A novel antibiotic named Clovibactin, extracted from previously uncultivable bacteria, has been found effective against harmful bacteria, including multi-resistant “superbugs”. Clovibactin’s unique mechanism of targeting multiple essential precursor molecules in the bacterial cell wall makes it difficult for bacteria to become resistant to it.
Researchers from Utrecht University, Bonn University (Germany), the German Center for Infection Research (DZIF), Northeastern University of Boston (USA), and the company NovoBiotic Pharmaceuticals (Cambridge, USA) now share the discovery of Clovibactin and its killing mechanism in the scientific journal Cell.
There is an urgent need for new antibiotics
Antimicrobial resistance is a major problem for human health and researchers worldwide are looking for new solutions. “We urgently need new antibiotics to combat bacteria that become increasingly resistant to most clinically used antibiotics,” says Dr. Markus Weingarth, a researcher from the Chemistry Department of Utrecht University.
“Clovibactin is different,” says Weingarth. “Since Clovibactin was isolated from bacteria that could not be grown before, pathogenic bacteria have not seen such an antibiotic before and had no time to develop resistance.”
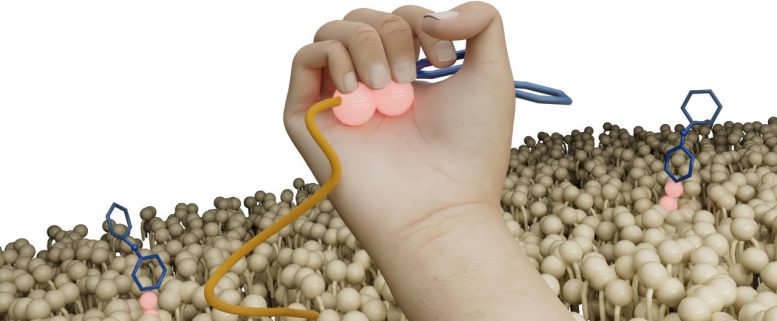
The newly discovered antibiotic Clovibactin uses an unsual cage-like binding motif to tightly wrap around special lipids in bacterial cell membranes. Credit: Markus Weingarth
Antibiotic from bacterial dark matter
Clovibactin was discovered by NovoBiotic Pharmaceuticals, a small US-based early-stage company, and microbiologist Prof. Kim Lewis from Northeastern University, Boston. Earlier, they developed a device that allows the growth of ‘bacterial dark matter’, which are so-called unculturable bacteria. Intriguingly, 99% of all bacteria are ‘unculturable’ and could not be grown in laboratories previously, hence they could not be mined for novel antibiotics. Using the device, called iCHip, the US researchers discovered Clovibactin in a bacterium isolated from sandy soil from North Carolina: E. terrae ssp. Carolina.
In the joint Cell publication, NovoBiotic Pharmaceuticals shows that Clovibactin successfully attacks a broad spectrum of bacterial pathogens. It was also successfully used to treat mice infected with the superbug Staphylococcus aureus.
A broad target spectrum
Clovibactin appears to have an unusual killing mechanism. It targets not just one, but three different precursor molecules that are all essential for the construction of the cell wall, an envelope-like structure that surrounds bacteria. This was discovered by the group of Prof. Tanja Schneider from the University of Bonn in Germany, one of the Cell paper’s co-authors.
Schneider: “The multi-target attack mechanism of Clovibactin blocks bacterial cell wall synthesis simultaneously at different positions. This improves the drug’s activity and substantially increases its robustness to resistance development.”
A cage-like structure
How exactly Clovibactin blocks the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall was unraveled by the team of Dr. Markus Weingarth from Utrecht University. They used a special technique called solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) that allowed them to study Clovibactin’s mechanism under similar conditions as in bacteria.
“Clovibactin wraps around the pyrophosphate like a tightly fitting glove. Like a cage that encloses its target” says Weingarth. This is what gives Clovibactin its name, which is derived from the Greek word “Klouvi”, which means cage. The remarkable aspect of Clovibactin’s mechanism is that it only binds to the immutable pyrophosphate that is common to cell wall precursors, but it ignores that variable sugar-peptide part of the targets. “As Clovibactin only binds to the immutable, conserved part of its targets, bacteria will have a much harder time developing any resistance against it. In fact, we did not observe any resistance to Clovibactin in our studies.”
Fibrils capture the targets
Clovibactin can do even more. Upon binding the target molecules, it self-assembles into large fibrils on the surface of bacterial membranes. These fibrils are stable for a long time and thereby ensure that the target molecules remain sequestered for as long as necessary to kill bacteria.
“Since these fibrils only form on bacterial membranes and not on human membranes, they are presumably also the reason why Clovibactin selectively damages bacterial cells but is not toxic to human cells,” says Weingarth. “Clovibactin hence has potential for the design of improved therapeutics that kill bacterial pathogens without resistance development.”
Reference: “An antibiotic from an uncultured bacterium binds to an immutable target” by Rhythm Shukla, Aaron J. Peoples, Kevin C. Ludwig, Sourav Maity, Maik G.N. Derks, Stefania De Benedetti, Annika M. Krueger, Bram J.A. Vermeulen, Theresa Harbig, Francesca Lavore, Raj Kumar, Rodrigo V. Honorato, Fabian Grein, Kay Nieselt, Yangping Liu, Alexandre M.J.J. Bonvin, Marc Baldus, Ulrich Kubitscheck, Eefjan Breukink, Catherine Achorn and Markus Weingarth, 22 August 2023, Cell.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.07.038
News
Global Nanomaterial Regulation: A Country-by-Country Comparison
Nanomaterials are materials with at least one dimension smaller than 100 nanometres (about 100,000 times thinner than a human hair). Because of their tiny size, they have unique properties that can be useful in [...]
Pandemic Potential: Scientists Discover 3 Hotspots of Deadly Emerging Disease in the US
Virginia Tech researchers discovered six new rodent carriers of hantavirus and identified U.S. hotspots, highlighting the virus’s adaptability and the impact of climate and ecology on its spread. Hantavirus recently drew public attention following reports [...]
Studies detail high rates of long COVID among healthcare, dental workers
Researchers have estimated approximately 8% of Americas have ever experienced long COVID, or lasting symptoms, following an acute COVID-19 infection. Now two recent international studies suggest that the percentage is much higher among healthcare workers [...]
Melting Arctic Ice May Unleash Ancient Deadly Diseases, Scientists Warn
Melting Arctic ice increases human and animal interactions, raising the risk of infectious disease spread. Researchers urge early intervention and surveillance. Climate change is opening new pathways for the spread of infectious diseases such [...]
Scientists May Have Found a Secret Weapon To Stop Pancreatic Cancer Before It Starts
Researchers at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory have found that blocking the FGFR2 and EGFR genes can stop early-stage pancreatic cancer from progressing, offering a promising path toward prevention. Pancreatic cancer is expected to become [...]
Breakthrough Drug Restores Vision: Researchers Successfully Reverse Retinal Damage
Blocking the PROX1 protein allowed KAIST researchers to regenerate damaged retinas and restore vision in mice. Vision is one of the most important human senses, yet more than 300 million people around the world are at [...]
Differentiating cancerous and healthy cells through motion analysis
Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have found that the motion of unlabeled cells can be used to tell whether they are cancerous or healthy. They observed malignant fibrosarcoma [...]
This Tiny Cellular Gate Could Be the Key to Curing Cancer – And Regrowing Hair
After more than five decades of mystery, scientists have finally unveiled the detailed structure and function of a long-theorized molecular machine in our mitochondria — the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier. This microscopic gatekeeper controls how [...]
Unlocking Vision’s Secrets: Researchers Reveal 3D Structure of Key Eye Protein
Researchers have uncovered the 3D structure of RBP3, a key protein in vision, revealing how it transports retinoids and fatty acids and how its dysfunction may lead to retinal diseases. Proteins play a critical [...]
5 Key Facts About Nanoplastics and How They Affect the Human Body
Nanoplastics are typically defined as plastic particles smaller than 1000 nanometers. These particles are increasingly being detected in human tissues: they can bypass biological barriers, accumulate in organs, and may influence health in ways [...]
Measles Is Back: Doctors Warn of Dangerous Surge Across the U.S.
Parents are encouraged to contact their pediatrician if their child has been exposed to measles or is showing symptoms. Pediatric infectious disease experts are emphasizing the critical importance of measles vaccination, as the highly [...]
AI at the Speed of Light: How Silicon Photonics Are Reinventing Hardware
A cutting-edge AI acceleration platform powered by light rather than electricity could revolutionize how AI is trained and deployed. Using photonic integrated circuits made from advanced III-V semiconductors, researchers have developed a system that vastly [...]
A Grain of Brain, 523 Million Synapses, Most Complicated Neuroscience Experiment Ever Attempted
A team of over 150 scientists has achieved what once seemed impossible: a complete wiring and activity map of a tiny section of a mammalian brain. This feat, part of the MICrONS Project, rivals [...]
The Secret “Radar” Bacteria Use To Outsmart Their Enemies
A chemical radar allows bacteria to sense and eliminate predators. Investigating how microorganisms communicate deepens our understanding of the complex ecological interactions that shape our environment is an area of key focus for the [...]
Psychologists explore ethical issues associated with human-AI relationships
It's becoming increasingly commonplace for people to develop intimate, long-term relationships with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. At their extreme, people have "married" their AI companions in non-legally binding ceremonies, and at least two people [...]
When You Lose Weight, Where Does It Actually Go?
Most health professionals lack a clear understanding of how body fat is lost, often subscribing to misconceptions like fat converting to energy or muscle. The truth is, fat is actually broken down into carbon [...]