as they approach the source and decrease the pitch as they flow away. Measuring this Doppler-effect phenomenon allowed the researchers to record tiny changes in the brain's blood flow down to spatial regions just 100 micrometers wide, about the width of a human hair. This enabled them to simultaneously measure the activity of tiny neural populations, some as small as just 60 neurons, widely throughout the brain.
Unlocking Movement: Helping Paralyzed People Use Thought to Control Computers and Robotic Limbs
Innovative Application in Non-Human Primates
The researchers used functional ultrasound to measure brain activity from the posterior parietal cortex (PPC) of non-human primates, a region that governs the planning of movements and contributes to their execution. The region has been studied by the Andersen lab for decades using other techniques.
The animals were taught two tasks, requiring them to either plan to move their hand to direct a cursor on a screen, or plan to move their eyes to look at a specific part of the screen. They only needed to think about performing the task, not actually move their eyes or hands, as the BMI read the planning activity in their PPC.
"I remember how impressive it was when this kind of predictive decoding worked with electrodes two decades ago, and it's amazing now to see it work with a much less invasive method like ultrasound," says Shapiro.
Promising Results and Future Plans
The ultrasound data was sent in real-time to a decoder (previously trained to decode the meaning of that data using machine learning), and subsequently generated control signals to move a cursor to where the animal intended it to go. The BMI was able to successfully do this to eight radial targets with mean errors of less than 40 degrees.
"It's significant that the technique does not require the BMI to be recalibrated each day, unlike other BMIs," says Griggs. "As an analogy, imagine needing to recalibrate your computer mouse for up to 15 minutes each day before use."
Next, the team plans to study how BMIs based on ultrasound technology perform in humans, and to further develop the fUS technology to enable three-dimensional imaging for improved accuracy.
The paper is titled "Decoding motor plans using a closed-loop ultrasonic brain–machine interface" and was published in the journal Nature Neuroscience on November 30.
Reference: "Decoding motor plans using a closed-loop ultrasonic brain–machine interface" by Whitney S. Griggs, Sumner L. Norman, Thomas Deffieux, Florian Segura, Bruno-Félix Osmanski, Geeling Chau, Vasileios Christopoulos, Charles Liu, Mickael Tanter, Mikhail G. Shapiro and Richard A. Andersen, 30 November 2023, Nature Neuroscience.
DOI: 10.1038/s41593-023-01500-7
Whitney Griggs (PhD '23), UCLA-Caltech MD/PhD student, and Sumner Norman, former postdoctoral scholar now of Forest Neurotech, are the study's first authors. In addition to Griggs, Norman, and Andersen, Caltech coauthors are graduate student Geeling Chau and Vasileios Christopoulos, visiting associate in biology and biological engineering. Other coauthors are Charles Liu of USC; and Mickael Tanter, Thomas Deffieux, and Florian Segura of INSERM in Paris, France. Funding was provided by the National Eye Institute, a Josephine de Karman Fellowship, the UCLA-Caltech MSTP, the Della Martin Foundation, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the National Institutes of Health, the T&C Chen Brain-Machine Interface Center, and the Boswell Foundation.
News
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]
Analyzing Darwin’s specimens without opening 200-year-old jars
Scientists have successfully analyzed Charles Darwin's original specimens from his HMS Beagle voyage (1831 to 1836) to the Galapagos Islands. Remarkably, the specimens have been analyzed without opening their 200-year-old preservation jars. Examining 46 [...]
Scientists discover natural ‘brake’ that could stop harmful inflammation
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have uncovered a key mechanism that helps the body switch off inflammation—a breakthrough that could lead to new treatments for chronic diseases affecting millions worldwide. Inflammation is the [...]
A Forgotten Molecule Could Revive Failing Antifungal Drugs and Save Millions of Lives
Scientists have uncovered a way to make existing antifungal drugs work again against deadly, drug-resistant fungi. Fungal infections claim millions of lives worldwide each year, and current medical treatments are failing to keep pace. [...]