Detrimental Physiological Effects of Microgravity on the Brain and DNA


![]()
Microgravity imparts multiple deleterious effects on human physiology, which must be resolved as a prerequisite for enabling humans to engage in extended space expeditions. A summary of these negative impacts on various physiological systems is listed in Table 1 below. Nanomedicine might have the capacity to prevent or counteract the effects of microgravity (e.g., bone loss, neurological damage, soft tissue degradation, and detrimental ocular conditions to enable humans to endure prolonged missions to Mars and beyond, to the further reaches of deep space.![]()
| System | Microgravity Impact |
|---|---|
| Musculoskeletal System |
|
| Cardiovascular System |
|
| Sensory Motor System |
|
| Immune System |
|
| Wound Healing |
|
Table 1: Physiological impacts of microgravity (reconfigured from Blaber, et al.)
Here, we briefly articulate what might be possible through the application of advanced nanomedicine toward addressing the deleterious effects of microgravity on other critical soft tissues, such as the brain, spinal cord, nervous system, and DNA. The functionality of degraded or destroyed populations of neurons and glial cells, as well as neuronal circuitry might be nanomedically restored through the use of targeted nanocarriers, which may precisely transport the appropriate molecules, biomaterials, and stem cells to any damaged sites of the nervous system to initiate efficacious repairs. Multilayered electrospun polymeric nanofiber scaffolds (Figure 1) may be self-assembled from constituent components in vivo and used to support the growth of stem cells. Nanofiber scaffolds comprised of electrospun polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)/chitosan nanofibers (~Ø 221 nm) were demonstrated by Alhosseini et al. to create microscale pores at their interstices, which facilitated cell tethering and migration, the proliferation of blood vessels, as well as to enable cellular nutrient and waste exchange.

![]()
Figure 1: Electrospun polycaprolactone (PCL) nanofiber scaffold (Image credit: Koh and Strange)
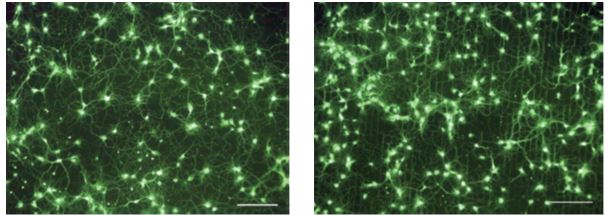
PC12 nerve cells from rat adrenal medulla were cultured on a PVA/chitosan nanofiber scaffold in vitro and observed to respond positively to the support. They also exhibited higher levels of attachment, propagation, migration, and viability in contrast to a pure PVA nanofiber scaffold. The presence of chitosan appeared to provide several physicochemical and biological factors that were amenable to the nerve cells including reduced nanofiber diameters, more surface resident amine and decreased water content. In a further neural engineering study by Jang et al., the growth of E18 rat hippocampal neurites traced the micropatterns of a substrate that were established by octadecyltrichlorosilane (OTS) and pristine carbon nanotubes (Figure 2), which biomimetically emulated extracellular matrices. It was suggested that a cell adhesion protein (poly-l-lysine (PLL)), which was coated onto the substrate, was a critical factor for attachment, guidance, and elongation.
![]()
Figure 2: Neuron networks (at seven divisions) shown on (a) carbon nanotube-only substrate and (b) patterned carbon nanotube/OTS substrate (Image credit: Jang et al.)
The nanomedical repair of the brain, at today’s level of sophistication, might involve the activation of renewable multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) (Figure 3), as described by Santos et al., which reside within two specific regions of the brain (germinal subventricular and hippocampal subgranular zones), to rejuvenate neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes. The activation of NSCs might be initiated via the delivery of targeted nanoparticles that bear payloads of neurogenesis-inducing biomolecules to these sites, while imparting negligible side effects. (Reynolds and Weiss, Gage et al., Quadrato and Giovanni, Kazanis, Gage, Bible et al.)
![]()
Figure 3: Neural stems cells (Image credit: The New York Academy of Sciences)
Further in the future, with the advent of mature Molecular Manufacturing (MM), it might be possible to affect real time brain repairs almost instantaneously via sophisticated indwelling nanomedical devices. This strategy may sustainably negate the deleterious effects of both ionizing radiation and microgravity toward addressing the possibility of cumulative damage manifesting in the brain as the result of prolonged exposure to the space environment.
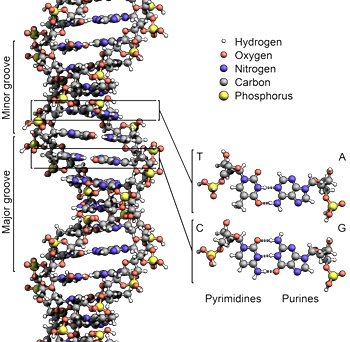
“A robust means for the preservation of the integrity and viability of DNA molecules and the proteins that they encode will be absolutely essential for long-haul human space travel and the eventual human habitation of the Moon, Mars, and beyond.” (Boehm) Within the nuclei of human cells (~Ø5-10 microns) there inherently exist a dozen species of protein based DNA repair mechanisms that are encoded by ~150 genes. Each of these self-assembling biological “nanomachines” is devoted to the repair of a specific type of damage to the DNA duplex. (Figure 4)
![]()
Figure 4: Illustration of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) (Image credit: Zephyris /Richard Wheeler)
In the space environment, microgravity in conjunction with ionizing radiation may negatively impact a number of DNA repair mechanisms. Subsequent to extensive studies of astronauts and cosmonauts it was revealed by Rowe that human exposure to microgravity induces a considerable decline in serum magnesium (Mg); an antioxidant and calcium blocker, which is critical for the binding of telomerase to DNA. Telomerase facilitates telomere elongation, chromosome stability, and the promotion of transcription and replication. Insufficient levels of magnesium results in oxidative stress, accelerated cell senescence, unstable DNA, as well as reduced protein synthesis and mitochondrial performance.
It was demonstrated that when human endothelial cells had no access to Mg for only two hours, they showed elevated levels of 8-hydroxy-deoxyguanine (in contrast to controls), which is a key DNA repair product that is generated in response to oxidative stress-induced DNA damage. To maintain ample concentrations of Mg under microgravity conditions, Mg loaded nanoparticles may have the capacity for the prolonged release of Mg ions, to sustain healthy plasma levels and those within intracellular compartments, which diminish over time and may not necessarily be related with concentrations in the plasma.
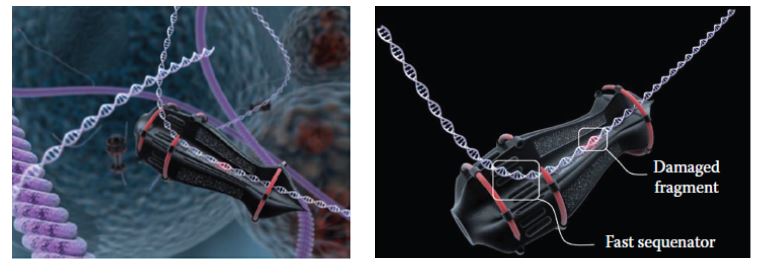
Svidinenko designed a conceptual sophisticated DNA repair nanorobot (Figure 5) that might transit along the duplex (similar to a bead on a chain). DNA damage would be detected immediately upon entering through the input port. When approaching the output port, the damaged DNA segment would be mechanically stabilized, where after the deficient base pairs would be removed and rapidly replaced by a dedicated “sequenator”, which could be considered as akin to the operation of a film-editing mechanism. The excised DNA segment would be then be discarded from a discharge port to be naturally degraded.
![]()
Figure 5: Conceptual DNA repair nanorobot (Image credit: Nanorobotmodels Medical Animation Studio)
News
The Brain’s Strange Way of Computing Could Explain Consciousness
Consciousness may emerge not from code, but from the way living brains physically compute. Discussions about consciousness often stall between two deeply rooted viewpoints. One is computational functionalism, which holds that cognition can be [...]
First breathing ‘lung-on-chip’ developed using genetically identical cells
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and AlveoliX have developed the first human lung-on-chip model using stem cells taken from only one person. These chips simulate breathing motions and lung disease in an individual, [...]
Cell Membranes May Act Like Tiny Power Generators
Living cells may generate electricity through the natural motion of their membranes. These fast electrical signals could play a role in how cells communicate and sense their surroundings. Scientists have proposed a new theoretical [...]
This Viral RNA Structure Could Lead to a Universal Antiviral Drug
Researchers identify a shared RNA-protein interaction that could lead to broad-spectrum antiviral treatments for enteroviruses. A new study from the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC), published in Nature Communications, explains how enteroviruses begin reproducing [...]
New study suggests a way to rejuvenate the immune system
Stimulating the liver to produce some of the signals of the thymus can reverse age-related declines in T-cell populations and enhance response to vaccination. As people age, their immune system function declines. T cell [...]
Nerve Damage Can Disrupt Immunity Across the Entire Body
A single nerve injury can quietly reshape the immune system across the entire body. Preclinical research from McGill University suggests that nerve injuries may lead to long-lasting changes in the immune system, and these [...]
Fake Science Is Growing Faster Than Legitimate Research, New Study Warns
New research reveals organized networks linking paper mills, intermediaries, and compromised academic journals Organized scientific fraud is becoming increasingly common, ranging from fabricated research to the buying and selling of authorship and citations, according [...]
Scientists Unlock a New Way to Hear the Brain’s Hidden Language
Scientists can finally hear the brain’s quietest messages—unlocking the hidden code behind how neurons think, decide, and remember. Scientists have created a new protein that can capture the incoming chemical signals received by brain [...]
Does being infected or vaccinated first influence COVID-19 immunity?
A new study analyzing the immune response to COVID-19 in a Catalan cohort of health workers sheds light on an important question: does it matter whether a person was first infected or first vaccinated? [...]
We May Never Know if AI Is Conscious, Says Cambridge Philosopher
As claims about conscious AI grow louder, a Cambridge philosopher argues that we lack the evidence to know whether machines can truly be conscious, let alone morally significant. A philosopher at the University of [...]
AI Helped Scientists Stop a Virus With One Tiny Change
Using AI, researchers identified one tiny molecular interaction that viruses need to infect cells. Disrupting it stopped the virus before infection could begin. Washington State University scientists have uncovered a method to interfere with a key [...]
Deadly Hospital Fungus May Finally Have a Weakness
A deadly, drug-resistant hospital fungus may finally have a weakness—and scientists think they’ve found it. Researchers have identified a genetic process that could open the door to new treatments for a dangerous fungal infection [...]











