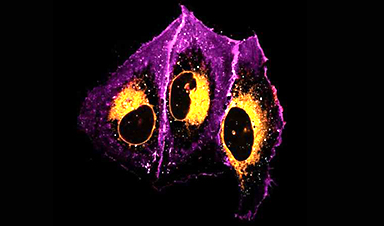
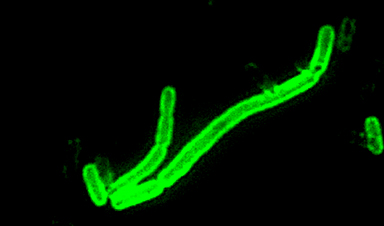
A new drug designed by scientists at Scripps Research can turn the COVID-19 virus into a harbinger of its own doom.
“What’s so neat about this drug is that we’re actually turning the virus against itself,” says senior author Stuart Lipton, MD, Ph.D., the Step Family Endowed Chair and Scripps Research professor. “We’re arming it with little molecular warheads that end up preventing it from infecting our cells; it’s our revenge on the virus.”
Before the COVID-19 pandemic, Lipton and his colleagues had long been studying variations of the drug memantine, which Lipton developed and patented in the 1990s for treating neurological diseases like Alzheimer’s. While memantine originated from an anti-influenza drug used in the 1960s, clinicians began investigating it for additional diseases after they noticed a woman with Parkinson’s symptoms improved when she took the drug for the flu.
“My team had made these antiviral drugs better for the brain, and when COVID-19 emerged, we wondered whether we had also, in the process, made any of them better antivirals,” says Lipton.
Lipton and his team tested a library of compounds similar to memantine in overall structure but covered with additional pharmacological warheads. They pinpointed the drug candidate designated NMT5 as having two key properties: It could recognize and attach to a pore on the surface of SARS-CoV-2, and it could chemically modify human ACE2 using a fragment of nitroglycerin as the warhead. The group realized this could turn the virus into a delivery vehicle for its own demise.
In the new paper, Lipton’s group characterized and tested NMT5 in isolated cells as well as animals. They showed how NMT5 attaches tightly to SARS-CoV-2 viral particles as the viruses move through the body. Then, they revealed the details of how the drug adds a chemical (similar to nitroglycerin) to certain molecules if it gets close enough. When the virus gets near ACE2 to infect a cell, that translates into NMT5 adding a “nitro group” to the receptor. When ACE2 is modified in this way, its structure temporarily shifts—for about 12 hours—so that the SARS-CoV-2 virus can no longer bind to it to cause infection.
In cell culture experiments testing how well the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 can attach to human ACE2 receptors, the drug prevented 95% of viral binding. In hamsters with COVID-19, NMT5 decreased virus levels by 100-fold, eliminated blood vessel damage in the animals’ lungs, and ameliorated inflammation. The drug also showed effectiveness against nearly a dozen other variants of COVID-19, including alpha, beta, gamma and delta strains.
Most anti-viral drugs work by directly blocking part of a virus—which can pressure the virus to evolve resistance to the drug. Since NMT5 is only using the virus as a carrier, the researchers think the drug is likely to be effective against many other variants of SARS-CoV-2.
“We expect this compound would continue to be effective even as new variants emerge, because it doesn’t rely on attacking parts of the virus that commonly mutate,” says Chang-ki Oh, a senior staff scientist and first author of the new paper.
Though they have only studied the compound in animal models, the team is now making a version of the drug to evaluate for human use, while carrying out additional safety and effectiveness trials in animals.
“These exciting findings suggest a new avenue for drug development that requires drug combinations for effective pandemic preparedness,” says co-author Arnab Chatterjee, Ph.D.
In addition to Lipton, Oh and Chatterjee, authors of the new paper are Tomohiro Nakamura, Nathan Beutler, Xu Zhang, Juan Piña-Crespo, Maria Talantova, Swagata Ghatak, Dorit Trudler, Lauren N. Carnevale, Scott R. McKercher, Malina A. Bakowski, Jolene K. Diedrich, Amanda J. Roberts, Ashley K. Woods, Victor Chi, Anil K. Gupta, Namir Shaabani, Hejun Liu, Ian A. Wilson, Dennis R. Burton, John R. Yates III and Thomas F. Rogers of Scripps Research; Mia A. Rosenfeld, Fiona L. Kearns, Lorenzo Casalino and Rommie E. Amaro of UCSD; and Cyrus Becker of EuMentis Therapeutics, Inc.
News
Overworked Brain Cells May Hold the Key to Parkinson’s
Scientists at Gladstone Institutes uncovered a surprising reason why dopamine-producing neurons, crucial for smooth body movements, die in Parkinson’s disease. In mice, when these neurons were kept overactive for weeks, they began to falter, [...]
Old tires find new life: Rubber particles strengthen superhydrophobic coatings against corrosion
Development of highly robust superhydrophobic anti-corrosion coating using recycled tire rubber particles. Superhydrophobic materials offer a strategy for developing marine anti-corrosion materials due to their low solid-liquid contact area and low surface energy. However, [...]
This implant could soon allow you to read minds
Mind reading: Long a science fiction fantasy, today an increasingly concrete scientific goal. Researchers at Stanford University have succeeded in decoding internal language in real time thanks to a brain implant and artificial intelligence. [...]
A New Weapon Against Cancer: Cold Plasma Destroys Hidden Tumor Cells
Cold plasma penetrates deep into tumors and attacks cancer cells. Short-lived molecules were identified as key drivers. Scientists at the Leibniz Institute for Plasma Science and Technology (INP), working with colleagues from Greifswald University Hospital and [...]
This Common Sleep Aid May Also Protect Your Brain From Alzheimer’s
Lemborexant and similar sleep medications show potential for treating tau-related disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease. New research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis shows that a commonly used sleep medication can restore normal sleep patterns and [...]
Sugar-Coated Nanoparticles Boost Cancer Drug Efficacy
A team of researchers at the University of Mississippi has discovered that coating cancer treatment carrying nanoparticles in a sugar-like material increases their treatment efficacy. They reported their findings in Advanced Healthcare Materials. Over a tenth of breast [...]
Nanoparticle-Based Vaccine Shows Promise in Fighting Cancer
In a study published in OncoImmunology, researchers from the German Cancer Research Center and Heidelberg University have created a therapeutic vaccine that mobilizes the immune system to target cancer cells. The researchers demonstrated that virus peptides combined [...]
Quantitative imaging method reveals how cells rapidly sort and transport lipids
Lipids are difficult to detect with light microscopy. Using a new chemical labeling strategy, a Dresden-based team led by André Nadler at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics (MPI-CBG) and [...]
Ancient DNA reveals cause of world’s first recorded pandemic
Scientists have confirmed that the Justinian Plague, the world’s first recorded pandemic, was caused by Yersinia pestis, the same bacterium behind the Black Death. Dating back some 1,500 years and long described in historical texts but [...]
“AI Is Not Intelligent at All” – Expert Warns of Worldwide Threat to Human Dignity
Opaque AI systems risk undermining human rights and dignity. Global cooperation is needed to ensure protection. The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) has changed how people interact, but it also poses a global risk to human [...]
Nanomotors: Where Are They Now?
First introduced in 2004, nanomotors have steadily advanced from a scientific curiosity to a practical technology with wide-ranging applications. This article explores the key developments, recent innovations, and major uses of nanomotors today. A [...]
Study Finds 95% of Tested Beers Contain Toxic “Forever Chemicals”
Researchers found PFAS in 95% of tested beers, with the highest levels linked to contaminated local water sources. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), better known as forever chemicals, are gaining notoriety for their ability [...]
Long COVID Symptoms Are Closer To A Stroke Or Parkinson’s Disease Than Fatigue
When most people get sick with COVID-19 today, they think of it as a brief illness, similar to a cold. However, for a large number of people, the illness doesn't end there. The World [...]
The world’s first AI Hospital, developed in China is transforming healthcare
Artificial Intelligence and its developments have had a revolutionary impact on society, and healthcare is not an exception. China has made massive strides in AI integrated healthcare, and continues to do so as AI [...]
Scientists Rewire Immune Cells To Supercharge Cancer-Fighting Power
Blocking a single protein boosts T cell metabolism and tumor-fighting strength. The discovery could lead to next-generation cancer immunotherapies. Scientists have identified a strategy to greatly enhance the cancer-fighting abilities of the immune system’s [...]
Scientists Discover 20 Percent of Human DNA Comes from a Mysterious Ancestor
Humans carry a complex genetic history that continues to reveal surprises. Scientists have found that 20% of our DNA may come from a mysterious ancestor, according to WP Tech. This discovery changes how we understand [...]