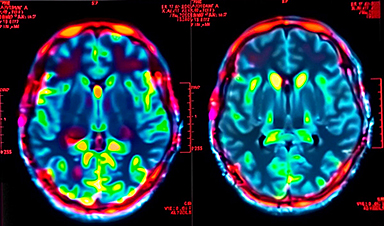
Using both mouse and human brain tissue, researchers at Yale School of Medicine have discovered that SARS-CoV-2 can directly infect the central nervous system and have begun to unravel some of the virus’s effects on brain cells.
The study, published today in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), may help researchers develop treatments for the various neurological symptoms associated with COVID-19.
Though COVID-19 is considered to primarily be a respiratory disease, SARS-CoV-2 can affect many other organs in the body, including, in some patients, the central nervous system, where infection is associated with a variety of symptoms ranging from headaches and loss of taste and smell to impaired consciousness, delirium, strokes, and cerebral hemorrhage.
“Understanding the full extent of viral invasion is crucial to treating patients, as we begin to try to figure out the long-term consequences of COVID-19, many of which are predicted to involve the central nervous system,” says Akiko Iwasaki, a professor at Yale School of Medicine.
Many questions remain to be answered, including whether SARS-CoV-2 can infect neurons or other types of brain cells. To address this question, a team led by Iwasaki and co-senior author Kaya Bilguvar, an associate professor at Yale School of Medicine, analyzed the ability of SARS-CoV-2 to invade human brain organoids, miniature 3D organs grown in the lab from human stem cells.
The researchers found that the virus was able to infect neurons in these organoids and use the neuronal cell machinery to replicate. The virus appears to facilitate its replication by boosting the metabolism of infected cells, while neighboring, uninfected neurons die as their oxygen supply is reduced.
SARS-CoV-2 enters lung cells by binding to a protein called ACE2, but whether this protein is present on the surface of brain cells is unclear. The Yale team determined that the ACE2 protein is, in fact, produced by neurons and that blocking this protein prevents the virus from human brain organoids.
SARS-CoV-2 was also able to infect the brains of mice genetically engineered to produce human ACE2, causing dramatic alterations in the brain’s blood vessels that could potentially disrupt the organ’s oxygen supply. Central nervous system infection was much more lethal in mice than infections limited to the lungs, the researchers found.
Image Credit: Lancet
Post by Amanda Scott, NA CEO. Follow her on twitter @tantriclens
Thanks to Heinz V. Hoenen. Follow him on twitter: @HeinzVHoenen
News
Does COVID increase the risk of Alzheimer’s disease?
Scientists discover that even mild COVID-19 can alter brain proteins linked to Alzheimer’s disease, potentially increasing dementia risk—raising urgent public health concerns. A recent study published in the journal Nature Medicine investigated whether both mild and [...]
New MRI Study Reveals How Cannabis Alters Brain Activity and Weakens Memory
A massive new study sheds light on how cannabis affects the brain, particularly during cognitive tasks. Researchers analyzed over 1,000 young adults and found that both heavy lifetime use and recent cannabis consumption significantly reduced brain [...]
How to Assess Nanotoxicity: Key Methods and Protocols
With their high surface area and enhanced physicochemical properties, nanomaterials play a critical role in drug delivery, consumer products, and environmental technologies. However, their nanoscale dimensions enable interactions with cellular components in complex and [...]
Nanotech drug delivery shows lasting benefits, reducing need for repeat surgeries
A nanotechnology-based drug delivery system developed at UVA Health to save patients from repeated surgeries has proved to have unexpectedly long-lasting benefits in lab tests – a promising sign for its potential to help human patients. [...]
Scientists Just Found DNA’s Building Blocks in Asteroid Bennu – Could This Explain Life’s Origins?
Japanese scientists detected all five nucleobases — building blocks of DNA and RNA — in samples returned from asteroid Bennu by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission. NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission brought back 121.6 grams of asteroid Bennu, unveiling nitrogen-rich organic matter, including DNA’s essential [...]
AI-Designed Proteins – Unlike Any Found in Nature – Revolutionize Snakebite Treatment
Scientists have pioneered a groundbreaking method to combat snake venom using newly designed proteins, offering hope for more effective, accessible, and affordable antivenom solutions. By utilizing advanced computational techniques and deep learning, this innovative [...]
New nanosystem offers hope for improved diagnosis and treatment of tongue cancer
A pioneering study has unveiled the Au-HN-1 nanosystem, a cutting-edge approach that promises to transform the diagnosis and treatment of tongue squamous cell carcinoma (TSCC). By harnessing gold nanoparticles coupled with the HN-1 peptide, [...]
Global Trust in Science Is Stronger Than Expected – What’s Next?
A landmark global survey conducted across 68 countries has found that public trust in scientists remains robust, with significant support for their active involvement in societal and political matters. The study highlights the public’s [...]
Microplastics in the bloodstream may pose hidden risks to brain health
In a recent study published in the journal Science Advances, researchers investigated the impact of microplastics on blood flow and neurobehavioral functions in mice. Using advanced imaging techniques, they observed that microplastics obstruct cerebral blood [...]
AI Surveillance: New Study Exposes Hidden Risks to Your Privacy
A new mathematical model enhances the evaluation of AI identification risks, offering a scalable solution to balance technological benefits with privacy protection. AI tools are increasingly used to track and monitor people both online [...]
Permafrost Thaw: Unleashing Ancient Pathogens and Greenhouse Gases
Permafrost is a fascinating yet alarming natural phenomenon. It refers to ground that remains frozen for at least two consecutive years. Mostly found in polar regions like Siberia, Alaska, and Canada, permafrost plays a [...]
Frequent social media use tied to higher levels of irritability
A survey led by researchers from the Center for Quantitative Health at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School has analyzed the association between self-reported social media use and irritability among US adults. Frequent [...]
Australian oysters’ blood could hold key to fighting drug-resistant superbugs
Protein found in Sydney rock oysters’ haemolymph can kill bacteria and boost some antibiotics’ effectiveness, scientists discover An antimicrobial protein found in the blood of an Australian oyster could help in the fight against [...]
First U.S. H5N1 Death Sparks Urgency: Scientists Warn Bird Flu Is Mutating Faster Than Expected
A human strain of H5N1 bird flu isolated in Texas shows mutations enabling better replication in human cells and causing more severe disease in mice compared to a bovine strain. While the virus isn’t [...]
AI Breakthrough in Nanotechnology Shatters Limits of Precision
At TU Graz, a pioneering research group is leveraging artificial intelligence to drastically enhance the way nanostructures are constructed. They aim to develop a self-learning AI system that can autonomously position molecules with unprecedented precision, potentially [...]
How Missing Sleep Lets Bad Memories Haunt Your Mind
Research reveals that a lack of sleep can hinder the brain’s ability to suppress unwanted memories and intrusive thoughts, emphasizing the importance of restful sleep for mental health. Sleep deprivation has been found to [...]