A study recently published in the journal Infection, Genetics and Evolution explored the attachment affinity of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and carbon nano-fullerene towards numerous molecular targets of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
Computational modeling of the 3D architectures of nano-fullerenes and CNTs was carried out, and molecule binding and molecular dynamic (MD) simulations were used to estimate the attachment affinity of the nanoparticles to the chosen target molecules. The research emphasizes the need of using carbon nanoparticles as a treatment for COVID-19.
COVID-19 Taking the World by Storm
The shocking COVID-19 epidemic attributed to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), first detected in Wuhan, China, in December of 2019, has since expanded globally. A virulent pathogen, SARS-CoV-2 belongs to the ß-coronavirus family and is a positive-stranded RNA virus. The spike glycoproteins that appear on the envelope give these pathogens a crown-like appearance. Other proteins in the viral structure include membrane and envelope proteins, nucleocapsid protein, and RNA dependent on RNA polymerase as structural proteins.
Inadequacy of Current Treatments
At first, anti-viral medications including remdesivir, lopinavir, chloroquine, and hydroxychloroquine were recommended for COVID-19 infection therapy. Recent assessments, however, proved the ineffectiveness of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine when combatting SARS-CoV-2. Several drugs are in the early phases of clinical development.
Novel variants of the virus have been discovered in various regions across the globe, with these mutations exhibiting enhanced transmission and pathogenicity, as well as reduced neutralization.
Vaccines are now available to treat COVID-19, although they have not yet reached populations in some countries. The variety of symptoms found in the patients, as well as asymptomatic transmission and vaccination resistance data, indicate that the creation of an alternative treatment answer is imminently needed.
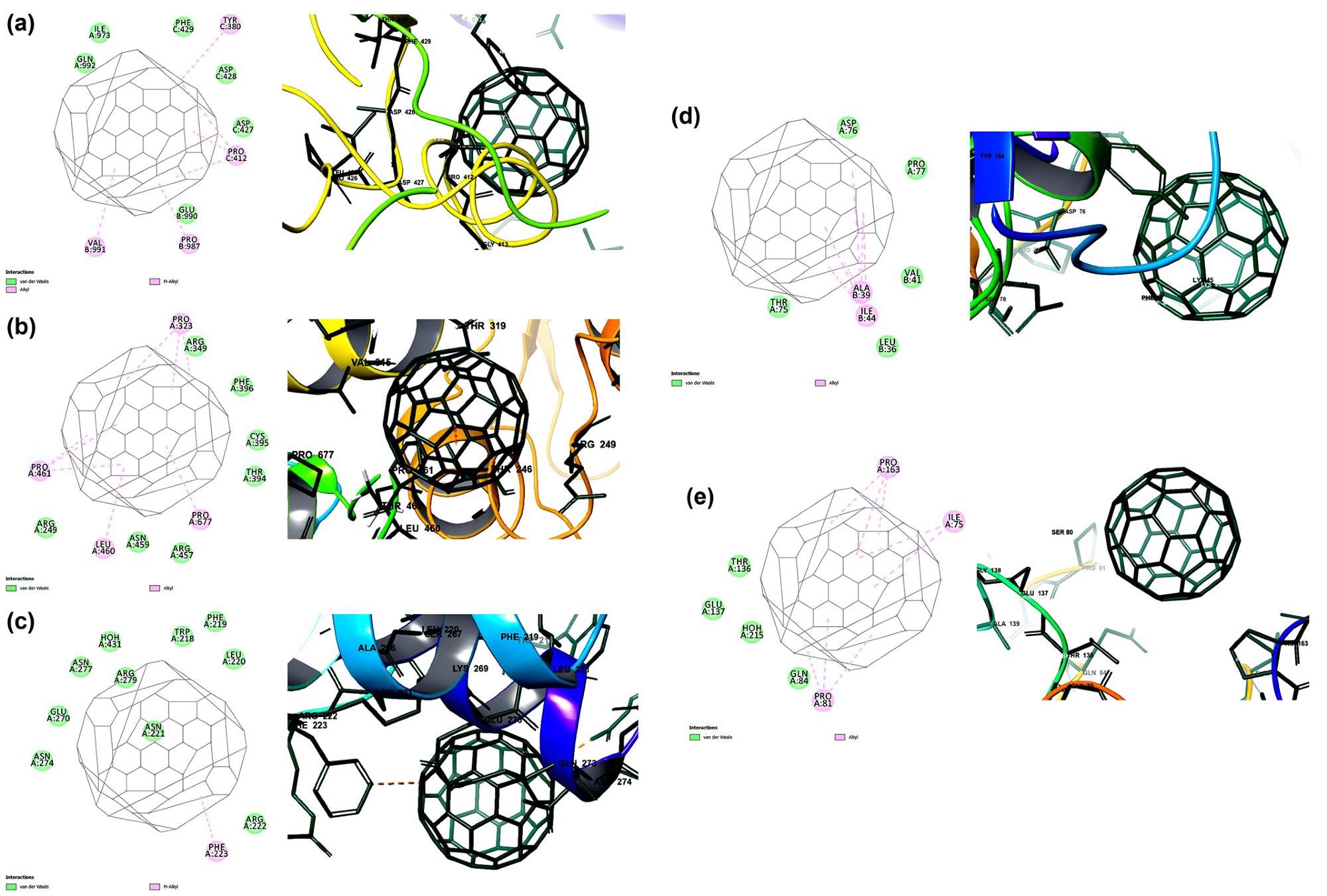
The binding potential of carbon nanofullerene towards the prioritized targets of SARS-CoV-2 is predicted by molecular docking. The binding affinity and interactions of carbon nano fullerene towards (a) spike glycoprotein (−13.7 kcal/mol), (b) RNA dependent RNA polymerase (−12.9 kcal/mol), (c) main protease (−11.4 kcal/mol), (d) papain-like protease (−10.6 kcal/mol) and (d) RNA binding domain of nucleocapsid protein (−10.1 kcal/mol). Image Credit: Skariyachan, S. et al
Nanotechnology and Computational Biology
Modern developments in nanotechnology have revealed the possibility of using nanoparticles such as CNTs and nano-fullerenes to target various areas of SARS-CoV-2, blocking its pathogenic effects. Carbon nanotubes are being touted as potential therapeutic materials owing to excellent mechanical capabilities, structural soundness, and tunability of functional groups.
Nanomaterials may be used to create nano-based COVID-19 protective devices and disinfectants. Furthermore, nanoparticles could be employed to function as antigen carriers or serve as an adjuvant medication for use concurrently with the upcoming COVID-19 vaccines.
The team used computation-based virtual screening and MD simulations to determine the binding capability of carbon nanotubes and nano-fullerenes to numerous putative target areas of the virus. Carbon nano-fullerenes have a potential affinity for SARS-CoV-2 targets, and carbon nanotubes have demonstrated possible interactions that might limit the virus’s harmful mechanism.
Identifying Structural Properties of Recognized Targets
Spike glycoproteins are the principal target of antibodies and are important in stimulating entrance into cells through the transmembrane spike. The transmembrane spike is composed of two functional subunits that are in charge of attaching to receptors of host cells and fusing the membranes of the virus and cells.
Each virus may identify distinct places of attachment and entrance by connecting with specific areas of the receptors in the host cell unit, depending on the type of viral strain. The major constituent of the viral machinery is responsible for replication and transcription; the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) is required for the survival of these viruses. Treatments targeting this area would be an excellent strategy.
The primary protease is an enzyme that is also involved in viral replication and transcription. The major protease is required for the digestion of viral RNA-translated polyproteins. Inhibiting this enzyme may aid in the prevention of viral replication. As a result, these proteins were chosen in the study because they might be potential therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
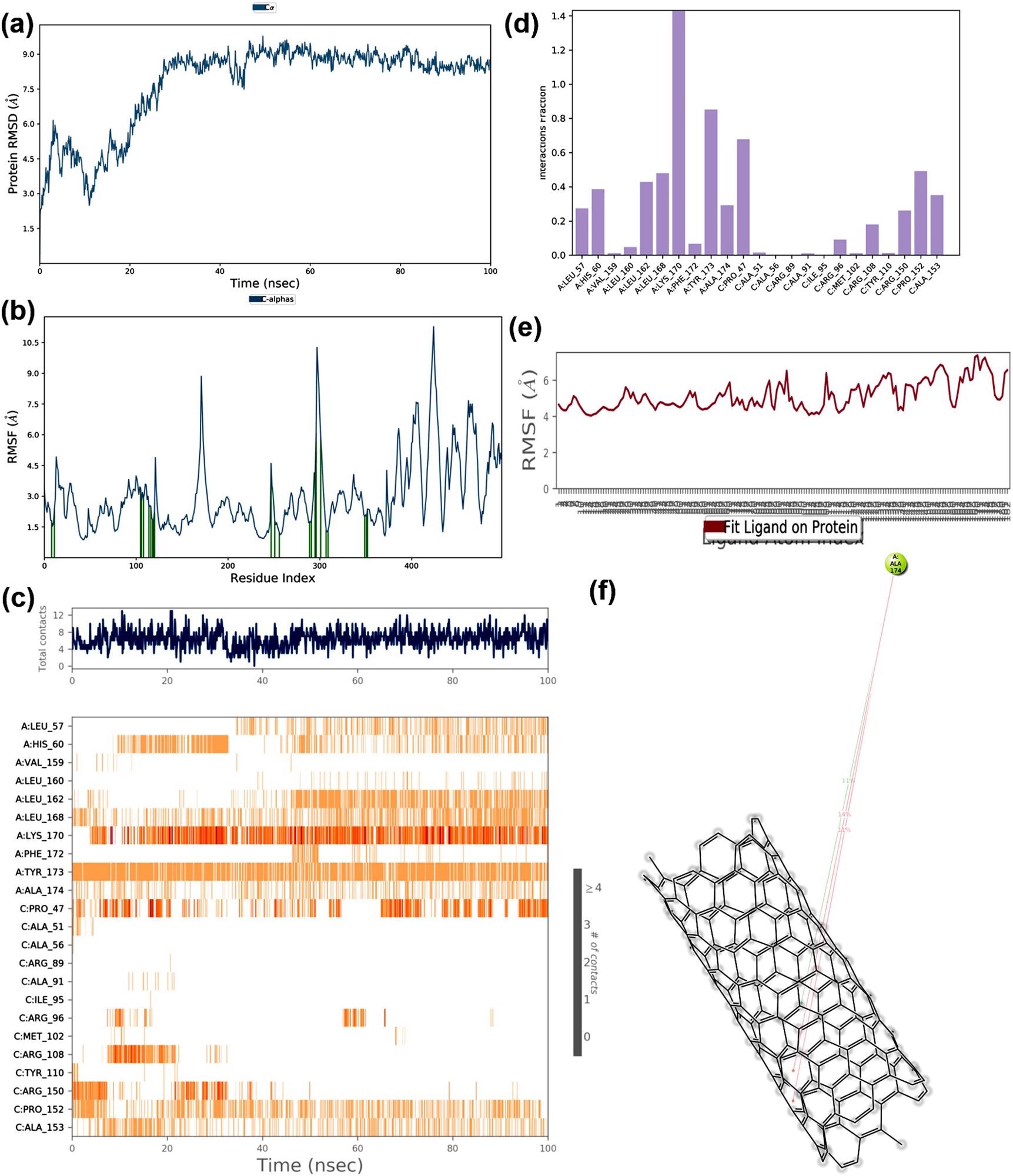
The MD simulation trajectories of RNA binding domain of the nucleocapsid protein and nano tube complex (a) RMSD: Protein RMSD (Å) on the y-axis and time on the x-axis (b) Protein RMSF (Å) on the y-axis and residues on the x-axis (c) Protein-ligand contacts over the simulation course, (d) histogram representing interaction fraction on the y-axis and residues on the x-axis (e) Ligand RMSF (Å) on the y-axis and atoms on the x-axis and (f) Major interactions that occur during MD simulation. Image Credit: Skariyachan, S. et al
Conclusions
It may initially seem unimpressive that the targets adopt this orientation only after adsorption on hydrophobic surfaces. However, there is potential for various orientations concerning the adsorption process on hydrophobic or charged areas. Therefore, understanding the interaction modeling of many orientations is critical.
The present research lays the groundwork for future laboratory tests and exploratory trials. Despite the nanoparticles’ apparent toxic nature, they might be employed as possible leads for blocking the coronavirus target areas. Research has shown the success of their use in target-specified treatments, drug transportation processes, cancer-related therapies, and other applications.
The MD simulation tests indicated that the priority entities and nanoparticles undergo dynamic interactions, which are steady and promising. When compared to carbon-fullerenes, nanotubes have the higher binding energy of the two carbon nanoparticles.
News
Challenging Previous Beliefs: Japanese Scientists Discover Hidden Protector of Heart
A Japanese research team found that the oxidized form of glutathione (GSSG) may protect heart tissue by modifying a key protein, potentially offering a novel therapeutic approach for ischemic heart failure. A new study [...]
Millions May Have Long COVID – So Why Can’t They Get Diagnosed?
Millions of people in England may be living with Long Covid without even realizing it. A large-scale analysis found that nearly 10% suspect they might have the condition but remain uncertain, often due to [...]
Researchers Reveal What Happens to Your Brain When You Don’t Get Enough Sleep
What if poor sleep was doing more than just making you tired? Researchers have discovered that disrupted sleep in older adults interferes with the brain’s ability to clean out waste, leading to memory problems [...]
How to prevent chronic inflammation from zombie-like cells that accumulate with age
In humans and other multicellular organisms, cells multiply. This defining feature allows embryos to grow into adulthood, and enables the healing of the many bumps, bruises and scrapes along the way. Certain factors can [...]
Breakthrough for long Covid patients who lost sense of smell
A breakthrough nasal surgery has restored the sense of smell for a dozen long Covid patients. Experts at University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust successfully employed a technique typically used for correcting blocked nasal passages, [...]
Scientists Invent Plastic That Can Dissolve In Seawater In Just A Few Hours
Plastic waste and pollution in the sea have been among the most serious environmental problems for decades, causing immense damage to marine life and ecosystems. However, a breakthrough discovery may offer a game-changing solution. [...]
Muscles from the 3D printer
Swiss researchers have developed a method for printing artificial muscles out of silicone. In the future, these could be used on both humans and robots. Swiss researchers have succeeded in printing artificial muscles out [...]
Beneficial genetic changes observed in regular blood donors
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have identified genetic changes in blood stem cells from frequent blood donors that support the production of new, non-cancerous cells. Understanding the differences in the mutations that accumulate [...]
Shocking Amounts of Microplastics in the Brain – It Could Be Increasing Our Risk of Dementia
The brain has higher concentrations of plastic particles compared to other organs, with increased levels found in dementia patients. In a comprehensive commentary published in Brain Medicine, researchers highlight alarming new evidence of microplastic accumulation [...]
Baffling Scientists for Centuries: New Study Unravels Mystery of Static Electricity
ISTA physicists demonstrate that contact electrification depends on the contact history of materials. For centuries, static electricity has intrigued and perplexed scientists. Now, researchers from the Waitukaitis group at the Institute of Science and [...]
Tumor “Stickiness” – Scientists Develop Potential New Way To Predict Cancer’s Spread
UC San Diego researchers have developed a device that predicts breast cancer aggressiveness by measuring tumor cell adhesion. Weakly adherent cells indicate a higher risk of metastasis, especially in early-stage DCIS. This innovation could [...]
Scientists Just Watched Atoms Move for the First Time Using AI
Scientists have developed a groundbreaking AI-driven technique that reveals the hidden movements of nanoparticles, essential in materials science, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. By integrating artificial intelligence with electron microscopy, researchers can now visualize atomic-level changes that were [...]
Scientists Sound Alarm: “Safe” Antibiotic Has Led to an Almost Untreatable Superbug
A recent study reveals that an antibiotic used for liver disease patients may increase their risk of contracting a dangerous superbug. An international team of researchers has discovered that rifaximin, a commonly prescribed antibiotic [...]
Scientists Discover Natural Compound That Stops Cancer Progression
A discovery led by OHSU was made possible by years of study conducted by University of Portland undergraduates. Scientists have discovered a natural compound that can halt a key process involved in the progression [...]
Scientists Just Discovered an RNA That Repairs DNA Damage – And It’s a Game-Changer
Our DNA is constantly under threat — from cell division errors to external factors like sunlight and smoking. Fortunately, cells have intricate repair mechanisms to counteract this damage. Scientists have uncovered a surprising role played by [...]
What Scientists Just Discovered About COVID-19’s Hidden Death Toll
COVID-19 didn’t just claim lives directly—it reshaped mortality patterns worldwide. A major international study found that life expectancy plummeted across most of the 24 analyzed countries, with additional deaths from cardiovascular disease, substance abuse, and mental [...]