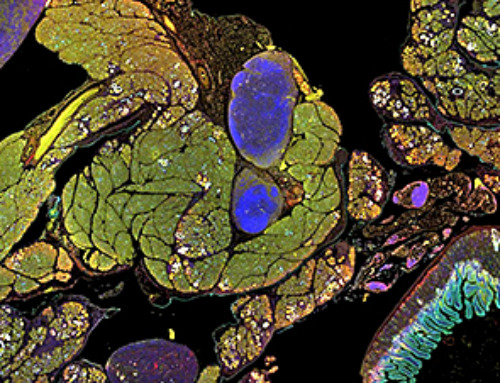
Human cells contain ribosomes, a complex machine that produces proteins for the rest of the body. Now the researchers have come closer to understanding how the ribosome works.
“It is amazing that we can visualize the atomic details of the ribosome. Because they are tiny – around 20-30 nanometers.”
So says Associate Professor Eva Kummer from the Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Protein Research, who is responsible for the new study published in Nature Communications.
And don’t worry if you don’t know how much a nanometer is. It is around one billionth of a meter.
The Ribosome
The ribosome is a part of the human cell consisting of ribosomal RNA and ribosomal proteins.
The ribosome is like a factory that builds proteins by following a set of instructions inherent in the genes.
Ribosomes are found floating in the cell cytosol, cellular organelles such as mitochondria or the protoplasm of bacteria.
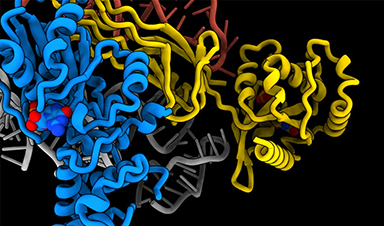
Using electron microscopy, Eva Kummer and her colleagues Giang Nguyen and Christina Ritter have managed to produce a 3D model of a part of the human cell, the ribosome, which is no more than 30 nanometers in diameter.
More specifically, they have taken snapshots of how a ribosome is made.
“It is important to understand how the ribosome is built and how it works, because it is the only cell particle that produces proteins in humans and all other living organisms. And without proteins, life would cease to exist,” says Eva Kummer.
Proteins are the primary building blocks of the human body. Your heart, lungs, brain, and basically your whole body is made of proteins produced by the ribosome.
“From the outside, the human body looks pretty simple, but then consider the fact that every part of the body consists of millions of molecules, that are extremely complex, and that they all know what to do – that is pretty breathtaking,” says Eva Kummer.
The complex assembling process of the ribosome. Credit: Eva Kummer
Folding, Assembling, and Moving to the Right Place
Before ribosomes can start to produce proteins, they first need to be assembled from over 80 different components.
Eva Kummer and her colleagues have obtained 3D models of three different stages of ribosome assembly.
“It is a complex particle with lots of different parts – many proteins and RNA components – that must be folded, assembled, and moved to the right place. It does not all happen at once. Ribosome assembly is a gradual process involving several stages,” she explains.
Out of the three stages, the 3D model describing the earliest time point in the assembly is the most interesting, according to Eva Kummer, as no one has been able to describe it before.
“At this stage, we can tell e.g. that a specific protein called GTPBP10 is eager to interact with a so-called RNA component that forms a long helix,” Eva Kummer says and adds:
“In fact, towards the bottom of that helix is the catalytic center of the ribosome, which is where proteins are made. This is why it is so important that the helix is folded and placed correctly. ”
To achieve this, GTPBP10 grabs the helix and puts it in the right position for protein synthesis.
This is just one of the many stages of ribosome assembly which the new study has shed light on – insight that may pave the way for more knowledge of various diseases.
“Errors in ribosome assembly severely reduce the capacity of our cells to make proteins. These are for example proteins that convert the energy from the food we eat into energy coins that the body can use to run all sorts of cellular processes. Now, if the mitochondrial ribosome does not work, our body cannot produce enough energy coins anymore and this leads to diseases such as neurodegenerative disorders and heart conditions. And during aging, the production of these energy coins also works less and less efficiently,” Eva Kummer says and adds:
“The first step is understanding how things work. Only then can you try to change them.”
You can read “Structural insights into the role of GTPBP10 in the RNA maturation of the mitoribosome“ in Nature Communications.
Reference: “Structural insights into the role of GTPBP10 in the RNA maturation of the mitoribosome” by Thu Giang Nguyen, Christina Ritter and Eva Kummer, 2 December 2023, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-43599-z
News
Global Nanomaterial Regulation: A Country-by-Country Comparison
Nanomaterials are materials with at least one dimension smaller than 100 nanometres (about 100,000 times thinner than a human hair). Because of their tiny size, they have unique properties that can be useful in [...]
Pandemic Potential: Scientists Discover 3 Hotspots of Deadly Emerging Disease in the US
Virginia Tech researchers discovered six new rodent carriers of hantavirus and identified U.S. hotspots, highlighting the virus’s adaptability and the impact of climate and ecology on its spread. Hantavirus recently drew public attention following reports [...]
Studies detail high rates of long COVID among healthcare, dental workers
Researchers have estimated approximately 8% of Americas have ever experienced long COVID, or lasting symptoms, following an acute COVID-19 infection. Now two recent international studies suggest that the percentage is much higher among healthcare workers [...]
Melting Arctic Ice May Unleash Ancient Deadly Diseases, Scientists Warn
Melting Arctic ice increases human and animal interactions, raising the risk of infectious disease spread. Researchers urge early intervention and surveillance. Climate change is opening new pathways for the spread of infectious diseases such [...]
Scientists May Have Found a Secret Weapon To Stop Pancreatic Cancer Before It Starts
Researchers at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory have found that blocking the FGFR2 and EGFR genes can stop early-stage pancreatic cancer from progressing, offering a promising path toward prevention. Pancreatic cancer is expected to become [...]
Breakthrough Drug Restores Vision: Researchers Successfully Reverse Retinal Damage
Blocking the PROX1 protein allowed KAIST researchers to regenerate damaged retinas and restore vision in mice. Vision is one of the most important human senses, yet more than 300 million people around the world are at [...]
Differentiating cancerous and healthy cells through motion analysis
Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have found that the motion of unlabeled cells can be used to tell whether they are cancerous or healthy. They observed malignant fibrosarcoma [...]
This Tiny Cellular Gate Could Be the Key to Curing Cancer – And Regrowing Hair
After more than five decades of mystery, scientists have finally unveiled the detailed structure and function of a long-theorized molecular machine in our mitochondria — the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier. This microscopic gatekeeper controls how [...]
Unlocking Vision’s Secrets: Researchers Reveal 3D Structure of Key Eye Protein
Researchers have uncovered the 3D structure of RBP3, a key protein in vision, revealing how it transports retinoids and fatty acids and how its dysfunction may lead to retinal diseases. Proteins play a critical [...]
5 Key Facts About Nanoplastics and How They Affect the Human Body
Nanoplastics are typically defined as plastic particles smaller than 1000 nanometers. These particles are increasingly being detected in human tissues: they can bypass biological barriers, accumulate in organs, and may influence health in ways [...]
Measles Is Back: Doctors Warn of Dangerous Surge Across the U.S.
Parents are encouraged to contact their pediatrician if their child has been exposed to measles or is showing symptoms. Pediatric infectious disease experts are emphasizing the critical importance of measles vaccination, as the highly [...]
AI at the Speed of Light: How Silicon Photonics Are Reinventing Hardware
A cutting-edge AI acceleration platform powered by light rather than electricity could revolutionize how AI is trained and deployed. Using photonic integrated circuits made from advanced III-V semiconductors, researchers have developed a system that vastly [...]
A Grain of Brain, 523 Million Synapses, Most Complicated Neuroscience Experiment Ever Attempted
A team of over 150 scientists has achieved what once seemed impossible: a complete wiring and activity map of a tiny section of a mammalian brain. This feat, part of the MICrONS Project, rivals [...]
The Secret “Radar” Bacteria Use To Outsmart Their Enemies
A chemical radar allows bacteria to sense and eliminate predators. Investigating how microorganisms communicate deepens our understanding of the complex ecological interactions that shape our environment is an area of key focus for the [...]
Psychologists explore ethical issues associated with human-AI relationships
It's becoming increasingly commonplace for people to develop intimate, long-term relationships with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. At their extreme, people have "married" their AI companions in non-legally binding ceremonies, and at least two people [...]
When You Lose Weight, Where Does It Actually Go?
Most health professionals lack a clear understanding of how body fat is lost, often subscribing to misconceptions like fat converting to energy or muscle. The truth is, fat is actually broken down into carbon [...]