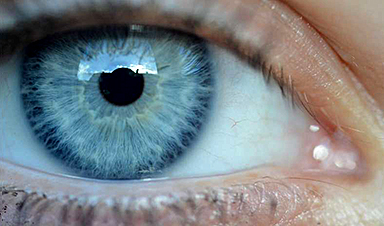
Cornell University researchers have found that the pupil is key to understanding how, and when, the brain forms strong, long-lasting memories.
By studying mice equipped with brain electrodes and tiny eye-tracking cameras, the researchers determined that new memories are being replayed and consolidated when the pupil is contracted during a substage of non-REM sleep. When the pupil is dilated, the process repeats for older memories.
The brain’s ability to separate these two substages of sleep with a previously unknown micro-structure is what prevents “catastrophic forgetting” in which the consolidation of one memory wipes out another one.
The findings could lead to better memory enhancement techniques for humans and may help computer scientists train artificial neural networks to be more efficient. The study, published in Nature, was led by assistant professors Azahara Oliva and Antonio Fernandez-Ruiz.
Over the course of a month, a group of mice was taught a variety of tasks, such as collecting water or cookie rewards in a maze. Then the mice were outfitted with brain electrodes and tiny spy cameras that hung in front of their eyes to track their pupil dynamics. One day, the mice learned a new task and when they fell asleep, the electrodes captured their neural activity and the cameras recorded the changes to their pupils.
“Non-REM sleep is when the actual memory consolidation happens, and these moments are very, very short periods of time undetectable by humans, like 100 milliseconds,” Oliva said. “How does the brain distribute these screenings of memory that are very fast and very short throughout the overall night? And how does that separate the new knowledge coming in, in a way that it doesn’t interfere with old knowledge that we already have in our minds?”
The recordings showed that the temporal structure of sleeping mice is more varied, and more akin to the sleep stages in humans, than previously thought. By interrupting the mice‘s sleep at different moments and later testing how well they recalled their learned tasks, the researchers were able to parse the processes.
When a mouse enters a substage of non-REM sleep, its pupil shrinks, and it’s here the recently learned tasks—i.e., the new memories—are being reactivated and consolidated while previous knowledge is not. Conversely, older memories are replayed and integrated when the pupil is dilated.
“It’s like new learning, old knowledge, new learning, old knowledge, and that is fluctuating slowly throughout the sleep,” Oliva said. “We are proposing that the brain has this intermediate timescale that separates the new learning from the old knowledge.”
More information: Sleep micro-structure organizes memory replay, Nature (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-08340-w
News
How Everyday Plastics Quietly Turn Into DNA-Damaging Nanoparticles
The same unique structure that makes plastic so versatile also makes it susceptible to breaking down into harmful micro- and nanoscale particles. The world is saturated with trillions of microscopic and nanoscopic plastic particles, some smaller [...]
AI Outperforms Physicians in Real-World Urgent Care Decisions, Study Finds
The study, conducted at the virtual urgent care clinic Cedars-Sinai Connect in LA, compared recommendations given in about 500 visits of adult patients with relatively common symptoms – respiratory, urinary, eye, vaginal and dental. [...]
Challenging the Big Bang: A Multi-Singularity Origin for the Universe
In a study published in the journal Classical and Quantum Gravity, Dr. Richard Lieu, a physics professor at The University of Alabama in Huntsville (UAH), which is a part of The University of Alabama System, suggests that [...]
New drug restores vision by regenerating retinal nerves
Vision is one of the most crucial human senses, yet over 300 million people worldwide are at risk of vision loss due to various retinal diseases. While recent advancements in retinal disease treatments have [...]
Shingles vaccine cuts dementia risk by 20%, new study shows
A shingles shot may do more than prevent rash — it could help shield the aging brain from dementia, according to a landmark study using real-world data from the UK. A routine vaccine could [...]
AI Predicts Sudden Cardiac Arrest Days Before It Strikes
AI can now predict deadly heart arrhythmias up to two weeks in advance, potentially transforming cardiac care. Artificial intelligence could play a key role in preventing many cases of sudden cardiac death, according to [...]
NanoApps Medical is a Top 20 Feedspot Nanotech Blog
There is an ocean of Nanotechnology news published every day. Feedspot saves us a lot of time and we recommend it. We have been using it since 2018. Feedspot is a freemium online RSS [...]
This Startup Says It Can Clean Your Blood of Microplastics
This is a non-exhaustive list of places microplastics have been found: Mount Everest, the Mariana Trench, Antarctic snow, clouds, plankton, turtles, whales, cattle, birds, tap water, beer, salt, human placentas, semen, breast milk, feces, testicles, [...]
New Blood Test Detects Alzheimer’s and Tracks Its Progression With 92% Accuracy
The new test could help identify which patients are most likely to benefit from new Alzheimer’s drugs. A newly developed blood test for Alzheimer’s disease not only helps confirm the presence of the condition but also [...]
The CDC buried a measles forecast that stressed the need for vaccinations
This story was originally published on ProPublica, a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive our biggest stories as soon as they’re published. ProPublica — Leaders at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [...]
Light-Driven Plasmonic Microrobots for Nanoparticle Manipulation
A recent study published in Nature Communications presents a new microrobotic platform designed to improve the precision and versatility of nanoparticle manipulation using light. Led by Jin Qin and colleagues, the research addresses limitations in traditional [...]
Cancer’s “Master Switch” Blocked for Good in Landmark Study
Researchers discovered peptides that permanently block a key cancer protein once thought untreatable, using a new screening method to test their effectiveness inside cells. For the first time, scientists have identified promising drug candidates [...]
AI self-cloning claims: A new frontier or a looming threat?
Chinese scientists claim that some AI models can replicate themselves and protect against shutdown. Has artificial intelligence crossed the so-called red line? Chinese researchers have published two reports on arXiv claiming that some artificial [...]
New Drug Turns Human Blood Into Mosquito-Killing Weapon
Nitisinone, a drug for rare diseases, kills mosquitoes when present in human blood and may become a new tool to fight malaria, offering longer-lasting, environmentally safer effects than ivermectin. Controlling mosquito populations is a [...]
DNA Microscopy Creates 3D Maps of Life From the Inside Out
What if you could take a picture of every gene inside a living organism—not with light, but with DNA itself? Scientists at the University of Chicago have pioneered a revolutionary imaging technique called volumetric DNA microscopy. It builds [...]
Scientists Just Captured the Stunning Process That Shapes Chromosomes
Scientists at EMBL have captured how human chromosomes fold into their signature rod shape during cell division, using a groundbreaking method called LoopTrace. By observing overlapping DNA loops forming in high resolution, they revealed that large [...]