Tiny particles called quantum dots reduce symptoms in mice primed to develop a type of Parkinson’s disease, and also block formation of the toxic protein clumps in Alzheimer’s. They could one day be a novel treatment for these brain disorders, although tests in people are some years away.
Quantum dots are just a few nanometres in size – so small they become subject to some of the strange effects of quantum physics. They have useful electronic and fluorescent properties and are found in some TV screens and LED lights.
Unlike most medicines, their tiny size means they can pass from bloodstream into the brain. Byung Hee Hong of Seoul National University in the South Korea and his colleagues wondered if they would affect the molecules involved in Parkinson’s or other brain disorders.
Parkinson’s disease involves gradually worsening tremors and movement problems. It is thought to be caused by a protein called synuclein found in nerve cells folding into the wrong shape, which triggers a chain reaction of misfolding in nearby synuclein molecules. This leads to a build-up of long strands or “fibrils” of the protein, killing neurons.
Quantum surprise
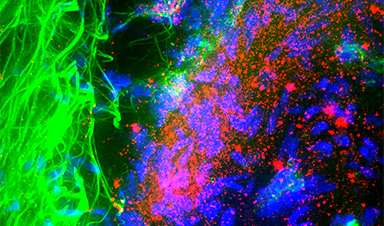
Hong’s team found that in a dish, quantum dots made from graphene – a form of carbon – bind to synuclein, and not only stop it from clumping into fibres, but also cause existing fibres to break up into individual molecules. “We didn’t expect the quantum dots to induce disaggregation of fibrils,” says Hong.
If the treatment affects people the same way, Hong says it is unclear how much benefit this would bring. “It’s hard to translate the results in mice to actual patients, whose systems are way more complicated. But we do believe quantum dots can make positive impacts to some extent.”
Image Credit: May C. Schiess, Roger Back, UT Medical School/Science Photo Library
News This Week
Does COVID increase the risk of Alzheimer’s disease?
Scientists discover that even mild COVID-19 can alter brain proteins linked to Alzheimer’s disease, potentially increasing dementia risk—raising urgent public health concerns. A recent study published in the journal Nature Medicine investigated whether both mild and [...]
New MRI Study Reveals How Cannabis Alters Brain Activity and Weakens Memory
A massive new study sheds light on how cannabis affects the brain, particularly during cognitive tasks. Researchers analyzed over 1,000 young adults and found that both heavy lifetime use and recent cannabis consumption significantly reduced brain [...]
How to Assess Nanotoxicity: Key Methods and Protocols
With their high surface area and enhanced physicochemical properties, nanomaterials play a critical role in drug delivery, consumer products, and environmental technologies. However, their nanoscale dimensions enable interactions with cellular components in complex and [...]
Nanotech drug delivery shows lasting benefits, reducing need for repeat surgeries
A nanotechnology-based drug delivery system developed at UVA Health to save patients from repeated surgeries has proved to have unexpectedly long-lasting benefits in lab tests – a promising sign for its potential to help human patients. [...]
Scientists Just Found DNA’s Building Blocks in Asteroid Bennu – Could This Explain Life’s Origins?
Japanese scientists detected all five nucleobases — building blocks of DNA and RNA — in samples returned from asteroid Bennu by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission. NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission brought back 121.6 grams of asteroid Bennu, unveiling nitrogen-rich organic matter, including DNA’s essential [...]
AI-Designed Proteins – Unlike Any Found in Nature – Revolutionize Snakebite Treatment
Scientists have pioneered a groundbreaking method to combat snake venom using newly designed proteins, offering hope for more effective, accessible, and affordable antivenom solutions. By utilizing advanced computational techniques and deep learning, this innovative [...]
New nanosystem offers hope for improved diagnosis and treatment of tongue cancer
A pioneering study has unveiled the Au-HN-1 nanosystem, a cutting-edge approach that promises to transform the diagnosis and treatment of tongue squamous cell carcinoma (TSCC). By harnessing gold nanoparticles coupled with the HN-1 peptide, [...]
Global Trust in Science Is Stronger Than Expected – What’s Next?
A landmark global survey conducted across 68 countries has found that public trust in scientists remains robust, with significant support for their active involvement in societal and political matters. The study highlights the public’s [...]












Leave A Comment