Researchers of the Institute of Biotechnology and Biomedicine (IBB-UAB) have generated four peptides, molecules smaller than proteins, capable of self-assembling in a controlled manner to form nanomaterials. The research, published in the journal ACS Nano, was conducted by Salvador Ventura, Marta Díaz Caballero and Susanna Navarro (IBB-UAB), and included the collaboration of Isabel Fuentes and Francesc Teixidor (Institute of Materials Science of Barcelona, ICMAB-CSIC).
In biotechnology, generating functional synthetic amyloid structures to form nanostructures by imitating the natural generation process is not new. The assembly of proteins into stable fibres allows creating supramolecular shapes that no isolated protein can create, and which are used as nanoconductors, photovoltaic structures, biosensors and catalysts.
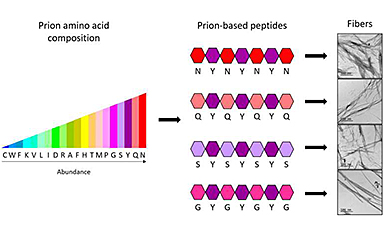
Quite recently, researchers began synthesizing prion protein sequences to form nanomaterials. The interest in these sequences lies in the fact that the proteins assemble in a slower and more controlled manner, forming highly ordered, nontoxic nanostructures. However, the fact that the sequence is so long, with over 150 amino acids, makes it very difficult and expensive to synthesise.
“We have demonstrated that an adequate design can permit the size of synthetic prion sequences to be reduced down to only 7 amino acids, while conserving the same properties. The four peptides we have fabricated are the shortest structures of this type created until now, and are capable of forming stable fibril assemblies,” says Salvador Ventura, researcher at the IBB and the UAB Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
Image Credit: Credit: IBB-UAB
News This Week
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]













Leave A Comment