Increased water consumption worldwide has resulted in low-quality water resources utilized for crop irrigation in the agricultural sector; however, these sources tend to be contaminated. New research published in the MDPI sustainability explores whether the addition of nanofertilizers can enhance these water sources.
Here, the team investigated the effects of nanofertilizers on saline water sources in tomato crops.
Harmful Effects of Conventional Fertilizers
Owing to the extensive utilization of mineral fertilizers and pesticides, traditional fertilizers have produced several ecological threats, including food poisoning and soil deterioration.
Excess nitrogen in the air and water from fertilizers can cause respiratory problems, heart illness, and many malignancies, as well as hinder agricultural development and boost hypoallergenic pollen output.
Keeping in mind the low effectiveness of traditional fertilizer use (ranging from 20 to 40 %), a large proportion of these fertilizers eluted into aquifers and ultimately streams, causing financial damage, eutrophication, and public health complications.
Are Nanofertilizers a Viable Option?
Considering these limitations of conventional fertilizers, nano fertilizers are an advantageous alternative. Nanofertilizers are thought to be interesting substances because they exhibit the distinctive properties of nanoparticles at the nanoscale.
Many studies have found advantages regarding the usage of nanofertilizers on agricultural plants such as hay, soy, potatoes, maize, and oats. Benefits include improved quality of the fruit, production, and storability, as well as reduced nutrient leakage into the soil following harvesting of crops.
Iron, copper, selenium, and zinc are the most frequent minerals that are already used as nutrient-based nanofertilizers.
Why Quality of the Irrigation Water Matters?
Irrigation quality of water is a constraining element in the agriculture industry worldwide, with different irrigation water quality parameters such as salinity and sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), sodium, manganese as well as toxic substances.
When irrigation water has a high salt concentration and toxic substances, the water loses quality and accumulates in soil samples and produced crops. This problem has been exacerbated by the extensive use of wastewater in the cultivation of crops, which contains various toxins that may continue throughout the food chain.
Many substances, including hydrogel, biochar, and nanomaterials, have been used to purify water sources. Nanomaterials have been utilized to remove contaminants such as cadmium and chromium from polluted water; however, the usefulness of nanofertilizers in increasing the productivity of farmed plants watered with poor water quality requires additional investigation.
Why Tomato Plants?
Tomato plants (Solanum Lycopersicum L.) are regarded as one of the most important vegetable crops worldwide due to their great gastronomic and commercial importance, in addition to their nutritious significance. As a result of their high oxide concentration, tomatoes are naturally strong in antioxidants and may defend against prostate cancer as well as protect human skin from UV radiation.
This crop has a long growing season and high water demands, and it can yield under a variety of conditions, including salt stress, dehydration, copper neurotoxicity, and continual watering with salty water. As a result, the current study was designed to determine if nanofertilizers (Cu and Se), either individually or in combination, can reduce the influence of salty water on tomatoes’ productivity and quality.
Result Findings
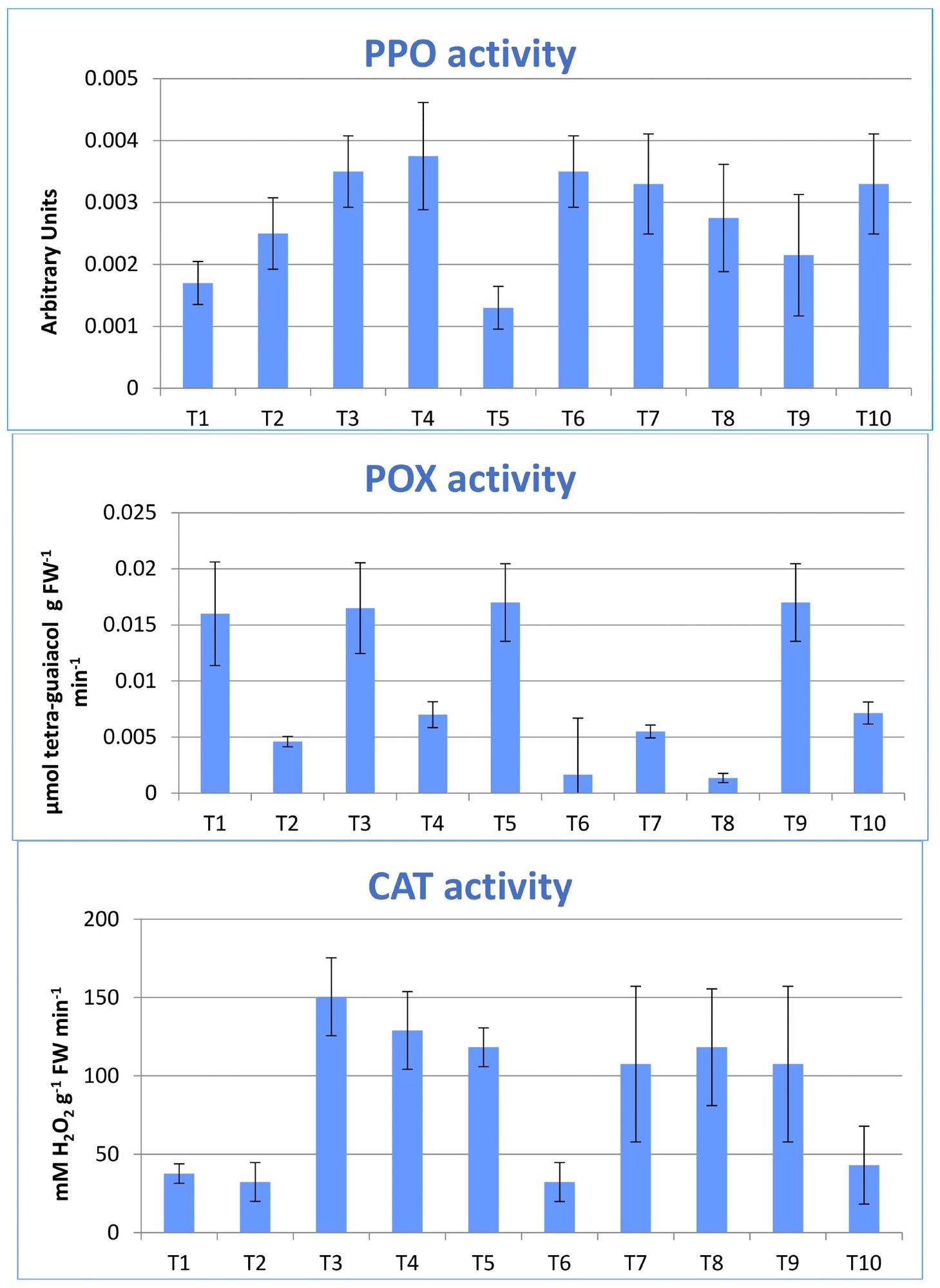
Undertreatment with average quality of water and coupled nano-Se, the longest branch growth (69.8 cm) was attained. The maximum chlorophyll concentration (79.7 SPAD) was measured following nano-Se administration and watering with low-quality water.
Among all tested properties, the number of branches per plant was the only one that had a non-significant influence on vegetative development. The highest amount of fruit yield (2.07 kg plant-1) and total soluble solid content (9.24 %) was acquired under irrigated agriculture using low quality of water (IW3) and 100 mg L-1 of nano-Cu.
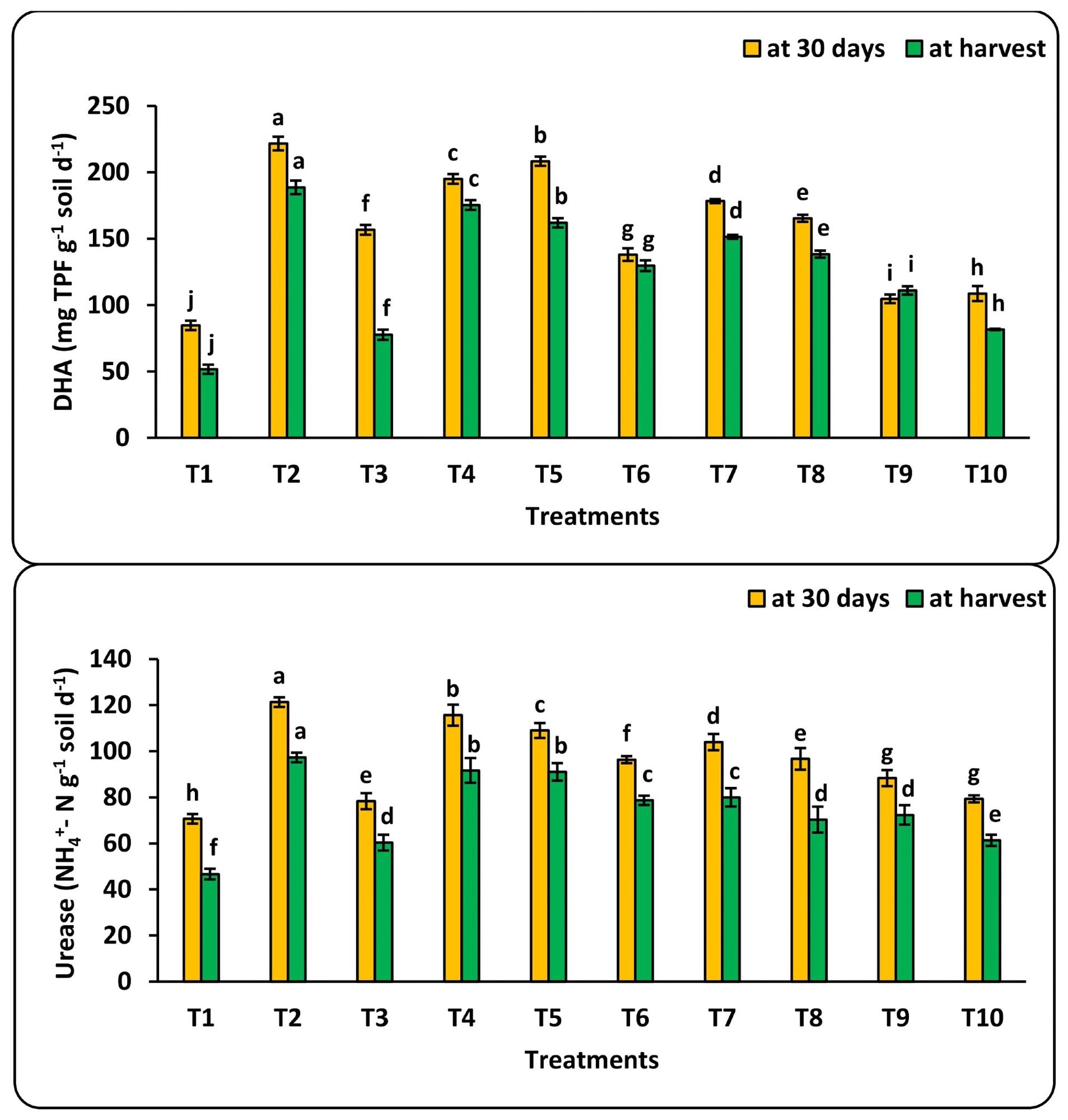
The highest value of vitamin C content (mg 100 g-1 FW) was achieved under fertigation using low water quality (IW3) and a combination of 100 mg L-1 of nano-Se and nano-Cu. Furthermore, the microbiological populations of bacterium, fungi, and actinobacteria increased after 30 days of transplantation and declined in all treatment at harvests due to the negative effect of poor irrigation water quality.
In short, the controlled utilization of bio-nano fertilizers was deemed successful in boosting the productivity as well as the quality of the produced crops.
News
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]
Analyzing Darwin’s specimens without opening 200-year-old jars
Scientists have successfully analyzed Charles Darwin's original specimens from his HMS Beagle voyage (1831 to 1836) to the Galapagos Islands. Remarkably, the specimens have been analyzed without opening their 200-year-old preservation jars. Examining 46 [...]
Scientists discover natural ‘brake’ that could stop harmful inflammation
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have uncovered a key mechanism that helps the body switch off inflammation—a breakthrough that could lead to new treatments for chronic diseases affecting millions worldwide. Inflammation is the [...]
A Forgotten Molecule Could Revive Failing Antifungal Drugs and Save Millions of Lives
Scientists have uncovered a way to make existing antifungal drugs work again against deadly, drug-resistant fungi. Fungal infections claim millions of lives worldwide each year, and current medical treatments are failing to keep pace. [...]
Scientists Trap Thyme’s Healing Power in Tiny Capsules
A new micro-encapsulation breakthrough could turn thyme’s powerful health benefits into safer, smarter nanodoses. Thyme extract is often praised for its wide range of health benefits, giving it a reputation as a natural medicinal [...]
Scientists Develop Spray-On Powder That Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds
KAIST scientists have created a fast-acting, stable powder hemostat that stops bleeding in one second and could significantly improve survival in combat and emergency medicine. Severe blood loss remains the primary cause of death from [...]
Oceans Are Struggling To Absorb Carbon As Microplastics Flood Their Waters
New research points to an unexpected way plastic pollution may be influencing Earth’s climate system. A recent study suggests that microscopic plastic pollution is reducing the ocean’s capacity to take in carbon dioxide, a [...]
Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine – New book from Frank Boehm
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
New Book! NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Global Health Care Equivalency in the Age of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine and Artificial Intelligence
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]