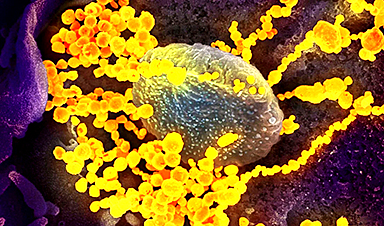
Omicron subvariant BA.2 – which was dominant worldwide early this year, including in Hong Kong – replicates more swiftly than other strains and causes faster programmed cell death in human brains, a new study has found.
Scientists from the University of Hong Kong and Chinese University of Hong Kong exposed brain cells developed in laboratories to Omicron subvariants, as well as the original coronavirus strain from the Wuhan outbreak and the Delta strain for comparison, to assess their neurological impact.
The study findings were published in a letter in peer-reviewed science journal Nature on November 20.
It is not the first study into neurological problems – such as disturbed brain function, inflammation and dementia – caused by Covid-19.
But the Hong Kong researchers aimed to find out if, and how, Omicron subvariants behaved differently in terms of impact on brain cells compared to earlier strains.
To do this, the scientists developed cells in the laboratory that mimicked human brain cells and challenged them with the Omicron variants BA.1 and BA.2, as well as the earlier Delta variant and the original, or wild-type, strain detected in Wuhan at the start of the pandemic.
They found that BA.2 replicated much faster than other strains in experiments on in vitro forebrain and midbrain cells. BA.2 was also found to induce a lower level of interferon – a protein released by the human body as a defence mechanism against viral infections – than other strains.
While all variants induced programmed cell death upon infection of brain cells, BA.2 “triggered a substantially higher magnitude” of programmed cell death compared with other strains in the experiments, the scientists said.
They also included two new Omicron variants – BA.4.1 and BA.5.2 – to test their ability to replicate in human brain cells. They found that BA.5.2, a close relative of BA.5 which has been dominant in Europe in recent months, replicated much faster than BA.4.1 in human brain cells.
Both BA.4.1 and BA.5.2 are offshoots of BA.2.
BA.5 and BA.4 have overtaken BA.2 in recent months, but BQ.1 – a descendant of BA.5 – is now the dominant strain in the United States and some European countries.
The scientists described the findings as “alarming” and called for further research on the neurological impact of Omicron variants.
“While most patients survived the infection, post-Covid-19 sequelae, including neurological manifestations, are common,” they wrote.
“The increased efficiency of BA.2 to replicate and cause apoptosis [programmed cell death] in the brain organoids is alarming, indicating that the long-term consequence of BA.2 infection in the central nervous system (CNS) should be closely monitored.”
Previous studies have suggested that neurological complications can cause long-Covid symptoms such as loss of taste and smell, impaired concentration, fatigue, pain and sleep disorders.
News
AI Unveils Hidden Nanoparticles – A Breakthrough in Early Disease Detection
Deep Nanometry (DNM) is an innovative technique combining high-speed optical detection with AI-driven noise reduction, allowing researchers to find rare nanoparticles like extracellular vesicles (EVs). Since EVs play a role in disease detection, DNM [...]
Inhalable nanoparticles could help treat chronic lung disease
Nanoparticles designed to release antibiotics deep inside the lungs reduced inflammation and improved lung function in mice with symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By Grace Wade Delivering medication to the lungs with inhalable nanoparticles [...]
New MRI Study Uncovers Hidden Lung Abnormalities in Children With Long COVID
Long COVID is more than just lingering symptoms—it may have a hidden biological basis that standard medical tests fail to detect. A groundbreaking study using advanced MRI technology has uncovered significant lung abnormalities in [...]
AI Struggles with Abstract Thought: Study Reveals GPT-4’s Limits
While GPT-4 performs well in structured reasoning tasks, a new study shows that its ability to adapt to variations is weak—suggesting AI still lacks true abstract understanding and flexibility in decision-making. Artificial Intelligence (AI), [...]
Turning Off Nerve Signals: Scientists Develop Promising New Pancreatic Cancer Treatment
Pancreatic cancer reprograms nerve cells to fuel its growth, but blocking these connections can shrink tumors and boost treatment effectiveness. Pancreatic cancer is closely linked to the nervous system, according to researchers from the [...]
New human antibody shows promise for Ebola virus treatment
New research led by scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) reveals the workings of a human antibody called mAb 3A6, which may prove to be an important component for Ebola virus therapeutics. [...]
Early Alzheimer’s Detection Test – Years Before Symptoms Appear
A new biomarker test can detect early-stage tau protein clumping up to a decade before it appears on brain scans, improving early Alzheimer’s diagnosis. Unlike amyloid-beta, tau neurofibrillary tangles are directly linked to cognitive decline. Years [...]
New mpox variant can spread rapidly across borders
International researchers, including from DTU National Food Institute, warn that the ongoing mpox outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) has the potential to spread across borders more rapidly. The mpox virus [...]
How far would you trust AI to make important decisions?
From tailored Netflix recommendations to personalized Facebook feeds, artificial intelligence (AI) adeptly serves content that matches our preferences and past behaviors. But while a restaurant tip or two is handy, how comfortable would you [...]
Can AI Really Think? Research Reveals Gaps in Logical Execution
While AI models can break down problems into structured steps, new research reveals they still fail at basic arithmetic and fact-checking—raising questions about their true reasoning abilities. Large Language Models (LLMs) have become indispensable [...]
Scientists Just Made Cancer Radiation Therapy Smarter, Safer, and More Precise
Scientists at UC San Francisco have developed a revolutionary cancer treatment that precisely targets tumors with radiation while sparing healthy tissues. By using a KRAS-targeting drug to mark cancer cells and attaching a radioactive [...]
Superbugs Are Losing to Science, Light, and a Little Spice
Texas A&M researchers have found that curcumin, when activated by light, can weaken antibiotic-resistant bacteria, restoring the effectiveness of conventional antibiotics. Curcumin: A Surprising Ally Against Superbugs In 2017, a woman admitted to a [...]
New Research Shatters the Perfect Pitch Myth
For decades, people believed absolute pitch was an exclusive ability granted only to those with the right genetics or early music training. But new research from the University of Surrey proves otherwise. It’s been [...]
Why Some Drinkers Suffer Devastating Liver Damage While Others Don’t
A study from Keck Medicine of USC found that heavy drinkers with diabetes, high blood pressure, or a large waistline are up to 2.4 times more likely to develop advanced liver disease. These conditions may amplify [...]
“Good” Cholesterol Could Be Bad for Your Eyes – New Study Raises Concerns
‘Good’ cholesterol may be linked to an increased risk of glaucoma in individuals over 55, while, paradoxically, ‘bad’ cholesterol may be associated with a lower risk. These findings challenge conventional beliefs about factors that [...]
Reawakening Dormant Nerve Cells: Groundbreaking Neurotechnology Restores Motor Function
A new electrical stimulation therapy for spinal muscle atrophy (SMA) has shown promise in reactivating motor neurons and improving movement. In a pilot clinical trial, three patients who received spinal cord stimulation for one [...]