The University of Warwick and QuantIC researchers at Heriot Watt University and the University of Glasgow performed a study in optical sensing, which could considerably enhance the precision of measuring nanoscopic structures.
QuantIC is part of the UK National Quantum Technologies Program and is the UK Quantum Technology Hub in Quantum Enhanced Imaging.
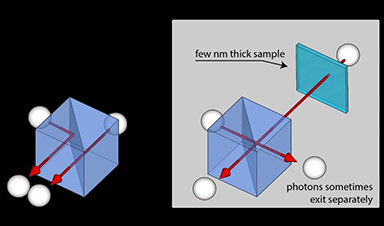
The researchers used pairs of photons, which are essential components of energy that make up light, to develop a method that determines the thickness of objects that are less than a 100,000th of the width of a human hair.
In the latest technique, two near-identical photons are fired onto a component called a beamsplitter and their subsequent behavior is monitored – with some 30,000 photons detected every second, and 500bn in use during an entire experiment.
Identical photons tend to ‘buddy up’ and continue to travel together – the outcome of a mild quantum interference effect. As a result of this, the team’s newly developed setup provides the same stability and precision as current one-photon methods that, owing to the equipment needed, are more expensive.
Providing a host of promising applications, such as research to better understand DNA, cell membranes, and even quality control for nanoscopic 2D materials of one atom’s thickness, for example, graphene, the latest study represents a major improvement on current two-photon techniques with up to 100 times better resolution.
Image Credit: University of Warwick
News This Week
5 Key Facts About Nanoplastics and How They Affect the Human Body
Nanoplastics are typically defined as plastic particles smaller than 1000 nanometers. These particles are increasingly being detected in human tissues: they can bypass biological barriers, accumulate in organs, and may influence health in ways [...]
Measles Is Back: Doctors Warn of Dangerous Surge Across the U.S.
Parents are encouraged to contact their pediatrician if their child has been exposed to measles or is showing symptoms. Pediatric infectious disease experts are emphasizing the critical importance of measles vaccination, as the highly [...]
AI at the Speed of Light: How Silicon Photonics Are Reinventing Hardware
A cutting-edge AI acceleration platform powered by light rather than electricity could revolutionize how AI is trained and deployed. Using photonic integrated circuits made from advanced III-V semiconductors, researchers have developed a system that vastly [...]
A Grain of Brain, 523 Million Synapses, Most Complicated Neuroscience Experiment Ever Attempted
A team of over 150 scientists has achieved what once seemed impossible: a complete wiring and activity map of a tiny section of a mammalian brain. This feat, part of the MICrONS Project, rivals [...]
The Secret “Radar” Bacteria Use To Outsmart Their Enemies
A chemical radar allows bacteria to sense and eliminate predators. Investigating how microorganisms communicate deepens our understanding of the complex ecological interactions that shape our environment is an area of key focus for the [...]
Psychologists explore ethical issues associated with human-AI relationships
It's becoming increasingly commonplace for people to develop intimate, long-term relationships with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. At their extreme, people have "married" their AI companions in non-legally binding ceremonies, and at least two people [...]
When You Lose Weight, Where Does It Actually Go?
Most health professionals lack a clear understanding of how body fat is lost, often subscribing to misconceptions like fat converting to energy or muscle. The truth is, fat is actually broken down into carbon [...]
How Everyday Plastics Quietly Turn Into DNA-Damaging Nanoparticles
The same unique structure that makes plastic so versatile also makes it susceptible to breaking down into harmful micro- and nanoscale particles. The world is saturated with trillions of microscopic and nanoscopic plastic particles, some smaller [...]











Leave A Comment