The impact of different kinds of commercial metallic nanoparticles (nanosized zero valent iron (nZVI), bimetal nZVI-Pd, and nano-magnetite (nFe3O4)) for the recovery of soil co-contaminated with Cr and PCBs are evaluated in a recent article published in the journal Scientific Reports.
The implementation of restoration solutions for soil degraded with a combination of pollutants (metal(loid)s and chemical products) has rarely been studied. The results suggest that the introduction of nZVI or nZVI-Pd, as well as pseudo-anaerobic settings, may well be employed to restore Cr and PCB-contaminated soil.
Soil Contamination Due to Chromium
Soil contamination is a global problem. It degrades the ecological functions supplied by the soil, reduces agricultural production, and has a negative influence on human health.
The bulk of contaminants come from man-made sources such as commercial activities, quarrying, public transit, and sewer waste treatment on soil.
The primary pollutants detected in European soils are metals and metalloids. As environmental pollutants, they are non-biodegradable and hence linger for long durations.
Due to its highly anti-corrosive characteristics, chromium (Cr) is extensively employed in a variety of industrial applications. Metallurgical operations, tanneries, wood processing, galvanizing, and petrochemical industries are just a few examples.
Cr (III), which presents as impermeable oxide and hydroxide cations, and Cr (VI), which emerges as oxyanion, are by far the most frequent types of Cr found as soil minerals.
Cr (III) is rejected by the electrostatic repulsion of soil and so stays in soil solution, accessible to crops and other creatures. As a result of its high mobility and bioavailability, Cr (VI) is 1000 times more hazardous than Cr (III).
Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs): A Major Soil Pollutant
Persistent organic pollutants (POPs), like metallic materials, are biological chemical compounds that are permanent, extremely poisonous, and micropollutants, posing a concern to the ecosystem.
PCBs are a class of synthetic organic chemicals classified as POPs by the Stockholm Convention of 2001 owing to their high public health hazard and breakdown resilience. PCBs may be created inadvertently as by-products in a variety of biochemical procedures that use chlorine and hydrocarbons.
PCBs have been linked to spillage from power equipment, waste distribution to soil, garbage furnace fumes, leaks during transportation, evaporation and sedimentation from surface waterways, and leakage from improper treatment and disposal.
Use of Nanoparticles for Soil Remediation
Compared to conventional physio-chemical approaches, nanoscience has recently allowed the development of new cost-effective and ecologically sound restoration solutions.
The increased particular surface area of nanoparticles leads to faster reaction kinetics with contaminants. Many distinct nanomaterials, such as carbon nanotubes, inorganic materials, and activated carbons, have been explored for cleanup purposes, but nano zero valent iron (nZVI) particulates are the most extensively deployed.
The application of magnetized nanomaterials, such as nano magnetite (nFe3O4), for the rehabilitation of metal(loid) contaminated streams has gained popularity in recent decades. This is because of their higher absorption capabilities and magnetic characteristics, which allow for better membrane separation from the solid material.
The major goal of this research was to compare the efficacy of three kinds of commercial magnetite nanoparticles (nZVI, nZVI-Pd, and nFe3O4) for the restoration of industrialized soil polluted with Cr and PCBs.
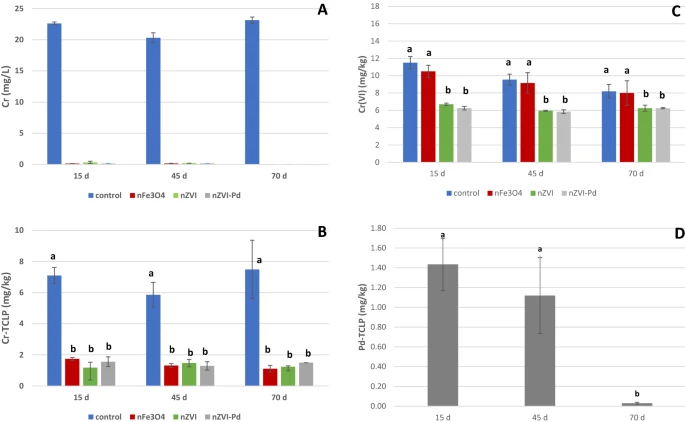
(A) Mean concentration of Cr (mg/L) in the aqueous extracts at the different sampling times. (B) Mean concentration of Cr (mg/kg) in TCLP extracts at the different sampling times. (C) Mean concentration of Cr(VI) (mg/kg) in soil samples at the different sampling times. For each sampling time, bars with the same letter do not differ significantly (p < 0.05). (D) Mean concentration of Pd (mg/kg) in TCLP extracts at the different sampling times for nZVI-Pd treated soils. Bars with the same letter do not differ significantly (p < 0.05). © Gil-Díaz, M., Pérez, R., Alonso, J., Miguel, E., Diez-Pascual, S. and Lobo, M., (2022)
Research Findings and Conclusion
When nZVI, nZVI-Pd, or nFe3O4 were added to soil polluted with Cr and PCBs, the leakage of Cr in the soil was greatly decreased, and the immobilization remained stable over a period of 70 days under the simulated conditions.
When contrasted to nFe3O4, Te nZVI and nZVI-Pd were more successful in converting Cr (VI) to Cr (III). The PCB levels in soils sprayed with the three kinds of iron nanoparticles fell considerably after 15 days of engagement between soil and nanoparticles.
Control soils demonstrated a drop in PCBs content during the 45-day sample period due to environmental remediation, reaching levels comparable to those seen in soil amended with nZVI and nZVI-Pd. In this case, biodegradation might be possible if the soil was just poisoned with PCBs, but not if it also included metals like Cr.
Tus, nZVI-based nanoparticles show modest performance in PCB-polluted soil cleanup. Both nZVI particles, on the other hand, achieved effective Cr absorption in soils.
The findings show that the introduction of nZVI or nZVI-Pd, as well as pseudo-anaerobic settings, might be employed to recover Cr and PCB-contaminated soils.
News
Researchers Reveal What Happens to Your Brain When You Don’t Get Enough Sleep
What if poor sleep was doing more than just making you tired? Researchers have discovered that disrupted sleep in older adults interferes with the brain’s ability to clean out waste, leading to memory problems [...]
How to prevent chronic inflammation from zombie-like cells that accumulate with age
In humans and other multicellular organisms, cells multiply. This defining feature allows embryos to grow into adulthood, and enables the healing of the many bumps, bruises and scrapes along the way. Certain factors can [...]
Breakthrough for long Covid patients who lost sense of smell
A breakthrough nasal surgery has restored the sense of smell for a dozen long Covid patients. Experts at University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust successfully employed a technique typically used for correcting blocked nasal passages, [...]
Scientists Invent Plastic That Can Dissolve In Seawater In Just A Few Hours
Plastic waste and pollution in the sea have been among the most serious environmental problems for decades, causing immense damage to marine life and ecosystems. However, a breakthrough discovery may offer a game-changing solution. [...]
Muscles from the 3D printer
Swiss researchers have developed a method for printing artificial muscles out of silicone. In the future, these could be used on both humans and robots. Swiss researchers have succeeded in printing artificial muscles out [...]
Beneficial genetic changes observed in regular blood donors
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have identified genetic changes in blood stem cells from frequent blood donors that support the production of new, non-cancerous cells. Understanding the differences in the mutations that accumulate [...]
Shocking Amounts of Microplastics in the Brain – It Could Be Increasing Our Risk of Dementia
The brain has higher concentrations of plastic particles compared to other organs, with increased levels found in dementia patients. In a comprehensive commentary published in Brain Medicine, researchers highlight alarming new evidence of microplastic accumulation [...]
Baffling Scientists for Centuries: New Study Unravels Mystery of Static Electricity
ISTA physicists demonstrate that contact electrification depends on the contact history of materials. For centuries, static electricity has intrigued and perplexed scientists. Now, researchers from the Waitukaitis group at the Institute of Science and [...]
Tumor “Stickiness” – Scientists Develop Potential New Way To Predict Cancer’s Spread
UC San Diego researchers have developed a device that predicts breast cancer aggressiveness by measuring tumor cell adhesion. Weakly adherent cells indicate a higher risk of metastasis, especially in early-stage DCIS. This innovation could [...]
Scientists Just Watched Atoms Move for the First Time Using AI
Scientists have developed a groundbreaking AI-driven technique that reveals the hidden movements of nanoparticles, essential in materials science, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. By integrating artificial intelligence with electron microscopy, researchers can now visualize atomic-level changes that were [...]
Scientists Sound Alarm: “Safe” Antibiotic Has Led to an Almost Untreatable Superbug
A recent study reveals that an antibiotic used for liver disease patients may increase their risk of contracting a dangerous superbug. An international team of researchers has discovered that rifaximin, a commonly prescribed antibiotic [...]
Scientists Discover Natural Compound That Stops Cancer Progression
A discovery led by OHSU was made possible by years of study conducted by University of Portland undergraduates. Scientists have discovered a natural compound that can halt a key process involved in the progression [...]
Scientists Just Discovered an RNA That Repairs DNA Damage – And It’s a Game-Changer
Our DNA is constantly under threat — from cell division errors to external factors like sunlight and smoking. Fortunately, cells have intricate repair mechanisms to counteract this damage. Scientists have uncovered a surprising role played by [...]
What Scientists Just Discovered About COVID-19’s Hidden Death Toll
COVID-19 didn’t just claim lives directly—it reshaped mortality patterns worldwide. A major international study found that life expectancy plummeted across most of the 24 analyzed countries, with additional deaths from cardiovascular disease, substance abuse, and mental [...]
Self-Propelled Nanoparticles Improve Immunotherapy for Non-Invasive Bladder Cancer
A study led by Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) and the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) in South Korea details the creation of urea-powered nanomotors that enhance immunotherapy for bladder cancer. The nanomotors [...]
Scientists Develop New System That Produces Drinking Water From Thin Air
UT Austin researchers have developed a biodegradable, biomass-based hydrogel that efficiently extracts drinkable water from the air, offering a scalable, sustainable solution for water access in off-grid communities, emergency relief, and agriculture. Discarded food [...]