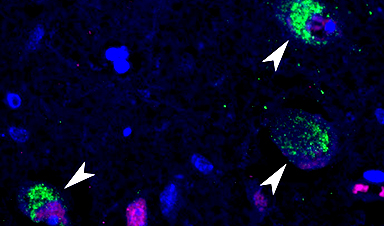
Autopsies of 44 people who died from COVID-19 in the first year of the pandemic showed researchers that disease-causing SARS-CoV-2 virus spread throughout the body – beyond just a respiratory disease – and remained in tissue for months. The study, from the National Institutes of Health and published in Nature, helped scientists broaden their perspectives on where SARS-CoV-2 could cause infection and persist, including the brain. The work also supported the rationale for a clinical trial evaluating the antiviral drug Paxlovid for the treatment of post-acute sequelae of COVID-19, also known as Long COVID.
Findings from the autopsies, which took place between April 2020 and March 2021, confirmed that SARS-CoV-2 primarily infected and damaged the airway and lungs. But scientists also found virus fragments (viral RNA) in 79 of 85 body locations, with some virus found up to 230 days after patient’s symptoms began. Scientists found virus in cardiovascular, lymphoid, gastrointestinal, renal, endocrine, reproductive, muscle, brain and other tissue – although none of these areas sustained significant inflammation compared to what they found in the respiratory tract. Scientists from NIH’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and Clinical Center led the work, closely collaborating with National Cancer Institute (NCI) pathologists, four other NIH institutes, the University of Maryland, and Maryland health care facilities in Salisbury and Towson.
“We show SARS-CoV-2 disseminates across the human body and brain early in infection at high levels and provide evidence of virus replication at multiple extrapulmonary sites during the first two weeks following symptom onset,” their study states. Virus can spread throughout the body and viral RNA may remain detectable for months even in cases with mild or no symptoms, they say.
Senior study author Dr. Daniel Chertow said prior to the work, “the thinking in the field was that SARS-CoV-2 was predominantly a respiratory virus.” Finding the viral fragments in tissue throughout the body – and sharing those findings with colleagues a year ago – helped scientists explore a relationship between the viral fragments and Long COVID.
Long COVID gets its name from the persistent symptoms some people experience after having COVID-19; symptoms can be debilitating, and the cause is not known. Though the study in Nature did not specifically explore Long COVID, finding the viral RNA throughout the body raised speculation that those fragments might contribute to the persistent symptoms, according to Dr. Chertow. Treating people with an effective COVID-19 antiviral such as Paxlovid could, therefore, eliminate the persistent symptoms.
The Paxlovid trial, now underway at Duke University, is part of the NIH-funded RECOVER project – Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery – and includes an extension of the autopsy work, according Dr. Stephen Hewitt of NCI, who collaborated on the paper in Nature, and serves on a steering committee for the RECOVER project.
He said one branch of RECOVER includes tissue pathology studies, and obtaining material from autopsies is in progress; these autopsies include people who both were vaccinated and infected with variants of concern – data not available in the earlier study that Dr. Chertow’s group led.
“We’re hoping to replicate the data on viral persistence and study the relationship with Long COVID,” Dr. Hewitt said, adding that the project is scheduled to last four years. “Less than a year in we have about 85 cases, and we are working to expand these efforts.”
News
We May Never Know if AI Is Conscious, Says Cambridge Philosopher
As claims about conscious AI grow louder, a Cambridge philosopher argues that we lack the evidence to know whether machines can truly be conscious, let alone morally significant. A philosopher at the University of [...]
AI Helped Scientists Stop a Virus With One Tiny Change
Using AI, researchers identified one tiny molecular interaction that viruses need to infect cells. Disrupting it stopped the virus before infection could begin. Washington State University scientists have uncovered a method to interfere with a key [...]
Deadly Hospital Fungus May Finally Have a Weakness
A deadly, drug-resistant hospital fungus may finally have a weakness—and scientists think they’ve found it. Researchers have identified a genetic process that could open the door to new treatments for a dangerous fungal infection [...]
Fever-Proof Bird Flu Variant Could Fuel the Next Pandemic
Bird flu viruses present a significant risk to humans because they can continue replicating at temperatures higher than a typical fever. Fever is one of the body’s main tools for slowing or stopping viral [...]
What could the future of nanoscience look like?
Society has a lot to thank for nanoscience. From improved health monitoring to reducing the size of electronics, scientists’ ability to delve deeper and better understand chemistry at the nanoscale has opened up numerous [...]
Scientists Melt Cancer’s Hidden “Power Hubs” and Stop Tumor Growth
Researchers discovered that in a rare kidney cancer, RNA builds droplet-like hubs that act as growth control centers inside tumor cells. By engineering a molecular switch to dissolve these hubs, they were able to halt cancer [...]
Platelet-inspired nanoparticles could improve treatment of inflammatory diseases
Scientists have developed platelet-inspired nanoparticles that deliver anti-inflammatory drugs directly to brain-computer interface implants, doubling their effectiveness. Scientists have found a way to improve the performance of brain-computer interface (BCI) electrodes by delivering anti-inflammatory drugs directly [...]
After 150 years, a new chapter in cancer therapy is finally beginning
For decades, researchers have been looking for ways to destroy cancer cells in a targeted manner without further weakening the body. But for many patients whose immune system is severely impaired by chemotherapy or radiation, [...]
Older chemical libraries show promise for fighting resistant strains of COVID-19 virus
SARS‑CoV‑2, the virus that causes COVID-19, continues to mutate, with some newer strains becoming less responsive to current antiviral treatments like Paxlovid. Now, University of California San Diego scientists and an international team of [...]
Lower doses of immunotherapy for skin cancer give better results, study suggests
According to a new study, lower doses of approved immunotherapy for malignant melanoma can give better results against tumors, while reducing side effects. This is reported by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in the Journal of the National [...]
Researchers highlight five pathways through which microplastics can harm the brain
Microplastics could be fueling neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, with a new study highlighting five ways microplastics can trigger inflammation and damage in the brain. More than 57 million people live with dementia, [...]
Tiny Metal Nanodots Obliterate Cancer Cells While Largely Sparing Healthy Tissue
Scientists have developed tiny metal-oxide particles that push cancer cells past their stress limits while sparing healthy tissue. An international team led by RMIT University has developed tiny particles called nanodots, crafted from a metallic compound, [...]
Gold Nanoclusters Could Supercharge Quantum Computers
Researchers found that gold “super atoms” can behave like the atoms in top-tier quantum systems—only far easier to scale. These tiny clusters can be customized at the molecular level, offering a powerful, tunable foundation [...]
A single shot of HPV vaccine may be enough to fight cervical cancer, study finds
WASHINGTON -- A single HPV vaccination appears just as effective as two doses at preventing the viral infection that causes cervical cancer, researchers reported Wednesday. HPV, or human papillomavirus, is very common and spread [...]
New technique overcomes technological barrier in 3D brain imaging
Scientists at the Swiss Light Source SLS have succeeded in mapping a piece of brain tissue in 3D at unprecedented resolution using X-rays, non-destructively. The breakthrough overcomes a long-standing technological barrier that had limited [...]
Scientists Uncover Hidden Blood Pattern in Long COVID
Researchers found persistent microclot and NET structures in Long COVID blood that may explain long-lasting symptoms. Researchers examining Long COVID have identified a structural connection between circulating microclots and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). The [...]