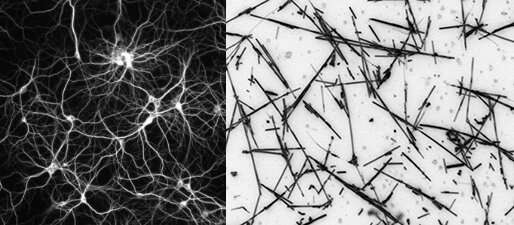
An international team led by scientists at the University of Sydney has demonstrated nanowire networks can exhibit both short- and long-term memory like the human brain.
“In this research we found higher-order cognitive function, which we normally associate with the human brain, can be emulated in non-biological hardware,” Dr. Loeffler said.
“This work builds on our previous research in which we showed how nanotechnology could be used to build a brain-inspired electrical device with neural network-like circuitry and synapse-like signaling.
“Our current work paves the way towards replicating brain-like learning and memory in non-biological hardware systems and suggests that the underlying nature of brain-like intelligence may be physical.”
Nanowire networks are a type of nanotechnology typically made from tiny, highly conductive silver wires that are invisible to the naked eye, covered in a plastic material, which are scattered across each other like a mesh. The wires mimic aspects of the networked physical structure of a human brain.
Advances in nanowire networks could herald many real-world applications, such as improving robotics or sensor devices that need to make quick decisions in unpredictable environments.
“This nanowire network is like a synthetic neural network because the nanowires act like neurons, and the places where they connect with each other are analogous to synapses,” senior author Professor Zdenka Kuncic, from the School of Physics, said.
“Instead of implementing some kind of machine learning task, in this study Dr. Loeffler has actually taken it one step further and tried to demonstrate that nanowire networks exhibit some kind of cognitive function.”
To test the capabilities of the nanowire network, the researchers gave it a test similar to a common memory task used in human psychology experiments, called the N-Back task.
For a person, the N-Back task might involve remembering a specific picture of a cat from a series of feline images presented in a sequence. An N-Back score of 7, the average for people, indicates the person can recognize the same image that appeared seven steps back.
“What we did here is manipulate the voltages of the end electrodes to force the pathways to change, rather than letting the network just do its own thing. We forced the pathways to go where we wanted them to go,” Dr. Loeffler said.
“When we implement that, its memory had much higher accuracy and didn’t really decrease over time, suggesting that we’ve found a way to strengthen the pathways to push them towards where we want them, and then the network remembers it.
“Neuroscientists think this is how the brain works, certain synaptic connections strengthen while others weaken, and that’s thought to be how we preferentially remember some things, how we learn and so on.”
The researchers said when the nanowire network is constantly reinforced, it reaches a point where that reinforcement is no longer needed because the information is consolidated into memory.
“It’s kind of like the difference between long-term memory and short-term memory in our brains,” Professor Kuncic said.
“If we want to remember something for a long period of time, we really need to keep training our brains to consolidate that, otherwise it just kind of fades away over time.
“One task showed that the nanowire network can store up to seven items in memory at substantially higher than chance levels without reinforcement training and near-perfect accuracy with reinforcement training.”
News
Oceans Are Struggling To Absorb Carbon As Microplastics Flood Their Waters
New research points to an unexpected way plastic pollution may be influencing Earth’s climate system. A recent study suggests that microscopic plastic pollution is reducing the ocean’s capacity to take in carbon dioxide, a [...]
Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine – New book from Frank Boehm
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
New Book! NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Global Health Care Equivalency in the Age of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine and Artificial Intelligence
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
Miller School Researchers Pioneer Nanovanilloid-Based Brain Cooling for Traumatic Injury
A multidisciplinary team at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine has developed a breakthrough nanodrug platform that may prove beneficial for rapid, targeted therapeutic hypothermia after traumatic brain injury (TBI). Their work, published in ACS [...]
COVID-19 still claims more than 100,000 US lives each year
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention researchers report national estimates of 43.6 million COVID-19-associated illnesses and 101,300 deaths in the US during October 2022 to September 2023, plus 33.0 million illnesses and 100,800 deaths [...]
Nanomedicine in 2026: Experts Predict the Year Ahead
Progress in nanomedicine is almost as fast as the science is small. Over the last year, we've seen an abundance of headlines covering medical R&D at the nanoscale: polymer-coated nanoparticles targeting ovarian cancer, Albumin recruiting nanoparticles for [...]
Lipid nanoparticles could unlock access for millions of autoimmune patients
Capstan Therapeutics scientists demonstrate that lipid nanoparticles can engineer CAR T cells within the body without laboratory cell manufacturing and ex vivo expansion. The method using targeted lipid nanoparticles (tLNPs) is designed to deliver [...]
The Brain’s Strange Way of Computing Could Explain Consciousness
Consciousness may emerge not from code, but from the way living brains physically compute. Discussions about consciousness often stall between two deeply rooted viewpoints. One is computational functionalism, which holds that cognition can be [...]
First breathing ‘lung-on-chip’ developed using genetically identical cells
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and AlveoliX have developed the first human lung-on-chip model using stem cells taken from only one person. These chips simulate breathing motions and lung disease in an individual, [...]
Cell Membranes May Act Like Tiny Power Generators
Living cells may generate electricity through the natural motion of their membranes. These fast electrical signals could play a role in how cells communicate and sense their surroundings. Scientists have proposed a new theoretical [...]
This Viral RNA Structure Could Lead to a Universal Antiviral Drug
Researchers identify a shared RNA-protein interaction that could lead to broad-spectrum antiviral treatments for enteroviruses. A new study from the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC), published in Nature Communications, explains how enteroviruses begin reproducing [...]
New study suggests a way to rejuvenate the immune system
Stimulating the liver to produce some of the signals of the thymus can reverse age-related declines in T-cell populations and enhance response to vaccination. As people age, their immune system function declines. T cell [...]
Nerve Damage Can Disrupt Immunity Across the Entire Body
A single nerve injury can quietly reshape the immune system across the entire body. Preclinical research from McGill University suggests that nerve injuries may lead to long-lasting changes in the immune system, and these [...]
Fake Science Is Growing Faster Than Legitimate Research, New Study Warns
New research reveals organized networks linking paper mills, intermediaries, and compromised academic journals Organized scientific fraud is becoming increasingly common, ranging from fabricated research to the buying and selling of authorship and citations, according [...]
Scientists Unlock a New Way to Hear the Brain’s Hidden Language
Scientists can finally hear the brain’s quietest messages—unlocking the hidden code behind how neurons think, decide, and remember. Scientists have created a new protein that can capture the incoming chemical signals received by brain [...]