| A research team headed by chemist Prof Bart Jan Ravoo and biochemist Prof Volker Gerke has designed nanocontainers made of sugar and protein components. These containers are taken up by cells through natural processes and can thereby transport substances that normally cannot penetrate the cell membrane – such as drugs or labelled substances for the investigation of cell functions – into cells. | |
| The study was published in Advanced Science (“Biodegradable and Dual-Responsive Polypeptide-Shelled Cyclodextrin-Containers for Intracellular Delivery of Membrane-Impermeable Cargo”). | |
 |
|
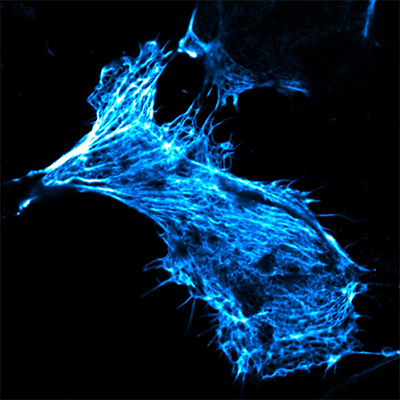
| Living human cancer cell in cell culture, its actin skeleton stained with fluorescent phalloidin. This toxic substance was only able to enter the cell by means of the newly developed nanocontainers. (Image: Kudruk & Pottanam Chali et al./Adv Sci 2021 (modified colours)) | |
| Nanocontainers can transport substances into cells where they can then take effect. This is the method used in, for example, the mRNA vaccines currently being employed against Covid-19 as well as certain cancer drugs. In research, similar transporters can also be used to deliver labelled substances into cells in order to study basic cellular functions. | |
| To take advantage of their full potential, scientists are conducting intensive research into how nanocontainers interact with biological environments and how they have to be chemically constructed to deliver cargo into cells in the gentlest and most controllable way possible. | |
| Scientists at the University of Münster have recently developed a new type of nanocontainer that is constructed entirely from biological components. Unlike other cargo transporters, these are not based on lipids but on sugar compounds which are sealed with a shell of protein structures – so-called polypeptides – the thickness of which is precisely tailored. | |
| “We do produce the components of our nanocontainers synthetically, but they are taken up by cells and – due to the overall structure we have developed – also degraded by them just like naturally occurring substances,” explains chemist Prof Bart Jan Ravoo. | |
| “For the degradation of the container shell inside the cell, we make use of two naturally occurring mechanisms – as a result, the transported substances are released rapidly, as soon as they arrive in the cell,” adds biochemist Prof Volker Gerke. | |
| The scientists want to use the tiny nanocontainers, which are about 150 nanometers in diameter, to load cells with labelled biologically relevant lipids that can be used to study transport processes occurring within the cell membrane. In addition, they plan to further develop the chemical design of the containers in such a way that they are, for example, only taken up by certain types of cells or only release their cargo when stimulated by external light. | |
| In the future, transport systems built from sugar and protein components might also be suitable for applications in living organisms to deliver drugs specifically into certain tissues and cells. | |
| Details on methods and results: | |
Bioinspired materials organize themselves, forming cargo-carrying containers |
|
| To synthesize the new cargo transporters, the scientists used sugar compounds (modified cyclodextrins) that are similar in structure – and thus behaviour – to certain lipids naturally found in every cell. Similar to the protective cell membrane lipids, the sugar structures arrange themselves, forming a shell in which they enclose the substances to be transported. However, because the resulting container is still leaky and would lose its cargo over time, the scientists added protein structures (polypeptides) that form a sealing layer around the container. | |
| “To test how thick the sealing layer needed to be, we varied the length of the peptide sequences and tailored them so that the containers stably encapsulated their cargo,” explains Sharafudheen Pottanam Chali, a chemistry doctoral student and one of the study’s two lead authors. | |
Nanocontainers that use a natural pathway into cells |
|
| In the next step, the scientists investigated whether and how the newly developed nanocontainers were taken up by cells. Their hypothesis was that this happens via so-called endocytosis. In this process, the cells internalize a part of their cell membrane and pinch it off, creating small vesicles called endosomes in which extracellular material is transported into the cell. To test this, the scientists used a sugar compound (dextran) known to be taken up by endocytosis. They treated their cell cultures with red fluorescent dextran and, at the same time, added nanocontainers filled with a green fluorescent cargo (pyranine). | |
| “In the fluorescence microscope, it became visible that both substances were taken up into the cells equally and their fluorescence overlapped visibly – therefore we could conclude that the nanocontainers, just like the dextran, were efficiently taken up by the cells through the endosomal transport process,” explains Sergej Kudruk, a biochemistry doctoral student and also a lead author of the study. | |
| The scientists confirmed this for two different cell types – human blood vessel cells and cancer cells. | |
Container shell is degraded by enzymes in the cells’ endosomes |
|
| Conditions inside the endosomes differ from those of the cellular environment, something which the scientists already were considering when designing their nanocontainers. They constructed the containers in such a way that the altered environment in the endosomes destabilizes and partially degrades the polypeptide shell – the nanocontainers thus become leaky and release their cargo into the inside of the cell. | |
| “When the containers are taken up into endosomes, two types of enzymes, which we knew to be present in endosomes and which can contribute to the degradation of the shell at specific sites, come into play,” explains Sergej Kudruk. | |
| “So-called reductases degrade the disulfide bridges that were previously established to crosslink the peptide molecules of our nanocontainers – in addition, peptidases cleave the peptide molecules themselves,” adds Sharafudheen Pottanam Chali. | |
| The scientists also tested the degradability of the container shell outside the cell. To do so, they loaded the containers with a fluorescent dye and simulated part of the complex endosomal microenvironment by using the enzyme trypsin as well as reducing agents. After treatment, the dye leaked out immediately. |
News
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]
Analyzing Darwin’s specimens without opening 200-year-old jars
Scientists have successfully analyzed Charles Darwin's original specimens from his HMS Beagle voyage (1831 to 1836) to the Galapagos Islands. Remarkably, the specimens have been analyzed without opening their 200-year-old preservation jars. Examining 46 [...]
Scientists discover natural ‘brake’ that could stop harmful inflammation
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have uncovered a key mechanism that helps the body switch off inflammation—a breakthrough that could lead to new treatments for chronic diseases affecting millions worldwide. Inflammation is the [...]
A Forgotten Molecule Could Revive Failing Antifungal Drugs and Save Millions of Lives
Scientists have uncovered a way to make existing antifungal drugs work again against deadly, drug-resistant fungi. Fungal infections claim millions of lives worldwide each year, and current medical treatments are failing to keep pace. [...]






















