MIT researchers develop "FrameDiff," a computational tool that uses generative AI to craft new protein structures, with the aim of accelerating drug development and improving gene therapy.
MIT's CSAIL researchers have developed a computational tool, FrameDiff, which employs generative AI to create new protein structures. It uses machine learning to model protein "backbones" and adjust them in 3D, crafting proteins beyond known designs. This breakthrough could accelerate drug development and enhance gene therapy by creating proteins that bind more efficiently, with potential applications in biotechnology, targeted drug delivery, and more.
Biology is a wondrous yet delicate tapestry. At the heart is DNA, the master weaver that encodes proteins, responsible for orchestrating the many biological functions that sustain life within the human body. However, our body is akin to a finely tuned instrument, susceptible to losing its harmony. After all, we're faced with an ever-changing and relentless natural world: pathogens, viruses, diseases, and cancer.
To advance our capabilities in protein engineering, MIT CSAIL researchers came up with "FrameDiff," a computational tool for creating new protein structures beyond what nature has produced. The machine learning approach generates "frames" that align with the inherent properties of protein structures, enabling it to construct novel proteins independently of preexisting designs, facilitating unprecedented protein structures.
"In nature, protein design is a slow-burning process that takes millions of years. Our technique aims to provide an answer to tackling human-made problems that evolve much faster than nature's pace," says MIT CSAIL PhD student Jason Yim, a lead author on a new paper about the work. "The aim, with respect to this new capacity of generating synthetic protein structures, opens up a myriad of enhanced capabilities, such as better binders. This means engineering proteins that can attach to other molecules more efficiently and selectively, with widespread implications related to targeted drug delivery and biotechnology, where it could result in the development of better biosensors. It could also have implications for the field of biomedicine and beyond, offering possibilities such as developing more efficient photosynthesis proteins, creating more effective antibodies, and engineering nanoparticles for gene therapy."
Framing FrameDiff
Proteins have complex structures, made up of many atoms connected by chemical bonds. The most important atoms that determine the protein's 3D shape are called the "backbone," kind of like the spine of the protein. Every triplet of atoms along the backbone shares the same pattern of bonds and atom types. Researchers noticed this pattern can be exploited to build machine learning algorithms using ideas from differential geometry and probability. This is where the frames come in: Mathematically, these triplets can be modeled as rigid bodies called "frames" (common in physics) that have a position and rotation in 3D.
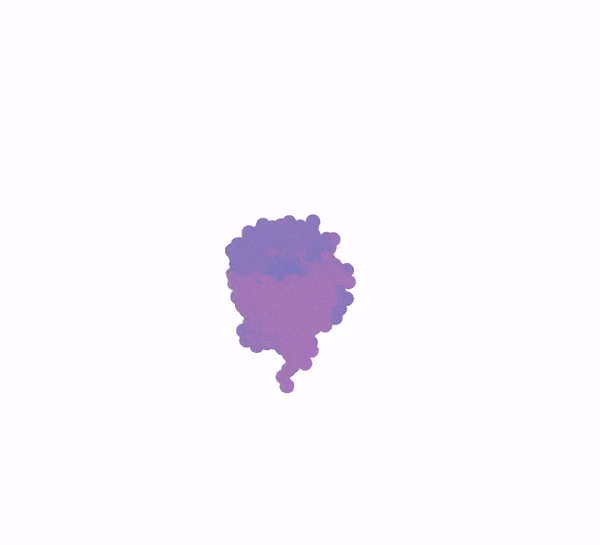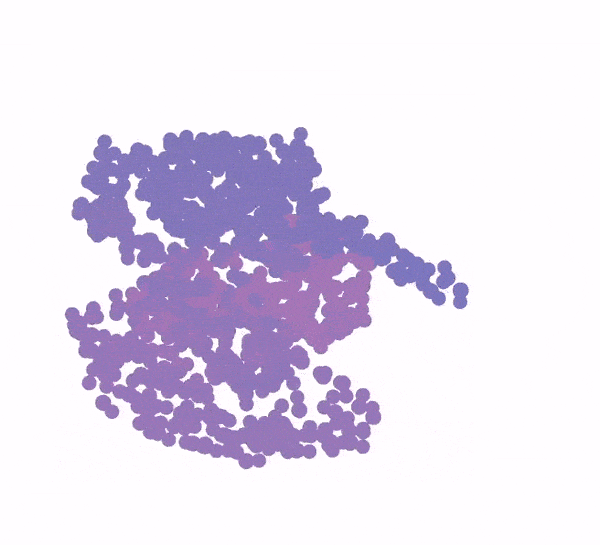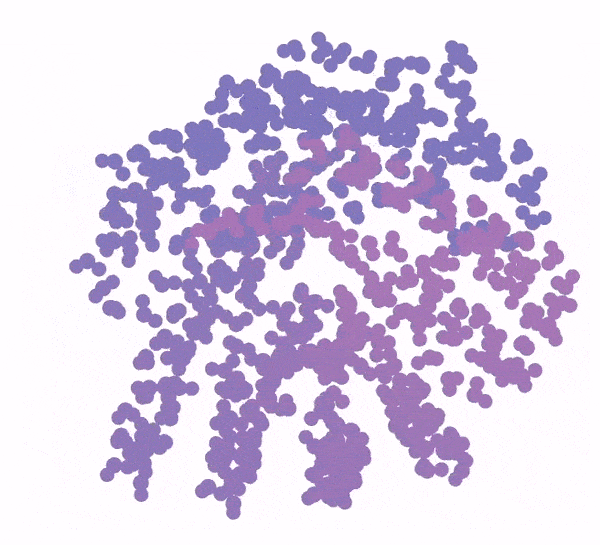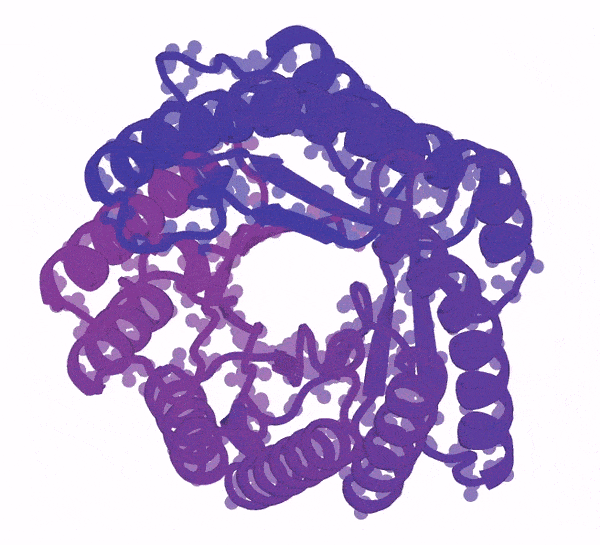
Generation of a protein structure with FrameDiff. Credit: Ian Haydon/Institute for Protein Design
These frames equip each triplet with enough information to know about its spatial surroundings. The task is then for a machine learning algorithm to learn how to move each frame to construct a protein backbone. By learning to construct existing proteins, the algorithm hopefully will generalize and be able to create new proteins never seen before in nature.
Training a model to construct proteins via "diffusion" involves injecting noise that randomly moves all the frames and blurs what the original protein looked like. The algorithm's job is to move and rotate each frame until it looks like the original protein. Though simple, the development of diffusion on frames requires techniques in stochastic calculus on Riemannian manifolds. On the theory side, the researchers developed "SE(3) diffusion" for learning probability distributions that nontrivially connects the translations and rotations components of each frame.
The subtle art of diffusion
In 2021, DeepMind introduced AlphaFold2, a deep learning algorithm for predicting 3D protein structures from their sequences. When creating synthetic proteins, there are two essential steps: generation and prediction. Generation means the creation of new protein structures and sequences, while "prediction" means figuring out what the 3D structure of a sequence is. It's no coincidence that AlphaFold2 also used frames to model proteins. SE(3) diffusion and FrameDiff were inspired to take the idea of frames further by incorporating frames into diffusion models, a generative AI technique that has become immensely popular in image generation, like Midjourney, for example.
The shared frames and principles between protein structure generation and prediction meant the best models from both ends were compatible. In collaboration with the Institute for Protein Design at the University of Washington, SE(3) diffusion is already being used to create and experimentally validate novel proteins. Specifically, they combined SE(3) diffusion with RosettaFold2, a protein structure prediction tool much like AlphaFold2, which led to "RFdiffusion." This new tool brought protein designers closer to solving crucial problems in biotechnology, including the development of highly specific protein binders for accelerated vaccine design, engineering of symmetric proteins for gene delivery, and robust motif scaffolding for precise enzyme design.
Future endeavors for FrameDiff involve improving generality to problems that combine multiple requirements for biologics such as drugs. Another extension is to generalize the models to all biological modalities including DNA and small molecules. The team posits that by expanding FrameDiff's training on more substantial data and enhancing its optimization process, it could generate foundational structures boasting design capabilities on par with RFdiffusion, all while preserving the inherent simplicity of FrameDiff.
"Discarding a pretrained structure prediction model [in FrameDiff] opens up possibilities for rapidly generating structures extending to large lengths," says Harvard University computational biologist Sergey Ovchinnikov. The researchers' innovative approach offers a promising step toward overcoming the limitations of current structure prediction models. Even though it's still preliminary work, it's an encouraging stride in the right direction. As such, the vision of protein design, playing a pivotal role in addressing humanity's most pressing challenges, seems increasingly within reach, thanks to the pioneering work of this MIT research team."
Yim wrote the paper alongside Columbia University postdoc Brian Trippe, French National Center for Scientific Research in Paris' Center for Science of Data researcher Valentin De Bortoli, Cambridge University postdoc Emile Mathieu, and Oxford University professor of statistics and senior research scientist at DeepMind Arnaud Doucet. MIT professors Regina Barzilay and Tommi Jaakkola advised the research.
The team's work was supported, in part, by the MIT Abdul Latif Jameel Clinic for Machine Learning in Health, EPSRC grants and a Prosperity Partnership between Microsoft Research and Cambridge University, the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship Program, NSF Expeditions grant, Machine Learning for Pharmaceutical Discovery and Synthesis consortium, the DTRA Discovery of Medical Countermeasures Against New and Emerging threats program, the DARPA Accelerated Molecular Discovery program, and the Sanofi Computational Antibody Design grant. This research will be presented at the International Conference on Machine Learning in July.
News
AI Helped Scientists Stop a Virus With One Tiny Change
Using AI, researchers identified one tiny molecular interaction that viruses need to infect cells. Disrupting it stopped the virus before infection could begin. Washington State University scientists have uncovered a method to interfere with a key [...]
Deadly Hospital Fungus May Finally Have a Weakness
A deadly, drug-resistant hospital fungus may finally have a weakness—and scientists think they’ve found it. Researchers have identified a genetic process that could open the door to new treatments for a dangerous fungal infection [...]
Fever-Proof Bird Flu Variant Could Fuel the Next Pandemic
Bird flu viruses present a significant risk to humans because they can continue replicating at temperatures higher than a typical fever. Fever is one of the body’s main tools for slowing or stopping viral [...]
What could the future of nanoscience look like?
Society has a lot to thank for nanoscience. From improved health monitoring to reducing the size of electronics, scientists’ ability to delve deeper and better understand chemistry at the nanoscale has opened up numerous [...]
Scientists Melt Cancer’s Hidden “Power Hubs” and Stop Tumor Growth
Researchers discovered that in a rare kidney cancer, RNA builds droplet-like hubs that act as growth control centers inside tumor cells. By engineering a molecular switch to dissolve these hubs, they were able to halt cancer [...]
Platelet-inspired nanoparticles could improve treatment of inflammatory diseases
Scientists have developed platelet-inspired nanoparticles that deliver anti-inflammatory drugs directly to brain-computer interface implants, doubling their effectiveness. Scientists have found a way to improve the performance of brain-computer interface (BCI) electrodes by delivering anti-inflammatory drugs directly [...]
After 150 years, a new chapter in cancer therapy is finally beginning
For decades, researchers have been looking for ways to destroy cancer cells in a targeted manner without further weakening the body. But for many patients whose immune system is severely impaired by chemotherapy or radiation, [...]
Older chemical libraries show promise for fighting resistant strains of COVID-19 virus
SARS‑CoV‑2, the virus that causes COVID-19, continues to mutate, with some newer strains becoming less responsive to current antiviral treatments like Paxlovid. Now, University of California San Diego scientists and an international team of [...]
Lower doses of immunotherapy for skin cancer give better results, study suggests
According to a new study, lower doses of approved immunotherapy for malignant melanoma can give better results against tumors, while reducing side effects. This is reported by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in the Journal of the National [...]
Researchers highlight five pathways through which microplastics can harm the brain
Microplastics could be fueling neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, with a new study highlighting five ways microplastics can trigger inflammation and damage in the brain. More than 57 million people live with dementia, [...]
Tiny Metal Nanodots Obliterate Cancer Cells While Largely Sparing Healthy Tissue
Scientists have developed tiny metal-oxide particles that push cancer cells past their stress limits while sparing healthy tissue. An international team led by RMIT University has developed tiny particles called nanodots, crafted from a metallic compound, [...]
Gold Nanoclusters Could Supercharge Quantum Computers
Researchers found that gold “super atoms” can behave like the atoms in top-tier quantum systems—only far easier to scale. These tiny clusters can be customized at the molecular level, offering a powerful, tunable foundation [...]
A single shot of HPV vaccine may be enough to fight cervical cancer, study finds
WASHINGTON -- A single HPV vaccination appears just as effective as two doses at preventing the viral infection that causes cervical cancer, researchers reported Wednesday. HPV, or human papillomavirus, is very common and spread [...]
New technique overcomes technological barrier in 3D brain imaging
Scientists at the Swiss Light Source SLS have succeeded in mapping a piece of brain tissue in 3D at unprecedented resolution using X-rays, non-destructively. The breakthrough overcomes a long-standing technological barrier that had limited [...]
Scientists Uncover Hidden Blood Pattern in Long COVID
Researchers found persistent microclot and NET structures in Long COVID blood that may explain long-lasting symptoms. Researchers examining Long COVID have identified a structural connection between circulating microclots and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). The [...]
This Cellular Trick Helps Cancer Spread, but Could Also Stop It
Groups of normal cbiells can sense far into their surroundings, helping explain cancer cell migration. Understanding this ability could lead to new ways to limit tumor spread. The tale of the princess and the [...]