A study in Scientific Reports evaluated a photoacoustic polydopamine-indocyanine green (PDA-ICG) nanoprobe for detecting senescent cells. Senescent cells play a role in tumor progression and therapeutic resistance, with potential adverse effects such as inflammation and tissue disruption. The PDA-ICG nanoprobe offers a method for identifying these cells, with implications for cancer diagnostics and treatment.
Background
Cellular senescence is a stable cell cycle arrest triggered by stressors such as DNA damage, oxidative stress, and oncogenic signaling. Senescent cells produce pro-inflammatory cytokines, growth factors, and proteases, collectively known as the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP).
This phenomenon contributes to tumor progression and age-related diseases. Accurately identifying and visualizing these cells in vivo is crucial for understanding their role in cancer biology and developing targeted therapies.
Traditional methods for detecting senescent cells, such as β-galactosidase staining and immunohistochemistry, have limitations in terms of specificity and sensitivity. The introduction of advanced imaging techniques, particularly those utilizing nanoprobes, offers a promising avenue for enhancing the detection of senescent cells.
The PDA-ICG nanoprobe combines the photothermal properties of polydopamine with the fluorescence of indocyanine green, enabling both photoacoustic imaging and fluorescence imaging. This dual functionality is expected to improve the visualization of senescent cells.
The Current Study
The study used experimental techniques to evaluate the performance of the PDA-ICG nanoprobe. Human cancer cell lines, A549 and SK-MEL-103, were cultured and treated with varying concentrations of PDA-ICG to assess cell viability and nanoprobe internalization.
The MTS assay measured cell viability after treatment, and flow cytometry assessed nanoprobe internalization in live cells. After treatment, cells were washed to remove excess probes and stained with DAPI for flow cytometric analysis. Data were processed using FlowJo software to identify live, single-cell populations with internalized nanoprobe.
Cells were treated with chemotherapeutic agents, cisplatin and palbociclib, for a specified duration. After drug removal, the cells were stained with β-galactosidase to identify senescent cells. RNA extraction and quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) were performed to measure the expression levels of senescence-associated genes.
Western blotting was conducted to analyze protein expression related to senescence, including p21 and pRb. Confocal microscopy was utilized to visualize the cellular localization of the PDA-ICG nanoprobe and assess its potential for imaging senescent cells.
Results and Discussion
The results showed that the PDA-ICG nanoprobe was successfully internalized into cancer cells, with flow cytometry confirming significantly higher uptake in treated cells than controls. The MTS assay indicated no adverse effects on cell viability at the tested concentrations, supporting its potential for safe in vivo application.
The study also found that treatment with cisplatin and palbociclib successfully induced senescence in the respective cell lines, as evidenced by increased β-galactosidase activity. The expression of senescence-associated genes was significantly elevated in treated cells, further confirming the induction of senescence.
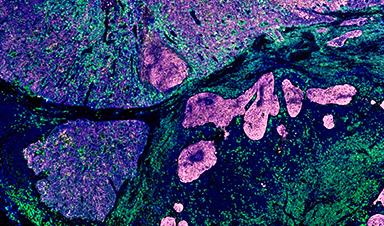
Confocal microscopy highlighted the PDA-ICG nanoprobe’s imaging capabilities, revealing distinct localization patterns within the cells. The nanoprobe’s dual imaging modality allowed for more precise visualization of senescent cells than traditional methods. The findings suggest that the PDA-ICG nanoprobe could serve as a valuable tool for studying the dynamics of senescence in cancer and other diseases.
The ability to visualize senescent cells in real time may facilitate the development of targeted therapies that eliminate these cells from the tumor microenvironment, potentially improving patient outcomes.
Conclusion
The study successfully demonstrated the utility of the PDA-ICG nanoprobe for detecting senescent cells in cancer. Combining the advantages of photoacoustic and fluorescence imaging, this innovative approach offers a promising strategy for enhancing the visualization of senescence in vivo. The findings underscore the importance of accurately identifying senescent cells in the context of cancer biology and therapeutic interventions.
Future research should focus on optimizing the nanoprobe for clinical applications and exploring its potential in various cancer models. The ability to monitor senescence dynamically could lead to significant advancements in cancer diagnostics and treatment, ultimately contributing to improved patient care and outcomes.
Journal Reference
Hartono, M., et al. (2024). Photoacoustic polydopamine-indocyanine green (PDA-ICG) nanoprobe for detection of senescent cells. Scientific Reports. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-79667-7, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-79667-7
News
The Secret “Radar” Bacteria Use To Outsmart Their Enemies
A chemical radar allows bacteria to sense and eliminate predators. Investigating how microorganisms communicate deepens our understanding of the complex ecological interactions that shape our environment is an area of key focus for the [...]
Psychologists explore ethical issues associated with human-AI relationships
It's becoming increasingly commonplace for people to develop intimate, long-term relationships with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. At their extreme, people have "married" their AI companions in non-legally binding ceremonies, and at least two people [...]
When You Lose Weight, Where Does It Actually Go?
Most health professionals lack a clear understanding of how body fat is lost, often subscribing to misconceptions like fat converting to energy or muscle. The truth is, fat is actually broken down into carbon [...]
How Everyday Plastics Quietly Turn Into DNA-Damaging Nanoparticles
The same unique structure that makes plastic so versatile also makes it susceptible to breaking down into harmful micro- and nanoscale particles. The world is saturated with trillions of microscopic and nanoscopic plastic particles, some smaller [...]
AI Outperforms Physicians in Real-World Urgent Care Decisions, Study Finds
The study, conducted at the virtual urgent care clinic Cedars-Sinai Connect in LA, compared recommendations given in about 500 visits of adult patients with relatively common symptoms – respiratory, urinary, eye, vaginal and dental. [...]
Challenging the Big Bang: A Multi-Singularity Origin for the Universe
In a study published in the journal Classical and Quantum Gravity, Dr. Richard Lieu, a physics professor at The University of Alabama in Huntsville (UAH), which is a part of The University of Alabama System, suggests that [...]
New drug restores vision by regenerating retinal nerves
Vision is one of the most crucial human senses, yet over 300 million people worldwide are at risk of vision loss due to various retinal diseases. While recent advancements in retinal disease treatments have [...]
Shingles vaccine cuts dementia risk by 20%, new study shows
A shingles shot may do more than prevent rash — it could help shield the aging brain from dementia, according to a landmark study using real-world data from the UK. A routine vaccine could [...]
AI Predicts Sudden Cardiac Arrest Days Before It Strikes
AI can now predict deadly heart arrhythmias up to two weeks in advance, potentially transforming cardiac care. Artificial intelligence could play a key role in preventing many cases of sudden cardiac death, according to [...]
NanoApps Medical is a Top 20 Feedspot Nanotech Blog
There is an ocean of Nanotechnology news published every day. Feedspot saves us a lot of time and we recommend it. We have been using it since 2018. Feedspot is a freemium online RSS [...]
This Startup Says It Can Clean Your Blood of Microplastics
This is a non-exhaustive list of places microplastics have been found: Mount Everest, the Mariana Trench, Antarctic snow, clouds, plankton, turtles, whales, cattle, birds, tap water, beer, salt, human placentas, semen, breast milk, feces, testicles, [...]
New Blood Test Detects Alzheimer’s and Tracks Its Progression With 92% Accuracy
The new test could help identify which patients are most likely to benefit from new Alzheimer’s drugs. A newly developed blood test for Alzheimer’s disease not only helps confirm the presence of the condition but also [...]
The CDC buried a measles forecast that stressed the need for vaccinations
This story was originally published on ProPublica, a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive our biggest stories as soon as they’re published. ProPublica — Leaders at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [...]
Light-Driven Plasmonic Microrobots for Nanoparticle Manipulation
A recent study published in Nature Communications presents a new microrobotic platform designed to improve the precision and versatility of nanoparticle manipulation using light. Led by Jin Qin and colleagues, the research addresses limitations in traditional [...]
Cancer’s “Master Switch” Blocked for Good in Landmark Study
Researchers discovered peptides that permanently block a key cancer protein once thought untreatable, using a new screening method to test their effectiveness inside cells. For the first time, scientists have identified promising drug candidates [...]
AI self-cloning claims: A new frontier or a looming threat?
Chinese scientists claim that some AI models can replicate themselves and protect against shutdown. Has artificial intelligence crossed the so-called red line? Chinese researchers have published two reports on arXiv claiming that some artificial [...]