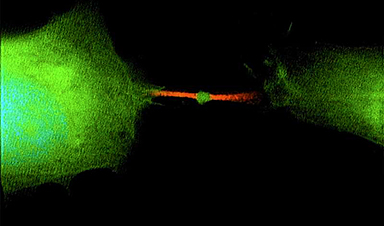
Once thought to be the trash can of the cell, a little bubble of cellular stuff called the midbody remnant is actually packing working genetic material with the power to change the fate of other cells—including turning them into cancer.
“One cell divides into three things: two cells and one midbody remnant, a new signaling organelle,” says Skop. “What surprised us is that the midbody is full of genetic information, RNA, that doesn’t have much to do with cell division at all, but likely functions in cell communication.”
In a study published today in the journal Developmental Cell, Skop’s lab and collaborators from the Pasteur Institute in Paris, Harvard Medical School, Boston University and the University of Utah analyzed the contents of midbodies—which form between the daughter cells during division—and tracked the interactions of the midbody remnants set free after cell division. Their results point to the midbody as a vehicle for the spread of cancer throughout the body.
“People thought the midbody was a place where things died or were recycled after cell division,” Skop says. “But one person’s trash is another person’s treasure. A midbody is a little packet of information cells use to communicate.”
The midbody’s involvement in cell signaling and stimulating cell proliferation has been investigated before, but Skop and her collaborators wanted to look inside the midbody remnants to learn more.
What the researchers found inside midbodies was RNA—which is a kind of working copy of DNA used to produce the proteins that make things happen in cells—and the cellular machinery necessary to turn that RNA into proteins. The RNA in midbodies tends to be blueprints not for the cell division process but for proteins involved in activities that steer a cell’s purpose, including pluripotency (the ability to develop into any of the body’s many different types of cells) and oncogenesis (the formation of cancerous tumors).
“A midbody remnant is very small. It’s a micron in size, a millionth of a meter,” Skop says. “But it’s like a little lunar lander. It’s got everything it needs to sustain that working information from the dividing cell. And it can drift away from the site of mitosis, get into your bloodstream and land on another cell far away.”
Many midbody remnants are reabsorbed by one of the daughter cells that shed them, but those that touch down on a distant surface, like a lunar lander, may instead be absorbed by a third cell. If that cell swallows the midbody, it may mistakenly begin using the enclosed RNA as if it were its own blueprints.
Previous research showed that cancer cells are more likely than stem cells to have ingested a midbody and its potentially fate-altering cargo. Stem cells, which give rise to new cells and are valuable for their pluripotency, spit a lot of midbodies back out, perhaps to maintain their pluripotency.
Future research may be able to harness the power of midbody RNA to deliver drugs to cancer cells or to keep them from dividing.
“We think our findings represent a huge target for cancer detection and therapeutics,” says Skop, whose work is supported by the National Institutes of Health.
The researchers identified a gene, called Arc, that is key to loading the midbody and midbody remnant with RNA. Taken up long ago from an ancient virus, Arc also plays a role in the way brain cells make memories.
“Loss of Arc leads to the loss of RNA in the midbody and a loss of the RNA information from getting to recipient cells,” Skop says. “We believe this memory gene is important for all cells to communicate RNA information.”
Sungjin Park, a senior scientist in Skop’s lab, is the lead author of the new study. Skop and collaborators also have a patent pending on two new methods that make it easier to isolate midbody structures from cell media or blood serum, improving cancer diagnostics.
News
This Tiny Cellular Gate Could Be the Key to Curing Cancer – And Regrowing Hair
After more than five decades of mystery, scientists have finally unveiled the detailed structure and function of a long-theorized molecular machine in our mitochondria — the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier. This microscopic gatekeeper controls how [...]
Unlocking Vision’s Secrets: Researchers Reveal 3D Structure of Key Eye Protein
Researchers have uncovered the 3D structure of RBP3, a key protein in vision, revealing how it transports retinoids and fatty acids and how its dysfunction may lead to retinal diseases. Proteins play a critical [...]
5 Key Facts About Nanoplastics and How They Affect the Human Body
Nanoplastics are typically defined as plastic particles smaller than 1000 nanometers. These particles are increasingly being detected in human tissues: they can bypass biological barriers, accumulate in organs, and may influence health in ways [...]
Measles Is Back: Doctors Warn of Dangerous Surge Across the U.S.
Parents are encouraged to contact their pediatrician if their child has been exposed to measles or is showing symptoms. Pediatric infectious disease experts are emphasizing the critical importance of measles vaccination, as the highly [...]
AI at the Speed of Light: How Silicon Photonics Are Reinventing Hardware
A cutting-edge AI acceleration platform powered by light rather than electricity could revolutionize how AI is trained and deployed. Using photonic integrated circuits made from advanced III-V semiconductors, researchers have developed a system that vastly [...]
A Grain of Brain, 523 Million Synapses, Most Complicated Neuroscience Experiment Ever Attempted
A team of over 150 scientists has achieved what once seemed impossible: a complete wiring and activity map of a tiny section of a mammalian brain. This feat, part of the MICrONS Project, rivals [...]
The Secret “Radar” Bacteria Use To Outsmart Their Enemies
A chemical radar allows bacteria to sense and eliminate predators. Investigating how microorganisms communicate deepens our understanding of the complex ecological interactions that shape our environment is an area of key focus for the [...]
Psychologists explore ethical issues associated with human-AI relationships
It's becoming increasingly commonplace for people to develop intimate, long-term relationships with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. At their extreme, people have "married" their AI companions in non-legally binding ceremonies, and at least two people [...]
When You Lose Weight, Where Does It Actually Go?
Most health professionals lack a clear understanding of how body fat is lost, often subscribing to misconceptions like fat converting to energy or muscle. The truth is, fat is actually broken down into carbon [...]
How Everyday Plastics Quietly Turn Into DNA-Damaging Nanoparticles
The same unique structure that makes plastic so versatile also makes it susceptible to breaking down into harmful micro- and nanoscale particles. The world is saturated with trillions of microscopic and nanoscopic plastic particles, some smaller [...]
AI Outperforms Physicians in Real-World Urgent Care Decisions, Study Finds
The study, conducted at the virtual urgent care clinic Cedars-Sinai Connect in LA, compared recommendations given in about 500 visits of adult patients with relatively common symptoms – respiratory, urinary, eye, vaginal and dental. [...]
Challenging the Big Bang: A Multi-Singularity Origin for the Universe
In a study published in the journal Classical and Quantum Gravity, Dr. Richard Lieu, a physics professor at The University of Alabama in Huntsville (UAH), which is a part of The University of Alabama System, suggests that [...]
New drug restores vision by regenerating retinal nerves
Vision is one of the most crucial human senses, yet over 300 million people worldwide are at risk of vision loss due to various retinal diseases. While recent advancements in retinal disease treatments have [...]
Shingles vaccine cuts dementia risk by 20%, new study shows
A shingles shot may do more than prevent rash — it could help shield the aging brain from dementia, according to a landmark study using real-world data from the UK. A routine vaccine could [...]
AI Predicts Sudden Cardiac Arrest Days Before It Strikes
AI can now predict deadly heart arrhythmias up to two weeks in advance, potentially transforming cardiac care. Artificial intelligence could play a key role in preventing many cases of sudden cardiac death, according to [...]
NanoApps Medical is a Top 20 Feedspot Nanotech Blog
There is an ocean of Nanotechnology news published every day. Feedspot saves us a lot of time and we recommend it. We have been using it since 2018. Feedspot is a freemium online RSS [...]