A new approach to brain tumor treatment using photodynamic therapy (PDT) with nanotechnology has been explored in a review published in the journal Biomedicines. Unlike radiotherapy and surgical resection, PDT can treat micro-invasive areas and protect critical brain tissue with a high probability of success.
Conventional Methods using PDT
Photodynamic therapy is a type of phototherapy that uses light and sensitizing chemical agents in combination with oxygen molecules to induce cell death. It is a two-stage remedy that incorporates light energy with a medicine (photosensitizer) designed to kill cancer cells and precancerous cells after they have been activated by light.
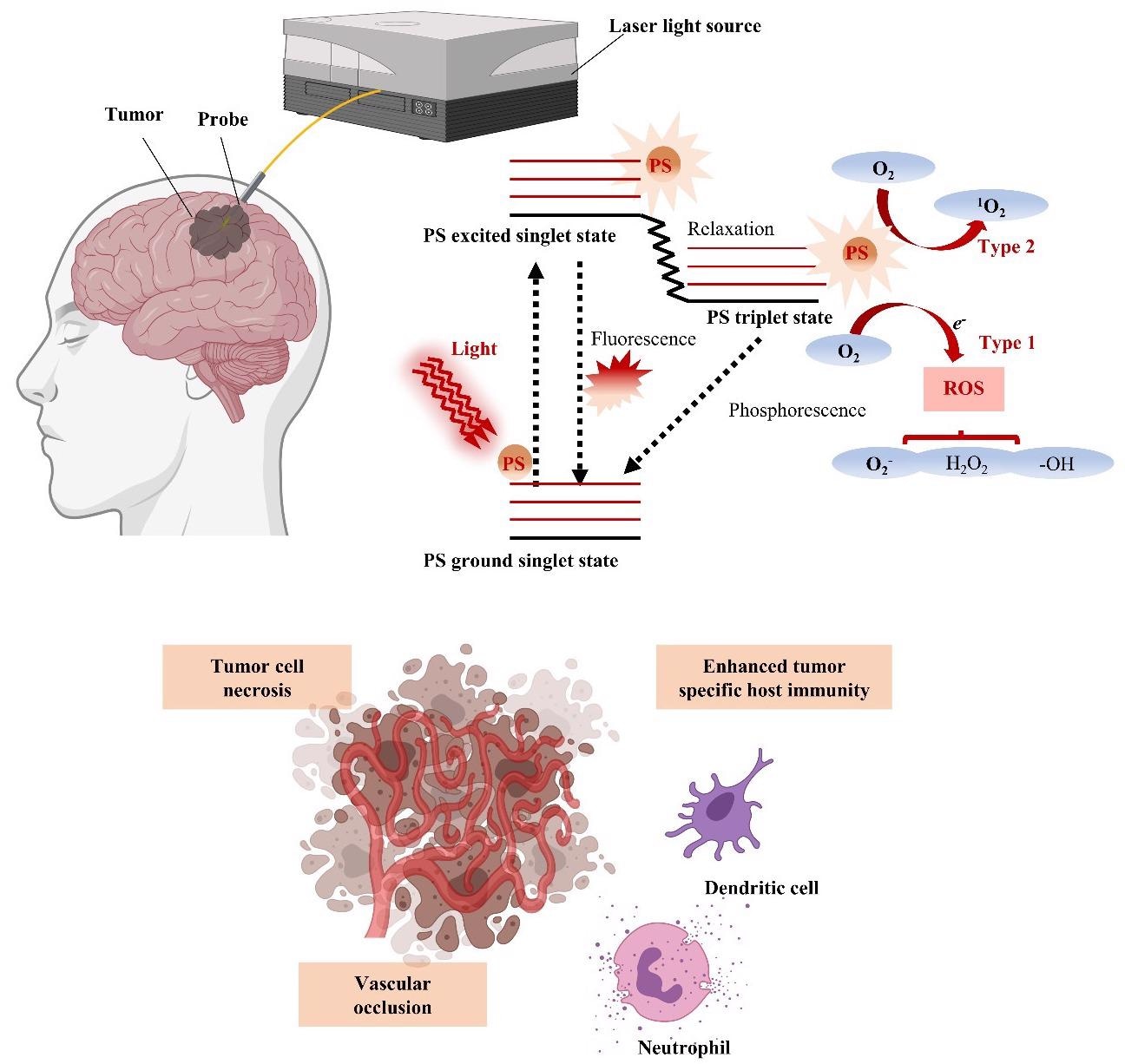
Schematic illustration of photodynamic therapy (PDT) for GBM treatment with energy diagram of the oxygen dependent response. If the photosensitizer (PS) in the ground singlet state is excited by the light wavelength, then the PS in the excited singlet state can convert to the excited triplet state via intersystem crossing. In the presence of molecular oxygen, the PS in the triplet state can undergo a Type 1 or Type 2 redox reaction, producing reactive oxygen species (ROS) that cause tumor cell necrosis, vascular occlusion, and tumor-specific host immunity. © Kim, H., and Lee, D. (2022).
Photosensitizers are initiated by a specific wavelength energy, which is typically generated by a laser. PDT has been shown to be effective in treating a variety of tumors, including melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and multidrug-resistant lung and mammary tumors.
PDT with Its Limited Efficacy
Following other oncology implementations, the interest in PDT as a high-grade glioma diagnosis stems from the essence of tumor growth and the limited efficacy of modern treatment options to this population of patients. Although surgical removal, partial radiation, and chemotherapy are important treatments for intracranial tumors, the obtrusive growth patterns, especially in the cerebrum’s central region, make total resection difficult.
As opposed to surgical resection and radiation, PDT can treat micro-invasive regions while preserving sensitive brain areas. These potential benefits over conventional therapies have been shown to improve results in clinical situations with low overall survival and a high incidence of iatrogenic damage.
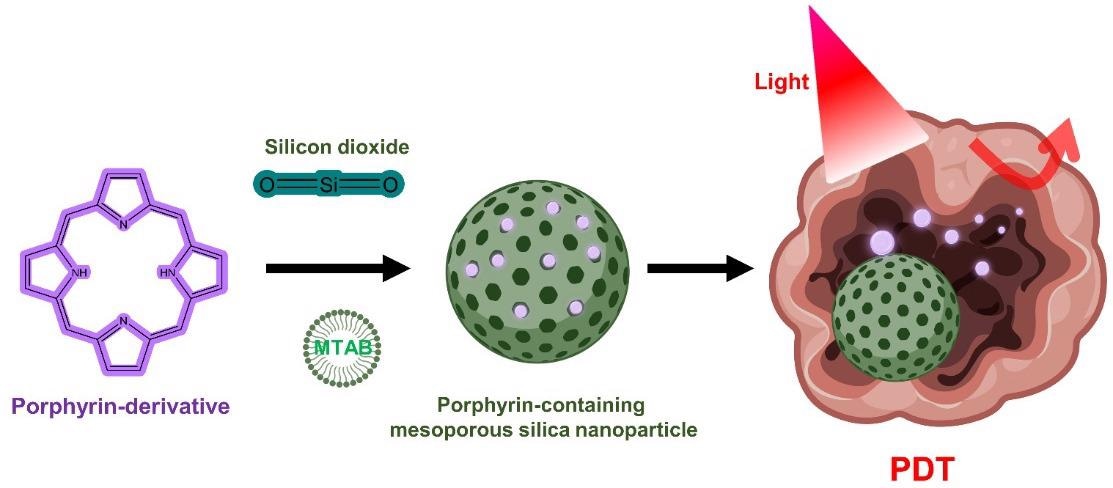
Porphyrin-containing mesoporous silica nanoparticles for PDT. © Kim, H., and Lee, D. (2022).
Nanomedicine as Opposed to Conventional Method
The rapidly growing areas of nanotechnology and nanomedicine are yielding nanostructured materials that may overcome the limitations of conventional clinical delivery methods. In fact, the existence of a functioning blood–brain barrier (BBB) inhibits therapeutic delivery to brain malignancies.
Many ways for temporarily opening the BBB by physical impact, including magnetic resonance (MR)-guided focussed ultrasound, have lately been researched to circumvent this barrier; however, this poses a technical problem.
One of the most promising solutions involves the utilization of multifunctional nanomedicines as drug delivery systems.
Advantages of Nanomedicine
The excellent physical and mechanical characteristics of nanocarriers vary based on their material, size, form (mesoporous microstructure, rod shape, particles), and ligand of choice. This enables enhanced brain-targeted administration of PS or therapeutic medicines.
Although many PS nanocapsules are still in the early phases of translation, major improvements in functional nanomedicines relying on BBB crossing have been accomplished in recent years.
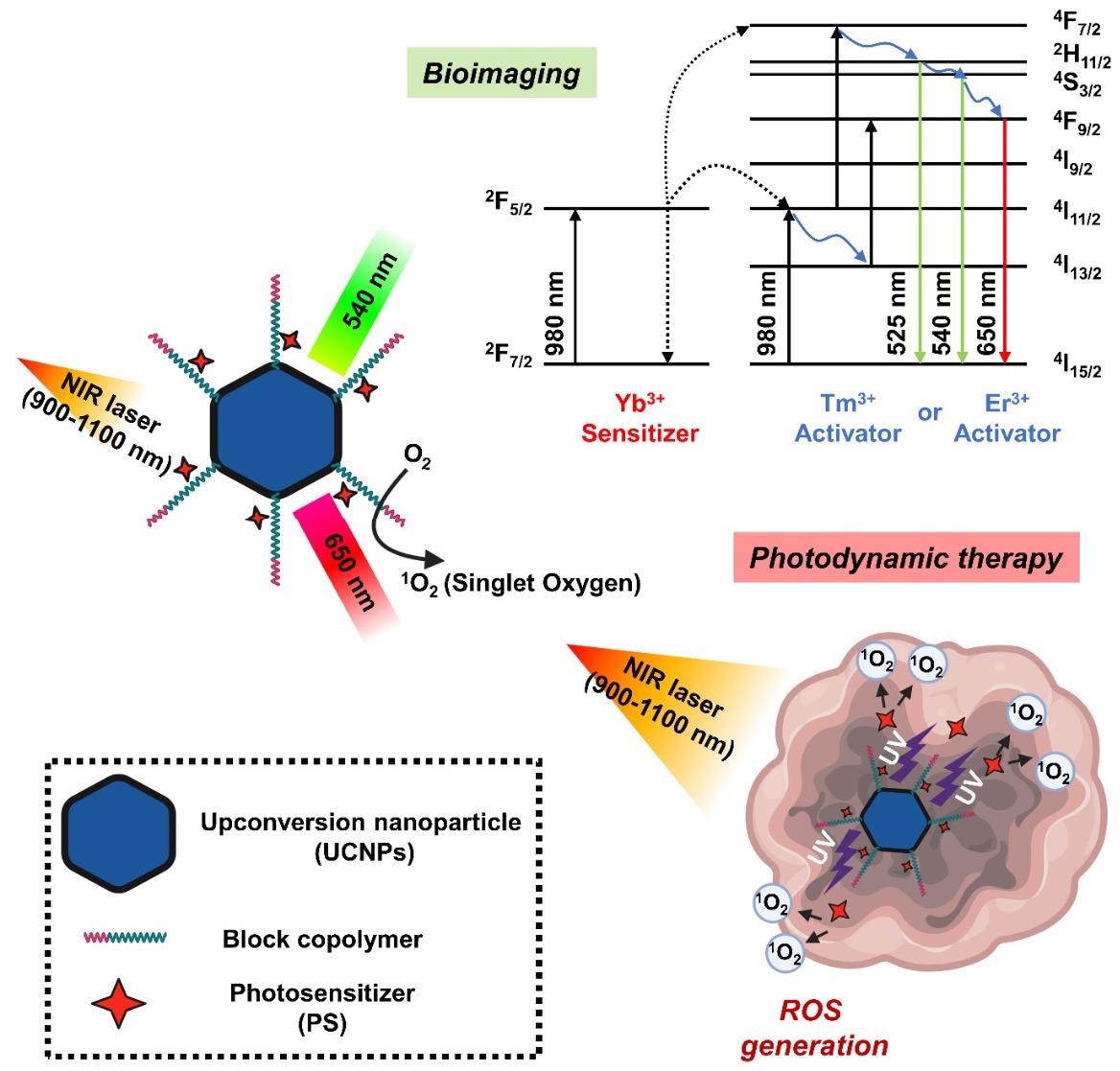
Schematic diagram showing the mechanism of photodynamic therapy and bioimaging through long-wavelength to short-wavelength conversion of upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs). © Kim, H., and Lee, D. (2022).
Another benefit of nanoparticles is that they may boost PS’s poor solubility, extend blood circulation, promote the targeted distribution and cellular absorption, and protect the medication from degradation.
Nanoparticles in PDT for Healing
Although contemporary PDT has considerably improved cancer patients’ quality of life and survival rates, it is critical to further enhance the therapeutic efficacy of nanocarriers to eliminate noticeable side effects.
In this respect, researchers have investigated a variety of nanocarriers, including polymers, liposomes, micelles, inorganic oxide, and new metal nanoparticles, to improve the therapeutic efficiency of photosensitizers.
First and foremost, nanocarriers must be used to effectively transport photosensitizers and singlet oxygen molecules to the target region in an ideal therapeutic range.
PDT is a dynamically evolving profession that is continually on the lookout for innovative technologies. To improve the efficacy and selectivity of PDT, molecular techniques based on nanotechnology are being explored. As a result, several novel organic and inorganic nanoparticles have already been discovered and produced for the targeted administration of photosensitizer medicines.
Nanoparticles may remedy the significant constraints of standard PS medication delivery.
Limitation of this Nanotechnology PDT
However, since intracranial brain tumors emerge from complex structures and distinct organs, such as those bordered by the blood–brain barrier, it is questionable if they can be completely removed using the same strategy as other cancers.
Further research is needed to determine if PDT may be utilized to treat malignant brain cancer that cannot be removed due to its location.
Ongoing research into the numerous PDTs described in this publication will decide whether breakthroughs in cancer research can reduce morbidity and mortality from intracranial malignancy and have the potential to change brain tumor therapy. As a result, although the development of new PDT technology is critical, establishing therapeutic guidelines via large-scale clinical practice should be prioritized.
Future Research in this Nanomedicine to Cure Brain Cancer
With the fast advancements in nanotechnology, researchers now have several synthetic approaches at their disposal to create gold nanoparticles with good shapes and characteristics for PDT applications.
In addition to the numerous physicochemical qualities listed above, the extra various synthesis potential should increase bioavailability and usefulness, indicating gold nanoparticles as a suitable choice for therapeutic cancer therapy.
News
Scientists Discover Why Some COVID Survivors Still Can’t Taste Food Years Later
A new study provides the first direct biological evidence explaining why some people continue to experience taste loss long after recovering from COVID-19. Researchers have uncovered specific biological changes in taste buds that could help [...]
Catching COVID significantly raises the risk of developing kidney disease, researchers find
Catching Covid significantly raises the risk of developing deadly kidney disease, research has shown. The virus was found to increase the chances that patients will develop the incurable condition by around 50 per cent. [...]
New Toothpaste Stops Gum Disease Without Harming Healthy Bacteria
Researchers have developed a targeted approach to combat periodontitis without disrupting the natural balance of the oral microbiome. The innovation could reshape how gum disease is treated while preserving beneficial bacteria. The human mouth [...]
Plastic Without End: Are We Polluting the Planet for Eternity?
The Kunming Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework calls for the elimination of plastic pollution by 2030. If that goal has been clearly set, why have meaningful measures that create real change still not been implemented? [...]
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]