| The painful feeling of receiving an injection through a hypodermic needle or with the unpleasant sensation of swallowing a large pill is a globally familiar sensation. But what if a revolutionary and gentler way of administering drugs was in the works? | |
| For over two decades, researchers have been investigating various types of microneedles as a minimally invasive method for transdermal drug delivery. Arrays of microneedles can be designed to be loaded with a drug or chemical, which they then release over time onto the blood stream after piercing slightly beyond the skin layers. | |
| Microneedles offer several advantages compared to other types of drug delivery. First, they are painless and cause virtually no damage to the skin nor bleeding. Second, they can be self-administered. Third, unlike traditional needles, the disposal of microneedles is much easier as they don’t leave behind hazardous waste. | |
| Unfortunately, there are still a few challenges that need to be addressed before microneedles become the next big thing in healthcare. One is their fabrication cost, which generally involves expensive molds, materials, and machinery. | |
| Another issue is the aggregation and degradation of proteins when microneedles are pre-loaded with a protein-based medicine, as these molecules are quite sensitive to external conditions such as temperature, acidity and salt concentration. | |
| In a recent study published in Biomacromolecules (“Facile Photolithographic Fabrication of Zwitterionic Polymer Microneedle with Protein Aggregation Inhibition for Transdermal Drug Delivery”), two research teams from Japan and Thailand collaborated to address the main limitations of existing microneedles. | |
| On the other hand, Dr. Paisan Khanchaitit and his team at the National Science and Technology Development Agency (NANOTEC), Thailand, perfected a microneedle fabrication method suitable for the industrial scale based on photolithography. | |
| By combining these two efforts, the teams managed to produce microneedles patches with several attractive properties and potential scalability to clinical settings. | |
| The microneedles themselves are made of a non-degradable, biocompatible hydrogel that also contains zwitterionic poly-sulfobetaine (poly-SPB). As reported in previous studies by the same authors, this polymer suppresses protein aggregation. Thus, the researchers incorporated it during the fabrication process and showed that the proteins pre-loaded in the microneedles were stable even when subjected to various external stresses. | |
| Additionally, the scientists developed a straightforward and cost-effective way to fabricate microneedle arrays made from the abovementioned materials. They resorted to photolithography, a process in which a photomask is used to selectively block UV light from reaching a target surface to control chemical reactions locally, as Dr. Khanchaitit explains: “UV light passing through the photomask generates free radicals in the polymer resin during the fabrication process, resulting in photopolymerization and the subsequent formation of 3D microneedle structure patterns on a clear and flexible substrate.” | |
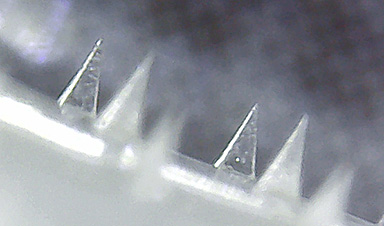
| This fabrication procedure requires inexpensive equipment only and takes about five minutes, yet produces four-point star-shaped microneedles with remarkable mechanical strength. | |
| To test the performance of these microneedle arrays for drug delivery, the researchers loaded them with 50 microliters of drug solutions containing rhodamine B as a dye alongside lysozyme and insulin as example proteins (see Figure above). | |
| Through various experiments on porcine skin, the teams verified that their microneedle patches offered both high drug-loading capacity and high drug-release rate. Moreover, they confirmed that the microneedles could both load and preserve various water-soluble drugs and proteins simultaneously, eliminating the need for refrigeration. | |
| Overall, the proposed microneedle arrays seem to be a remarkably promising platform for administering therapeutic drugs and vaccines, as Prof. Matsumura concludes: “The superior characteristics of our microneedles may change the way drugs are administered and could enable the development and delivery of advanced protein-based drugs for the treatment of various disorders.” Who knows what other revolutionary innovations in medicine wait for us in the future? |
News
Challenging Previous Beliefs: Japanese Scientists Discover Hidden Protector of Heart
A Japanese research team found that the oxidized form of glutathione (GSSG) may protect heart tissue by modifying a key protein, potentially offering a novel therapeutic approach for ischemic heart failure. A new study [...]
Millions May Have Long COVID – So Why Can’t They Get Diagnosed?
Millions of people in England may be living with Long Covid without even realizing it. A large-scale analysis found that nearly 10% suspect they might have the condition but remain uncertain, often due to [...]
Researchers Reveal What Happens to Your Brain When You Don’t Get Enough Sleep
What if poor sleep was doing more than just making you tired? Researchers have discovered that disrupted sleep in older adults interferes with the brain’s ability to clean out waste, leading to memory problems [...]
How to prevent chronic inflammation from zombie-like cells that accumulate with age
In humans and other multicellular organisms, cells multiply. This defining feature allows embryos to grow into adulthood, and enables the healing of the many bumps, bruises and scrapes along the way. Certain factors can [...]
Breakthrough for long Covid patients who lost sense of smell
A breakthrough nasal surgery has restored the sense of smell for a dozen long Covid patients. Experts at University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust successfully employed a technique typically used for correcting blocked nasal passages, [...]
Scientists Invent Plastic That Can Dissolve In Seawater In Just A Few Hours
Plastic waste and pollution in the sea have been among the most serious environmental problems for decades, causing immense damage to marine life and ecosystems. However, a breakthrough discovery may offer a game-changing solution. [...]
Muscles from the 3D printer
Swiss researchers have developed a method for printing artificial muscles out of silicone. In the future, these could be used on both humans and robots. Swiss researchers have succeeded in printing artificial muscles out [...]
Beneficial genetic changes observed in regular blood donors
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have identified genetic changes in blood stem cells from frequent blood donors that support the production of new, non-cancerous cells. Understanding the differences in the mutations that accumulate [...]
Shocking Amounts of Microplastics in the Brain – It Could Be Increasing Our Risk of Dementia
The brain has higher concentrations of plastic particles compared to other organs, with increased levels found in dementia patients. In a comprehensive commentary published in Brain Medicine, researchers highlight alarming new evidence of microplastic accumulation [...]
Baffling Scientists for Centuries: New Study Unravels Mystery of Static Electricity
ISTA physicists demonstrate that contact electrification depends on the contact history of materials. For centuries, static electricity has intrigued and perplexed scientists. Now, researchers from the Waitukaitis group at the Institute of Science and [...]
Tumor “Stickiness” – Scientists Develop Potential New Way To Predict Cancer’s Spread
UC San Diego researchers have developed a device that predicts breast cancer aggressiveness by measuring tumor cell adhesion. Weakly adherent cells indicate a higher risk of metastasis, especially in early-stage DCIS. This innovation could [...]
Scientists Just Watched Atoms Move for the First Time Using AI
Scientists have developed a groundbreaking AI-driven technique that reveals the hidden movements of nanoparticles, essential in materials science, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. By integrating artificial intelligence with electron microscopy, researchers can now visualize atomic-level changes that were [...]
Scientists Sound Alarm: “Safe” Antibiotic Has Led to an Almost Untreatable Superbug
A recent study reveals that an antibiotic used for liver disease patients may increase their risk of contracting a dangerous superbug. An international team of researchers has discovered that rifaximin, a commonly prescribed antibiotic [...]
Scientists Discover Natural Compound That Stops Cancer Progression
A discovery led by OHSU was made possible by years of study conducted by University of Portland undergraduates. Scientists have discovered a natural compound that can halt a key process involved in the progression [...]
Scientists Just Discovered an RNA That Repairs DNA Damage – And It’s a Game-Changer
Our DNA is constantly under threat — from cell division errors to external factors like sunlight and smoking. Fortunately, cells have intricate repair mechanisms to counteract this damage. Scientists have uncovered a surprising role played by [...]
What Scientists Just Discovered About COVID-19’s Hidden Death Toll
COVID-19 didn’t just claim lives directly—it reshaped mortality patterns worldwide. A major international study found that life expectancy plummeted across most of the 24 analyzed countries, with additional deaths from cardiovascular disease, substance abuse, and mental [...]